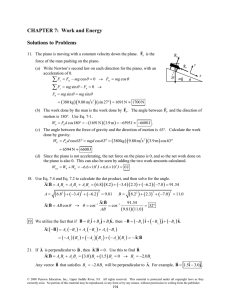
SolutionstoAssignedProblemsChapter7
... © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
... © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
Forces - Images
... • Mass is a measure of inertia. –Inertia describe an object’s resistance to change motion. Which would be more difficult to push? ...
... • Mass is a measure of inertia. –Inertia describe an object’s resistance to change motion. Which would be more difficult to push? ...
projectilessatellites and gravity
... will land at the same time even if their horizontal speeds are different. See Figures 14.1 and 14.3 on page 263. ...
... will land at the same time even if their horizontal speeds are different. See Figures 14.1 and 14.3 on page 263. ...
Name
... 4. How do you find the total net force if 2 forces are acting on an object in opposite directions? 5. Draw a diagram showing 2 forces acting on an object in opposite directions with a total net force of 3N to the left. ...
... 4. How do you find the total net force if 2 forces are acting on an object in opposite directions? 5. Draw a diagram showing 2 forces acting on an object in opposite directions with a total net force of 3N to the left. ...
Document
... Given: Negligible air resistance, (i.e. undergoing free fall) i.e. a = - 9.81 m s-2. To find the angle of the landing, the direction of the velocity needs to be determined. Thus the final horizontal and vertical velocities need to be found. Based on the table, ...
... Given: Negligible air resistance, (i.e. undergoing free fall) i.e. a = - 9.81 m s-2. To find the angle of the landing, the direction of the velocity needs to be determined. Thus the final horizontal and vertical velocities need to be found. Based on the table, ...
Problem 3.18 A raindrop of initial mass 0 M starts falling from rest
... Problem 3.18 A raindrop of initial mass M 0 starts falling from rest under the influence of gravity. Assume that the drop gains mass from the cloud at a rate proportional to the product of its instantaneous mass and its instantaneous velocity: dM = kMV , where k is a constant. dt Show that the speed ...
... Problem 3.18 A raindrop of initial mass M 0 starts falling from rest under the influence of gravity. Assume that the drop gains mass from the cloud at a rate proportional to the product of its instantaneous mass and its instantaneous velocity: dM = kMV , where k is a constant. dt Show that the speed ...
2009 Final Exam
... What is the magnitude of the acceleration of an object that changes its velocity from 2.8 m/s to 6.4 m/s over a distance of 15 m? (A) (B) ...
... What is the magnitude of the acceleration of an object that changes its velocity from 2.8 m/s to 6.4 m/s over a distance of 15 m? (A) (B) ...
Kepler`s Laws
... Kepler’s Laws Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) discovered three laws of planetary motion in the early seventeenth century. These laws were discovered empirically, after studying for many years data collected primarily by the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). The first mathematical derivation of K ...
... Kepler’s Laws Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) discovered three laws of planetary motion in the early seventeenth century. These laws were discovered empirically, after studying for many years data collected primarily by the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). The first mathematical derivation of K ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
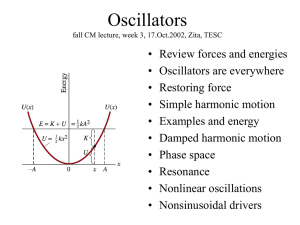
... model damping force proportional to velocity, Fd = - c v: S F = ma - k x - cx’ = m x” Simplify equation: multiply by m, insert w=k/m and g = c/(2m): Guess a solution: x = C e lt Sub in guessed x and solve resultant “characteristic equation” for l. ...
... model damping force proportional to velocity, Fd = - c v: S F = ma - k x - cx’ = m x” Simplify equation: multiply by m, insert w=k/m and g = c/(2m): Guess a solution: x = C e lt Sub in guessed x and solve resultant “characteristic equation” for l. ...
Work Energy Powerpoint
... Work is the component of force in the direction of displacement times the magnitude of the displacement or the component of displacement in the direction of force times the magnitude of the force. Remember that the result is a scalar. It is just the multiplication of the magnitudes of displaceme ...
... Work is the component of force in the direction of displacement times the magnitude of the displacement or the component of displacement in the direction of force times the magnitude of the force. Remember that the result is a scalar. It is just the multiplication of the magnitudes of displaceme ...