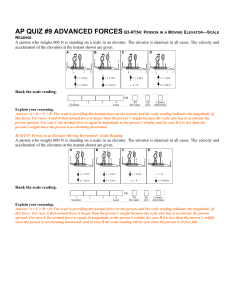
In Chapters 2 and 3 of this course the emphasis is
... In Chapters 2 and 3 of this course the emphasis is on kinematics, the mathematical description of motion. In Chapter 4, the heart of the course, we shift the emphasis to explaining why changes in motions occur. This branch of mechanics is called dynamics. Together, what we have learned and what we w ...
... In Chapters 2 and 3 of this course the emphasis is on kinematics, the mathematical description of motion. In Chapter 4, the heart of the course, we shift the emphasis to explaining why changes in motions occur. This branch of mechanics is called dynamics. Together, what we have learned and what we w ...
9 - tucek
... p1=pA1+pB1=0 pA1 + pA2 = pA2 + pB2 0 =pA2 + pB2 pA2 = -pB2 mAvA2=-mBvB2 so solve for vA2=-(mBvB2) ...
... p1=pA1+pB1=0 pA1 + pA2 = pA2 + pB2 0 =pA2 + pB2 pA2 = -pB2 mAvA2=-mBvB2 so solve for vA2=-(mBvB2) ...
electromagnetic theory
... scalar or vectors [There are other class of physical quantities called Tensors: scalars and vectors are special cases]. Scalars are quantities characterized by magnitude only and algebraic sign. A quantity that has direction as well as magnitude is called a vector. Both scalar and vector quantities ...
... scalar or vectors [There are other class of physical quantities called Tensors: scalars and vectors are special cases]. Scalars are quantities characterized by magnitude only and algebraic sign. A quantity that has direction as well as magnitude is called a vector. Both scalar and vector quantities ...
Types of Forces
... As mentioned above, the friction force is the force exerted by a surface as an object moves across it or makes an effort to move across it. For the purpose of our study of physics at The Physics Classroom, there are two types of friction force static friction and sliding friction. Sliding friction r ...
... As mentioned above, the friction force is the force exerted by a surface as an object moves across it or makes an effort to move across it. For the purpose of our study of physics at The Physics Classroom, there are two types of friction force static friction and sliding friction. Sliding friction r ...
PES 1110 Fall 2013, Spendier Lecture 21/Page 1 Today
... In order to apply all we have learned to object of finite size, we need to define the center of mass (com). The center of mass (com) of a system of particles is the position through all external forces appear to act. It is the position we give an extended object. In practice it is the point around w ...
... In order to apply all we have learned to object of finite size, we need to define the center of mass (com). The center of mass (com) of a system of particles is the position through all external forces appear to act. It is the position we give an extended object. In practice it is the point around w ...
1 Mechanical Equilibrium
... A force is needed to change an object’s state of motion. The downward force acting on an object is called weight, while any stretching force on an object (such as a force exerted by a rope or wire) is called tension. The SI (Système International) unit for force is the newton (N). A newton weighs ab ...
... A force is needed to change an object’s state of motion. The downward force acting on an object is called weight, while any stretching force on an object (such as a force exerted by a rope or wire) is called tension. The SI (Système International) unit for force is the newton (N). A newton weighs ab ...
Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity
... Example Problem: Driving Over A Rise A car of mass 1500 kg goes over a hill at a speed of 20 m/s. The shape of the hill is approximately circular, with a radius of 60 m, as in the figure at right. When the car is at the highest point of the hill, a. What is the force of gravity on the car? b. What ...
... Example Problem: Driving Over A Rise A car of mass 1500 kg goes over a hill at a speed of 20 m/s. The shape of the hill is approximately circular, with a radius of 60 m, as in the figure at right. When the car is at the highest point of the hill, a. What is the force of gravity on the car? b. What ...
Applying Newton`s Laws
... • The tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion is referred to as its inertia. ...
... • The tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion is referred to as its inertia. ...
N e w t o n` s L a w s
... Example: On a touchdown attempt, a 95 kg running back runs toward the end zone at 3.75 m/s. A 111kg linebacker moving at 4.10 m/s meets the runner in a head on collision. If the two players stick together what is their velocity immediately after the collision? ...
... Example: On a touchdown attempt, a 95 kg running back runs toward the end zone at 3.75 m/s. A 111kg linebacker moving at 4.10 m/s meets the runner in a head on collision. If the two players stick together what is their velocity immediately after the collision? ...