* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FORCES
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
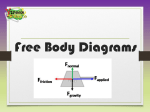
FORCES TYPES OF FORCES FREE BODY DIAGRAMS DETERMINING NET FORCE FORCES A force is a push or pull acting upon an object Contact forces = Friction Tension Normal Air Resistance Applied force Spring force Distance forces = gravitational , electrical, magnetic TYPES OF FORCES Applied force = force applied to an object by a person or other object Gravity force = weight = attractive force between two objects Fgrav=m x g m=mass(kg) g=9.8m/s2 Normal force = the support force exerted upon an object which is in contact with another stable object TYPES OF FORCES Friction = force that opposes the sliding motion between two touching surfaces Static friction = force that prevents two surfaces from sliding past each other Air resistance = special type of frictional force - acts on objects as they travel through air Tension Force = force which is transmitted through a string ,rope, cable or wire when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends FREE BODY DIAGRAMS Used to show the relative size and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation Size of the arrow reflects the size of the force The direction of the arrow shows the direction which the force is acting All force arrows are labeled to show the exact type of force Represent the object with a box and draw the force arrows from the box outward FREE BODY DIAGRAMS F norm F frict F app F grav There can be any number of forces acting on the object Now do the practice problems work sheet. Determining Net Force Newton #1 = an object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Free body diagrams are used to determine if there is an unbalanced force in a given situation Determining Net Force F norm= 50N F tens=1200N F frict=20N F air=600N F grav=50N F grav=800N F grav=800N The net force is the sum of all the forces that act on an object. See examples F norm= 3N Net Force examples Ffrict=5N F app= 5N F net = ? F grav= 3 N F norm = 3 N F frict= 5 N F net = ? F grav = 3N Net Force - examples B A 50 N 200 N If F net = 0 N Find the value for A and B