Newton`s Laws of Motion
... motion at the same velocity, unless acted upon by a force. • “Law of Inertia” • The tendency of an object to remain in motion or at rest is called inertia. ...
... motion at the same velocity, unless acted upon by a force. • “Law of Inertia” • The tendency of an object to remain in motion or at rest is called inertia. ...
Newton`s Third Law.
... Action and Reaction • Newton’s third law states that when one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts an equal force and moves in the opposite direction. – Example: A frog jumping off a Lilly pad. ...
... Action and Reaction • Newton’s third law states that when one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts an equal force and moves in the opposite direction. – Example: A frog jumping off a Lilly pad. ...
Section 2 What Is a Force?
... Question of the Day Look around the room and think about the objects you see touching another object. A force is always exerted by one object on another object. Answer the following questions on your paper. Where do you see a force happening in the room right now? Which object is exerting the force, ...
... Question of the Day Look around the room and think about the objects you see touching another object. A force is always exerted by one object on another object. Answer the following questions on your paper. Where do you see a force happening in the room right now? Which object is exerting the force, ...
COURSE EXPECTATIONS COURSE CODE: PHYS
... COURSE CODE: PHYS-1006 COURSE NAME: GENERAL PHYSICS I: MECHANICS FACULTY MEMBER: WENFENG CHEN ...
... COURSE CODE: PHYS-1006 COURSE NAME: GENERAL PHYSICS I: MECHANICS FACULTY MEMBER: WENFENG CHEN ...
Slide 1
... Planets orbiting the Sun follow the law that P2=Da3 Where P is the orbital period and a is the distance of the object from the Sun. 9) Let us look at this for the circular orbit case. Is it that the orbits are simply larger, and take longer to traverse? v = Δx/Δt, so Δt = Δx/v Δx = C = 2πa, Δt = P = ...
... Planets orbiting the Sun follow the law that P2=Da3 Where P is the orbital period and a is the distance of the object from the Sun. 9) Let us look at this for the circular orbit case. Is it that the orbits are simply larger, and take longer to traverse? v = Δx/Δt, so Δt = Δx/v Δx = C = 2πa, Δt = P = ...
Newton`s Laws
... On Earth, every object will fall at the same rate (not counting air friction) The Acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 meaning that every second, a falling object accelerates 9.8 m/s In other words, every second something is falling it is moving 9.8 m/s faster If you drop a bowling ball and a match b ...
... On Earth, every object will fall at the same rate (not counting air friction) The Acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 meaning that every second, a falling object accelerates 9.8 m/s In other words, every second something is falling it is moving 9.8 m/s faster If you drop a bowling ball and a match b ...
Newton`s First Law
... Let’s start with an easy one, your weight. Remember that weight is relative – your mass isn’t changing (the amount of matter in you) but you weigh different amounts because of gravity Gravity’s acceleration is 9.8m/s2 On earth you take your weight to be what it is ...
... Let’s start with an easy one, your weight. Remember that weight is relative – your mass isn’t changing (the amount of matter in you) but you weigh different amounts because of gravity Gravity’s acceleration is 9.8m/s2 On earth you take your weight to be what it is ...
AP physics final AP test review Mechanics
... are common forces that can act centripetally to cause uniform circular motion. 26. Centripetal Force (A-184 #46) A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a package on the seat of the car to slide toward the right side of the car. Which of the follo ...
... are common forces that can act centripetally to cause uniform circular motion. 26. Centripetal Force (A-184 #46) A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a package on the seat of the car to slide toward the right side of the car. Which of the follo ...
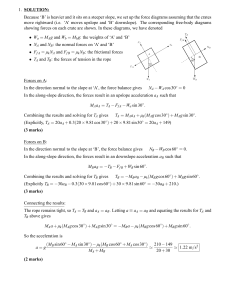
Revision
... Three blocks A, B and C of masses m, 2m and 2m respectively are placed on a smooth horizontal ...
... Three blocks A, B and C of masses m, 2m and 2m respectively are placed on a smooth horizontal ...
specimen
... A force F acts on an object. The object moves at an angle θ to this force. Explain why the work done W by the force in the direction of motion of the object is not just W = Fx ...
... A force F acts on an object. The object moves at an angle θ to this force. Explain why the work done W by the force in the direction of motion of the object is not just W = Fx ...