Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
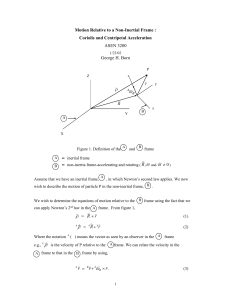
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
II 1 — Newton`s Laws - Carroll`s Cave of Knowledge
... II 1 — Newton’s Laws Newton’s First Law: A body will continue in its state of uniform motion (magnitude and direction) or rest until it is compelled to change due to a net force acting on it. This is sometimes referred to as the law of inertia. An objects inertia varies directly with its mass; how h ...
... II 1 — Newton’s Laws Newton’s First Law: A body will continue in its state of uniform motion (magnitude and direction) or rest until it is compelled to change due to a net force acting on it. This is sometimes referred to as the law of inertia. An objects inertia varies directly with its mass; how h ...
Chapter 5-6
... the blocks? 1.96 m/s2 (b) What is the tension in the string? 7.51 N [Answer] (a) To estimate the friction force, we need to know the normal force. Fr = N * k for the first block, N1 = m1 g = 1.3 * 9.81 N = 12.8 N for the second block, N2 = m2 g = 1.63 * 9.81 N = 16.0 N Fr1 = N1 * 0.27 = 3.44N; Fr2 = ...
... the blocks? 1.96 m/s2 (b) What is the tension in the string? 7.51 N [Answer] (a) To estimate the friction force, we need to know the normal force. Fr = N * k for the first block, N1 = m1 g = 1.3 * 9.81 N = 12.8 N for the second block, N2 = m2 g = 1.63 * 9.81 N = 16.0 N Fr1 = N1 * 0.27 = 3.44N; Fr2 = ...
Document
... The work done by forces on an object = changes in energy for that object. Work and Energy are measured in ...
... The work done by forces on an object = changes in energy for that object. Work and Energy are measured in ...
Topic 2 Problem Set
... work and answers on this sheet will not be counted. Show all your work on including formulas and substitutions. Minimum credit will be awarded for answers without work. Topic 2.1.1 1. A fly travels along the x-axis. His starting point is x = 16 m and his ending point is x = -25 m. His flight lasts 4 ...
... work and answers on this sheet will not be counted. Show all your work on including formulas and substitutions. Minimum credit will be awarded for answers without work. Topic 2.1.1 1. A fly travels along the x-axis. His starting point is x = 16 m and his ending point is x = -25 m. His flight lasts 4 ...
6 Flags Lab
... a. Weight vs. Mass vs. Apparent mass b. Newton’s Second Law (free body diagrams, net force, acceleration) c. Conservation of energy (overall concept and individual types of energy) d. Circular motion (include a diagram of Fc, ac, and velocity vectors) 2. For each section above, you will include the ...
... a. Weight vs. Mass vs. Apparent mass b. Newton’s Second Law (free body diagrams, net force, acceleration) c. Conservation of energy (overall concept and individual types of energy) d. Circular motion (include a diagram of Fc, ac, and velocity vectors) 2. For each section above, you will include the ...
Document
... One example of damped motion occurs when an object is attached to a spring and submerged in a viscous liquid The retarding force can be expressed as R bv where b is a constant ...
... One example of damped motion occurs when an object is attached to a spring and submerged in a viscous liquid The retarding force can be expressed as R bv where b is a constant ...
Force & Motion
... Magicians use this force to Pull a table cloth out from under Dishes on a table. The dishes Stay at rest as the cloth is Pulled out from under them. ...
... Magicians use this force to Pull a table cloth out from under Dishes on a table. The dishes Stay at rest as the cloth is Pulled out from under them. ...
Newtonian mechanics problem solving
... 4. Apply the impulse-momentum equation taking note that force and velocity are vectors and that direction of the vector plays an important part in the solution. For problems involving no external force acting on the system: 1. Use the law of conservation of momentum to solve the problem. Take note t ...
... 4. Apply the impulse-momentum equation taking note that force and velocity are vectors and that direction of the vector plays an important part in the solution. For problems involving no external force acting on the system: 1. Use the law of conservation of momentum to solve the problem. Take note t ...
Statics Lecture
... Dynamics Dynamics is the branch of Mechanics that deals with objects/materials that are accelerating due to an imbalance of forces. Examples: 1. A rollercoaster executing a loop (dynamics) 2. Flow of water from a hose (hydrodynamics) ...
... Dynamics Dynamics is the branch of Mechanics that deals with objects/materials that are accelerating due to an imbalance of forces. Examples: 1. A rollercoaster executing a loop (dynamics) 2. Flow of water from a hose (hydrodynamics) ...
File
... 15. If the action force is a hockey stick pushing a puck to the left, then the reaction force is the ___. a. puck pulling the hockey stick to the left b. puck pulling the hockey stick to the right c. puck pushing the hockey stick to the left d. puck pushing the hockey stick to the right ...
... 15. If the action force is a hockey stick pushing a puck to the left, then the reaction force is the ___. a. puck pulling the hockey stick to the left b. puck pulling the hockey stick to the right c. puck pushing the hockey stick to the left d. puck pushing the hockey stick to the right ...























