Unit 4 Lessons 9
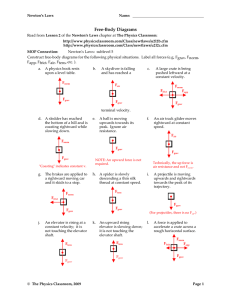
... Remember! A force is a push or a pull An unbalanced force changes an object’s motion Objects have inertia and resist forces that try to change their motion Friction is the force between two surfaces that oppose motion Unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate according to the equation: ...
... Remember! A force is a push or a pull An unbalanced force changes an object’s motion Objects have inertia and resist forces that try to change their motion Friction is the force between two surfaces that oppose motion Unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate according to the equation: ...
LetsrideonanElevator
... parabola. By modifying the flight path, any value for the apparent gravity may be produced. http://www.youtube.com/wat ch?v=2V9h42yspbo ...
... parabola. By modifying the flight path, any value for the apparent gravity may be produced. http://www.youtube.com/wat ch?v=2V9h42yspbo ...
Acceleration
... • Demonstrate your understanding of directions and signs for velocity, displacement, and acceleration. • Solve problems involving a free-falling body in a gravitational field. ...
... • Demonstrate your understanding of directions and signs for velocity, displacement, and acceleration. • Solve problems involving a free-falling body in a gravitational field. ...
Document
... 9) The time it takes to get to the top of its path is the same as the time to get from the top back to the ground. 10)The range of the projectile (where it lands) depends on its initial speed and angle of elevation ...
... 9) The time it takes to get to the top of its path is the same as the time to get from the top back to the ground. 10)The range of the projectile (where it lands) depends on its initial speed and angle of elevation ...
May 2008
... A particle of mass m has a velocity v relative to the Earth as it traverses the solar system at the orbital radius of the Earth around the Sun. The initial velocity v is the value far enough outside the gravitational well of Earth that the Earth’s gravitational effects need to be accounted for in wh ...
... A particle of mass m has a velocity v relative to the Earth as it traverses the solar system at the orbital radius of the Earth around the Sun. The initial velocity v is the value far enough outside the gravitational well of Earth that the Earth’s gravitational effects need to be accounted for in wh ...
1 Newton`s Second Law
... Read this passage from the text and answer the questions that follow. Acceleration and Weight Newton’s second law of motion explains the weight of objects. Weight is a measure of the force of gravity pulling on an object of a given mass. It’s the force (F) in the acceleration equation that was intro ...
... Read this passage from the text and answer the questions that follow. Acceleration and Weight Newton’s second law of motion explains the weight of objects. Weight is a measure of the force of gravity pulling on an object of a given mass. It’s the force (F) in the acceleration equation that was intro ...
Exam 1B #2
... sweeps out a cone as the bob rotates.) The bob has a mass of 0.040 kg, the string has length L = 0.90 m and negligible mass, and the bob follows a circular path of circumference 0.96 m. ...
... sweeps out a cone as the bob rotates.) The bob has a mass of 0.040 kg, the string has length L = 0.90 m and negligible mass, and the bob follows a circular path of circumference 0.96 m. ...
Balanced Forces
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net or unbalanced force. ...
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net or unbalanced force. ...