Unit 1
... • Every mass exerts a force of attraction on every other mass. The strength of the force is proportional to the product of the masses divided by the square of the distance between them – Simply put, everything pulls on ...
... • Every mass exerts a force of attraction on every other mass. The strength of the force is proportional to the product of the masses divided by the square of the distance between them – Simply put, everything pulls on ...
FORCES
... m=mass(kg) g=9.8m/s2 Normal force = the support force exerted upon an object which is in contact with another stable object ...
... m=mass(kg) g=9.8m/s2 Normal force = the support force exerted upon an object which is in contact with another stable object ...
force
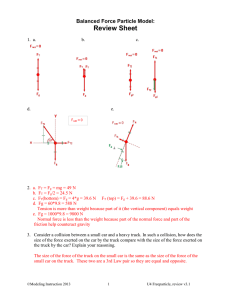
... 2. A baseball accelerates downward at 9.8 m/s2. If the gravitational force is the only force acting on the baseball and is 1.4 N, what is the baseball’s mass? ...
... 2. A baseball accelerates downward at 9.8 m/s2. If the gravitational force is the only force acting on the baseball and is 1.4 N, what is the baseball’s mass? ...
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION
... For example, pushes and pulls are forces. We must be careful to think about a force as acting on one object from (or due to ) another object. ...
... For example, pushes and pulls are forces. We must be careful to think about a force as acting on one object from (or due to ) another object. ...
ME 242 Chapter 13
... Problems involving velocity, displacement and conservative force systems can be solved using the conservation of energy equation. • Potential energy: Draw two diagrams: one with the body located at its initial position and one at the final position. Compute the potential energy at each position usin ...
... Problems involving velocity, displacement and conservative force systems can be solved using the conservation of energy equation. • Potential energy: Draw two diagrams: one with the body located at its initial position and one at the final position. Compute the potential energy at each position usin ...
Test A ICP 2nd and 3rd law
... 13. A baseball player bats a ball with a force of 1000 N. The ball exerts a force on the bat of a. Less than 1000 N b. More than 1000 N c. 1000 N d. Not enough information – depends on the mass of the ball. 14. A person is attracted towards the center of the earth by a 500 N gravitational force. The ...
... 13. A baseball player bats a ball with a force of 1000 N. The ball exerts a force on the bat of a. Less than 1000 N b. More than 1000 N c. 1000 N d. Not enough information – depends on the mass of the ball. 14. A person is attracted towards the center of the earth by a 500 N gravitational force. The ...
Forces Accelerate
... 4. Write down the three ways that velocity can change (three ways to accelerate). a. ________________________ b.____________________ c. _____________________ Now check out how fast things go when they fall to Earth. If you fall even only 10 meters you can get hurt badly or even be killed. 5. Calcula ...
... 4. Write down the three ways that velocity can change (three ways to accelerate). a. ________________________ b.____________________ c. _____________________ Now check out how fast things go when they fall to Earth. If you fall even only 10 meters you can get hurt badly or even be killed. 5. Calcula ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... would continue in motion with the same speed and direction - forever! (Or at least to the end of the table top.) ...
... would continue in motion with the same speed and direction - forever! (Or at least to the end of the table top.) ...
8-2 The Principle of Superposition
... on a line with a distance r between neighboring balls. Step 1 – How many forces does each ball experience in each case? Each ball experiences two gravitational forces, one from each of the other balls. We can neglect any other interactions. Step 2 – Consider Case 1. Is the force that the ball of mas ...
... on a line with a distance r between neighboring balls. Step 1 – How many forces does each ball experience in each case? Each ball experiences two gravitational forces, one from each of the other balls. We can neglect any other interactions. Step 2 – Consider Case 1. Is the force that the ball of mas ...
force
... • Mass can only be changed by adding or removing matter from the object • Weight can be changed by moving to a different planet, or by changing the mass • Weight is dependant on the mass of an object and the acceleration due to gravity, which changes from place to place. ...
... • Mass can only be changed by adding or removing matter from the object • Weight can be changed by moving to a different planet, or by changing the mass • Weight is dependant on the mass of an object and the acceleration due to gravity, which changes from place to place. ...
1. Unless acted on by an external net force, an object
... 19. The 2.0 kg head of an axe strikes a tree horizontally at 40 m/s. The blade penetrates 0.040 m into the tree. What is the average force exerted by the blade on this tree? A. 2. 0 × 101 N B. 2. 0 × 103 N C. 2. 0 × 10 4 N D. 4. 0 × 10 4 N ...
... 19. The 2.0 kg head of an axe strikes a tree horizontally at 40 m/s. The blade penetrates 0.040 m into the tree. What is the average force exerted by the blade on this tree? A. 2. 0 × 101 N B. 2. 0 × 103 N C. 2. 0 × 10 4 N D. 4. 0 × 10 4 N ...