File - Ms. Quack`s Physics Page
... Newton’s First Law: Newton’s first law of motion states that an object in motion will remain in motion (with constant ________ and __________), and an object at rest will remain at rest, unless acted upon by an ________________ force. This means that if an object is moving with constant velocity OR ...
... Newton’s First Law: Newton’s first law of motion states that an object in motion will remain in motion (with constant ________ and __________), and an object at rest will remain at rest, unless acted upon by an ________________ force. This means that if an object is moving with constant velocity OR ...
study guide for module #10
... 8. In order to get his broken-down car moving, a man must exert an enormous amount of force. Once it is moving, however, the man need not exert nearly as much force to keep it moving. Why? 9. A child is pushing her toy across the room with a constant velocity to the east. If the static friction betw ...
... 8. In order to get his broken-down car moving, a man must exert an enormous amount of force. Once it is moving, however, the man need not exert nearly as much force to keep it moving. Why? 9. A child is pushing her toy across the room with a constant velocity to the east. If the static friction betw ...
How Do I Move? Chapter 7 Biomechanics Centre of Mass
... Sir Isaac Newton developed these laws to explain why things move the way they do ...
... Sir Isaac Newton developed these laws to explain why things move the way they do ...
Chapter 5 – Force and Motion I
... - The acceleration component along a given axis is caused only by the sum of the force components along the same axis, and not by force components along any other axis. - System: collection of bodies. - External force: any force on the bodies inside the system. III. Particular forces: -Gravitational ...
... - The acceleration component along a given axis is caused only by the sum of the force components along the same axis, and not by force components along any other axis. - System: collection of bodies. - External force: any force on the bodies inside the system. III. Particular forces: -Gravitational ...
SC81 Physics Curriculum Map 2010/2011 Revised 7/29/2010
... acceleration for an object in circular motion. 2. Calculate the magnitude of centripetal force and centripetal acceleration for an object in circular motion. S5 C2 PO 11 1. Predict how the force will change between two masses when the distance between them increases or decreases. Predict how the for ...
... acceleration for an object in circular motion. 2. Calculate the magnitude of centripetal force and centripetal acceleration for an object in circular motion. S5 C2 PO 11 1. Predict how the force will change between two masses when the distance between them increases or decreases. Predict how the for ...
Force due to gravity: A field force (a vector quantity) that always is
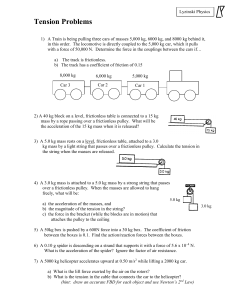
... a) the acceleration of the masses, and b) the magnitude of the tension in the string? c) the force in the bracket (while the blocks are in motion) that attaches the pulley to the ceiling 5) A 50kg box is pushed by a 600N force into a 30 kg box. The coefficient of friction between the boxes is 0.1. F ...
... a) the acceleration of the masses, and b) the magnitude of the tension in the string? c) the force in the bracket (while the blocks are in motion) that attaches the pulley to the ceiling 5) A 50kg box is pushed by a 600N force into a 30 kg box. The coefficient of friction between the boxes is 0.1. F ...
Section 3 - WordPress.com
... direction and finally travels at 40 kmhr-1 for 90 minutes in a South direction. Draw a vector representation of its trip and hence calculate its average velocity for the journey described. ...
... direction and finally travels at 40 kmhr-1 for 90 minutes in a South direction. Draw a vector representation of its trip and hence calculate its average velocity for the journey described. ...
Midterm Exam Study Guide
... ____ 50. Which of the following would exert the least amount of pressure on the ground? a. A woman standing in running shoes c. a woman standing in high heels b. A woman sitting on the ground d. a woman standing on skis ____ 51. A tennis ball and a solid steel ball of the same size are dropped at th ...
... ____ 50. Which of the following would exert the least amount of pressure on the ground? a. A woman standing in running shoes c. a woman standing in high heels b. A woman sitting on the ground d. a woman standing on skis ____ 51. A tennis ball and a solid steel ball of the same size are dropped at th ...
Chapter 7 Energy of a system Conceptual question Q7.1 Can kinetic
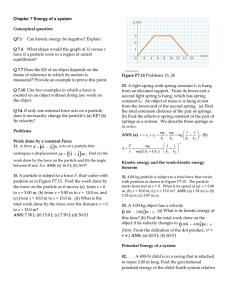
... particle within a system due to its intteaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = (2x + 4) N describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00 m, calculate (a) the work done by this force, (b) the change in the potential energy ...
... particle within a system due to its intteaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = (2x + 4) N describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00 m, calculate (a) the work done by this force, (b) the change in the potential energy ...