Solution Derivations for Capa #8
... field B, which is indicated by the dots in the figure (B out of the page). What can you conclude about the charge of each particle? (If your answers for charges of particles 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, are, respectively, +, 0, +, −, 0, then enter +0+-0 into the computer.) Use the right hand rule to find the ...
... field B, which is indicated by the dots in the figure (B out of the page). What can you conclude about the charge of each particle? (If your answers for charges of particles 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, are, respectively, +, 0, +, −, 0, then enter +0+-0 into the computer.) Use the right hand rule to find the ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: ____
... 21. How is mass the measure of inertia? 22. What does acceleration depend on? 23. What happens to the mass if an objects acceleration decreases? Increases? 24. What happens to the force if an objects acceleration decreases? Increases? 25. How do we express Newton’s Second Law mathematically? 26. Do ...
... 21. How is mass the measure of inertia? 22. What does acceleration depend on? 23. What happens to the mass if an objects acceleration decreases? Increases? 24. What happens to the force if an objects acceleration decreases? Increases? 25. How do we express Newton’s Second Law mathematically? 26. Do ...
Example 11-3.
... Important: the force in SHM is not constant, so the acceleration is not constant, so you can’t use the equations of kinematics. An object rotating in a circle (which is has a frequency and a period) is mathematically analogous to the SHM of a vibrating spring. ...
... Important: the force in SHM is not constant, so the acceleration is not constant, so you can’t use the equations of kinematics. An object rotating in a circle (which is has a frequency and a period) is mathematically analogous to the SHM of a vibrating spring. ...
PreLec3.pdf
... Recall last time: when the force of gravity is the only force (negligible air resistance), then the object is in “free-fall”. Question Since weight = mg = force of gravity on an object, heavier objects experience more gravitational force – so why don’t they fall faster than lighter ones ? ...
... Recall last time: when the force of gravity is the only force (negligible air resistance), then the object is in “free-fall”. Question Since weight = mg = force of gravity on an object, heavier objects experience more gravitational force – so why don’t they fall faster than lighter ones ? ...
PowerPoint
... • We can represent all forces acting on a body as if their vector sum were acting on a point at the center of mass with the mass of the entire body ...
... • We can represent all forces acting on a body as if their vector sum were acting on a point at the center of mass with the mass of the entire body ...
Physics and Beyond PowerPoint
... an object was moving “against its nature”, then a force of some kind was involved. • If there were no force then there would be no motion (except vertically : falling rocks and ...
... an object was moving “against its nature”, then a force of some kind was involved. • If there were no force then there would be no motion (except vertically : falling rocks and ...
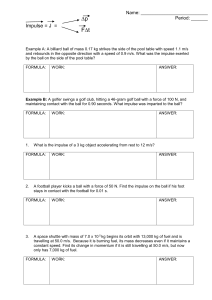
Worksheet 9 - Impulse
... What is the impulse of a 3 kg object accelerating from rest to 12 m/s? ...
... What is the impulse of a 3 kg object accelerating from rest to 12 m/s? ...
ME 3214 – Dynamics of Particles and Rigid Bodies Credits and
... a. Catalog Description: Kinematics and dynamics of particles. Motion relative to a translating and rotating observers; inertial reference systems; central forces and orbits. Kinematics and dynamics of groups of particles and rigid bodies. Lagrangian description of motion. b. Prerequisites: CE 2120 c ...
... a. Catalog Description: Kinematics and dynamics of particles. Motion relative to a translating and rotating observers; inertial reference systems; central forces and orbits. Kinematics and dynamics of groups of particles and rigid bodies. Lagrangian description of motion. b. Prerequisites: CE 2120 c ...
II. Describing Motion
... slope =speed steeper slope = faster speed straight line = constant speed flat line = no motion ...
... slope =speed steeper slope = faster speed straight line = constant speed flat line = no motion ...
force
... A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object's interaction with another object. Force is a quantity which is measured using the standard metric unit known as the Newton. ...
... A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object's interaction with another object. Force is a quantity which is measured using the standard metric unit known as the Newton. ...
4.01B Michelle was learning about forces today in her science class
... 2. If the car was moving at a high constant speed, which of the following statements must be true? a. The forces are balanced. b. There is an unbalanced force in the direction of motion. Michelle’s car broke down on the way home, and she had to push it off the road. As she pushed the car off the roa ...
... 2. If the car was moving at a high constant speed, which of the following statements must be true? a. The forces are balanced. b. There is an unbalanced force in the direction of motion. Michelle’s car broke down on the way home, and she had to push it off the road. As she pushed the car off the roa ...
U3H1 Problem Sheet 1 - Baltimore Polytechnic Institute
... Problem Sheet #1: Force, Energy, Work, Power, and Efficiency Definitions: a. ...
... Problem Sheet #1: Force, Energy, Work, Power, and Efficiency Definitions: a. ...
exam3_T112_solution
... Q28. Five objects of mass m are under a force F at a distance from an axis of rotation perpendicular to the page through the point A, as shown in Figure 14. The one (or ones) that has zero torque about the axes through A is: Fig# ...
... Q28. Five objects of mass m are under a force F at a distance from an axis of rotation perpendicular to the page through the point A, as shown in Figure 14. The one (or ones) that has zero torque about the axes through A is: Fig# ...
angular motion - Craigie High School
... Notice that the angular momentum of a rigid object about a fixed axis depends on the moment of inertia. Angular momentum is a vector quantity. The direction of this vector is at right angles to the plane containing v (since p = m v and mass is scalar) and r and lies along the axis of rotation. For i ...
... Notice that the angular momentum of a rigid object about a fixed axis depends on the moment of inertia. Angular momentum is a vector quantity. The direction of this vector is at right angles to the plane containing v (since p = m v and mass is scalar) and r and lies along the axis of rotation. For i ...
Force Law
... reaction: or, the mutual action of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to contrary ...
... reaction: or, the mutual action of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to contrary ...