Newton`s Laws PPT
... Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface there is a force acting on that object. Frictional force is the component of this force that is parallel to the surface. ...
... Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface there is a force acting on that object. Frictional force is the component of this force that is parallel to the surface. ...
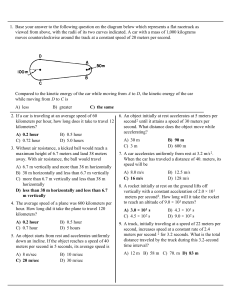
... Which statement best describes the transformation of energy that occurs between the t i and t f? A) Gravitational potential energy at t i is converted to internal energy at t f. B) Elastic potential energy at t i is converted to kinetic energy at t f. C) Both elastic potential energy and kinetic ene ...
Chapter 2
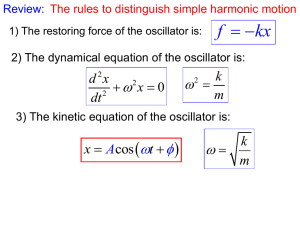
... A particle moves along x axis in simple harmonic motion. Its amplitude A=0.12m, period T=2s. When t=0, its displacement is x(0)=0.06m, moving to the positive direction of the equilibrium position. Find: 1) The kinetic equation of the simple harmonic motion. 2) t=T/4, the position, velocity and accel ...
... A particle moves along x axis in simple harmonic motion. Its amplitude A=0.12m, period T=2s. When t=0, its displacement is x(0)=0.06m, moving to the positive direction of the equilibrium position. Find: 1) The kinetic equation of the simple harmonic motion. 2) t=T/4, the position, velocity and accel ...
phys1443-fall04-111704
... What do you think does the term “An object is at its equilibrium” mean? The object is either at rest (Static Equilibrium) or its center of mass is moving with a constant velocity (Dynamic Equilibrium). When do you think an object is at its equilibrium? Translational Equilibrium: Equilibrium in linea ...
... What do you think does the term “An object is at its equilibrium” mean? The object is either at rest (Static Equilibrium) or its center of mass is moving with a constant velocity (Dynamic Equilibrium). When do you think an object is at its equilibrium? Translational Equilibrium: Equilibrium in linea ...
berncatcaptions1
... Paperclip Pedagogy for Calculus and Catenaries by the Boston LYM In his Lecture on the catenary, in assumption 2 Bernoulli states that if a section AC between points A and C on the chain is replaced by two weightless strings tangent to the curve at A and at C, with a weight equal to the missing chai ...
... Paperclip Pedagogy for Calculus and Catenaries by the Boston LYM In his Lecture on the catenary, in assumption 2 Bernoulli states that if a section AC between points A and C on the chain is replaced by two weightless strings tangent to the curve at A and at C, with a weight equal to the missing chai ...
Chapter 10 Forces
... 4. If an object starts out at rest and accelerates to 100 m/s, what is its initial speed? a. -100 m/s b. 0 m/s c. 100 m/s d. 32 m/s ...
... 4. If an object starts out at rest and accelerates to 100 m/s, what is its initial speed? a. -100 m/s b. 0 m/s c. 100 m/s d. 32 m/s ...
Descriptive Essay: The Night Market
... SECTION -CNote: Attempt any 03 questions form this sections including Q.No.19, which is compulsory. All question carry equal marks. Q.17. Factorize the following. (i) a3 - a2 + 2 (ii) x3 + x3 – 2y + 8y3 (iii) 8a3 + b2 + 27c3 - 18abc (iv) a4 + a2 +1 Q.18. Find the solution set of the following equati ...
... SECTION -CNote: Attempt any 03 questions form this sections including Q.No.19, which is compulsory. All question carry equal marks. Q.17. Factorize the following. (i) a3 - a2 + 2 (ii) x3 + x3 – 2y + 8y3 (iii) 8a3 + b2 + 27c3 - 18abc (iv) a4 + a2 +1 Q.18. Find the solution set of the following equati ...
