PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section V Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser
... and carries a current of 1.20 µA. In a vacuum, a proton moves parallel to the wire (opposite the current) with a constant velocity of 2.30 × 104 m/s at a constant distance d above the wire. Determine the value of d. You may ignore the magnetic field due to the Earth. ...
... and carries a current of 1.20 µA. In a vacuum, a proton moves parallel to the wire (opposite the current) with a constant velocity of 2.30 × 104 m/s at a constant distance d above the wire. Determine the value of d. You may ignore the magnetic field due to the Earth. ...
Mag. Fields
... To figure out the direction of magnetic force, use the following steps: F qv B 1. Point your fingers straight out in direction of first vector v 2. Twist your hand so when you curl your fingers, they point in the direction of B 3. Your thumb now points in the direction of v B 4. If q is negati ...
... To figure out the direction of magnetic force, use the following steps: F qv B 1. Point your fingers straight out in direction of first vector v 2. Twist your hand so when you curl your fingers, they point in the direction of B 3. Your thumb now points in the direction of v B 4. If q is negati ...
Roller coaster Activities
... pushes it toward the center of the circular path. This is the centripetal force. ...
... pushes it toward the center of the circular path. This is the centripetal force. ...
Solutions - American Association of Physics Teachers
... sphere is identical to that of a point mass. Which of the following best explains the discrepancy? (A) Because the experiment takes place very close to the surface of the sphere, it is no longer valid to replace the sphere with a point mass. (B) Because the particle strikes the ground, it is not in ...
... sphere is identical to that of a point mass. Which of the following best explains the discrepancy? (A) Because the experiment takes place very close to the surface of the sphere, it is no longer valid to replace the sphere with a point mass. (B) Because the particle strikes the ground, it is not in ...
Collisions – Impulse and Momentum
... 5. Rescale the Force vs time graph (The impulse graph) so that you can clearly see the data points where contact began, and contact ended. 6. Click on the Highlight Range icon near the top left of the impulse graph to make a highlight box appear on the impulse graph. Rescale the graph and the high ...
... 5. Rescale the Force vs time graph (The impulse graph) so that you can clearly see the data points where contact began, and contact ended. 6. Click on the Highlight Range icon near the top left of the impulse graph to make a highlight box appear on the impulse graph. Rescale the graph and the high ...
Lesson - NSTA Communities
... accelerating force. They can use the meter stick, markers, and stop watches to measure the speed of the accelerated body and the time the force acts. Students might need to practice pulling the loaded skateboard with a constant force. They can measure the final speed of the skateboard or its average ...
... accelerating force. They can use the meter stick, markers, and stop watches to measure the speed of the accelerated body and the time the force acts. Students might need to practice pulling the loaded skateboard with a constant force. They can measure the final speed of the skateboard or its average ...
AP QUIZ #5 2D MOTION AP FR Quiz #5 2D Motion
... Explain why you drew the graphs as you did and how you determined your answers. There are no forces in the horizontal direction (ignoring air resistance) so both rocks will have a constant horizontal velocity. Since Rock B is slower than Rock A, it will have a smaller horizontal velocity. Both rocks ...
... Explain why you drew the graphs as you did and how you determined your answers. There are no forces in the horizontal direction (ignoring air resistance) so both rocks will have a constant horizontal velocity. Since Rock B is slower than Rock A, it will have a smaller horizontal velocity. Both rocks ...
It is sometimes difficult to find the polarity of an
... 7. What is the rule for the residual charge of an object charged by conduction? By induction? ...
... 7. What is the rule for the residual charge of an object charged by conduction? By induction? ...
Problem Set 6 - Cabrillo College
... Assess: If all we want to know is the sign of the answer then we do not really need to compute or divide by the denominator—the total mass will certainly be positive and will not affect the sign of the answer. So we could have done a simple mental calculation of the numerator (82 3 110 2) to f ...
... Assess: If all we want to know is the sign of the answer then we do not really need to compute or divide by the denominator—the total mass will certainly be positive and will not affect the sign of the answer. So we could have done a simple mental calculation of the numerator (82 3 110 2) to f ...
PC4262 Remote Sensing - Centre for Remote Imaging, Sensing and
... So, in principal, given the initial position and velocity vectors, the position and velocity of the satellite at any instant t can be evaluated. In practice, evaluating the integrals in (3) and (4) is not straightforward. Note that the acceleration vector is expressed in terms of the instantaneous p ...
... So, in principal, given the initial position and velocity vectors, the position and velocity of the satellite at any instant t can be evaluated. In practice, evaluating the integrals in (3) and (4) is not straightforward. Note that the acceleration vector is expressed in terms of the instantaneous p ...
Experiment 1 - 6. Motion of spring pendulum
... each motion of them and a pendulum which is suspended by thread which is fixed length. And then observe the motion of object when you use spring, suspending weight, as pendulum. In this case, since the gravitational force acts on a pendulum as the restoring force with the restoring force of spring, ...
... each motion of them and a pendulum which is suspended by thread which is fixed length. And then observe the motion of object when you use spring, suspending weight, as pendulum. In this case, since the gravitational force acts on a pendulum as the restoring force with the restoring force of spring, ...
04_InstructorGuideWin
... These activities are good preparation for the critical demonstration of Day 1. Place a block in the center of the lecture table and ask students what force or forces are acting on the block. You’ll get lots of responses of “gravity.” If you inquire about other forces, a few will say “the normal forc ...
... These activities are good preparation for the critical demonstration of Day 1. Place a block in the center of the lecture table and ask students what force or forces are acting on the block. You’ll get lots of responses of “gravity.” If you inquire about other forces, a few will say “the normal forc ...
Horse and Wagon question: Answer
... involved, a clear explanation only hinges on a couple of simple points: An object accelerates (or not) because of the forces that push or pull on it. (Newton’s 2nd) Only the forces that act on an object can cancel. Forces that act on different objects don’t cancel- after all; they affect the mot ...
... involved, a clear explanation only hinges on a couple of simple points: An object accelerates (or not) because of the forces that push or pull on it. (Newton’s 2nd) Only the forces that act on an object can cancel. Forces that act on different objects don’t cancel- after all; they affect the mot ...
File
... Once again, what then is the force that is equal and opposite to the gravitational force exerted by the earth on the apple? ...
... Once again, what then is the force that is equal and opposite to the gravitational force exerted by the earth on the apple? ...
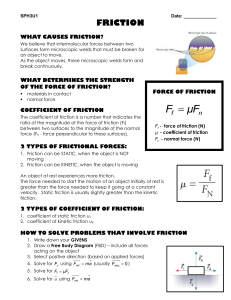
Lab3_Friction (donot print)
... applied force increases, the static frictional force increases, but the object still does not move until some maximum static frictional force is reached. At this point the applied force is sufficient to break the bonding between the block and the table, and the object moves. Once the object is slidi ...
... applied force increases, the static frictional force increases, but the object still does not move until some maximum static frictional force is reached. At this point the applied force is sufficient to break the bonding between the block and the table, and the object moves. Once the object is slidi ...
Q1. (a) Every object has a centre of mass. What is meant by the
... into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. Some electrical circuits are protected by a circuit breaker. These switch the circuit off if a fault causes a larger than normal current to flow. The diagram shows one type of circuit breaker. A normal current (15 A) is flowing. ...
... into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. Some electrical circuits are protected by a circuit breaker. These switch the circuit off if a fault causes a larger than normal current to flow. The diagram shows one type of circuit breaker. A normal current (15 A) is flowing. ...