F = 0 x = 0 F =
... Why were we told that the oscillations started toward the right? So that we would know whether we needed a positive or a negative sign out front. When the mass starts at zero, it can go either positive or negative in displacement. If we take to the right as positive, the equation will not need a neg ...
... Why were we told that the oscillations started toward the right? So that we would know whether we needed a positive or a negative sign out front. When the mass starts at zero, it can go either positive or negative in displacement. If we take to the right as positive, the equation will not need a neg ...
Stress, Strain, Virtual Power and Conservation Principles
... In vector and tensor calculus, subscript and superscript index notation is used to denote collections of variables, for instance, the set x1 ; x2 ; :::; xn is denoted by xi ; i = 1; 2; :::; n or by xi ; i = 1; 2; :::; n. Likewise, the set y 1 ; y 2 ; :::; y n is denoted as y j ; j = 1; 2; :::; n. N ...
... In vector and tensor calculus, subscript and superscript index notation is used to denote collections of variables, for instance, the set x1 ; x2 ; :::; xn is denoted by xi ; i = 1; 2; :::; n or by xi ; i = 1; 2; :::; n. Likewise, the set y 1 ; y 2 ; :::; y n is denoted as y j ; j = 1; 2; :::; n. N ...
Materialy/01/Applied Mechanics-Lectures/Applied Mechanics
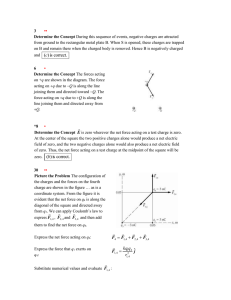
... Elastic force - elastic body - body for which any produced work is stored in a recoverable form - giving rise to variation of internal energy 3 N ...
... Elastic force - elastic body - body for which any produced work is stored in a recoverable form - giving rise to variation of internal energy 3 N ...
0 Gravity, Rotation, Shape of the Earth 0.1 Inertia. Conservation laws
... Newton’s first law of motion: A body at rest or in uniform motion will not change its velocity unless forces are applied. (Galileo) Newton’s second law of motion: The relationship between an object’s mass m, its acceleration ~a, and the applied force f~ is m~a = f~ Newton’s third law: action = react ...
... Newton’s first law of motion: A body at rest or in uniform motion will not change its velocity unless forces are applied. (Galileo) Newton’s second law of motion: The relationship between an object’s mass m, its acceleration ~a, and the applied force f~ is m~a = f~ Newton’s third law: action = react ...
Physics 430
... to be the center of the circle, we simply have: x x iy Ceiwt Note, however, that the position at t = 0 is not zero, but rather is x (0) xo iyo C This may seem confusing at first. If we chose our coordinate system to be the center of the circle, why doesn’t this set the initial condition ...
... to be the center of the circle, we simply have: x x iy Ceiwt Note, however, that the position at t = 0 is not zero, but rather is x (0) xo iyo C This may seem confusing at first. If we chose our coordinate system to be the center of the circle, why doesn’t this set the initial condition ...
Physics Lab Report Guide and Sample Report
... to state a question or hypothesis that you want to address. Method: You should include a summary of the lab procedure in your words; do not merely copy what is in the manual. This section should demonstrate your understanding of what exactly you measured and how you measured it. Data: In this sectio ...
... to state a question or hypothesis that you want to address. Method: You should include a summary of the lab procedure in your words; do not merely copy what is in the manual. This section should demonstrate your understanding of what exactly you measured and how you measured it. Data: In this sectio ...
Mag. Fields
... To figure out the direction of magnetic force, use the following steps: F qv B 1. Point your fingers straight out in direction of first vector v 2. Twist your hand so when you curl your fingers, they point in the direction of B 3. Your thumb now points in the direction of v B 4. If q is negati ...
... To figure out the direction of magnetic force, use the following steps: F qv B 1. Point your fingers straight out in direction of first vector v 2. Twist your hand so when you curl your fingers, they point in the direction of B 3. Your thumb now points in the direction of v B 4. If q is negati ...