Thermodynamics
... • Each molecule has a specific number of microstates, W, associated with it. • Entropy is S = k lnW where k is the Boltzmann constant, 1.38 1023 J/K. ...
... • Each molecule has a specific number of microstates, W, associated with it. • Entropy is S = k lnW where k is the Boltzmann constant, 1.38 1023 J/K. ...
Entropy - RIT - People
... • Heating Cycle, Geothermal Technology WFI Global • Cooling Cycle, Geothermal Technology WFI Global But again…What really is Entropy? ...
... • Heating Cycle, Geothermal Technology WFI Global • Cooling Cycle, Geothermal Technology WFI Global But again…What really is Entropy? ...
EGU2016-10322 - CO Meeting Organizer
... with Ae a pre-exponential constant related to the viscosity at infinite temperature, Be (J mol−1 ) a constant proportional to the potential energy barrier opposed to the cooperative rearrangement of the liquid structure and S conf (T ) (J mol−1 K−1 ) the melt configurational entropy. With expressing ...
... with Ae a pre-exponential constant related to the viscosity at infinite temperature, Be (J mol−1 ) a constant proportional to the potential energy barrier opposed to the cooperative rearrangement of the liquid structure and S conf (T ) (J mol−1 K−1 ) the melt configurational entropy. With expressing ...
Entropy in chemical thermodynamics
... The second law can also be used to predict whether a physical process will proceed spontaneously. Spontaneous changes in isolated systems occur with an increase in entropy. Correspondence The statistical definition of entropy matches up with the thermodynamic formula for calculating entropy, because ...
... The second law can also be used to predict whether a physical process will proceed spontaneously. Spontaneous changes in isolated systems occur with an increase in entropy. Correspondence The statistical definition of entropy matches up with the thermodynamic formula for calculating entropy, because ...
Chapter 10: Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The Third Law of Thermodynamics • The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a perfect crystal of any pure substance approaches zero as the temperature approaches absolute zero. • Because S is explicitly known (= 0) at 0 K, S values at other temps can be calculated. • The entropy of ...
... The Third Law of Thermodynamics • The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a perfect crystal of any pure substance approaches zero as the temperature approaches absolute zero. • Because S is explicitly known (= 0) at 0 K, S values at other temps can be calculated. • The entropy of ...
Entropy and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The total entropy of all systems taking part in a process never decreases. It remains the same only if the process is quasistatic. The entropy of an isolated (closed) system can never decrease. It remains the same only if all internal processes are quasistatic. Note that real processes are never exa ...
... The total entropy of all systems taking part in a process never decreases. It remains the same only if the process is quasistatic. The entropy of an isolated (closed) system can never decrease. It remains the same only if all internal processes are quasistatic. Note that real processes are never exa ...
0.1 Minimum Principles and Thermodynamic Potentials
... The minimum principle for G then states that for all states at a fixed T and P , the equilibrium state is that for which G is a minimum. The proof is very similar to that for A: the second law states that ∆Q ≤ T ∆S or 0 ≥ T ∆S + ∆U + P ∆V , if P is held fixed. But dG = dU − T dS + P dV , so dG ≤ 0 i ...
... The minimum principle for G then states that for all states at a fixed T and P , the equilibrium state is that for which G is a minimum. The proof is very similar to that for A: the second law states that ∆Q ≤ T ∆S or 0 ≥ T ∆S + ∆U + P ∆V , if P is held fixed. But dG = dU − T dS + P dV , so dG ≤ 0 i ...
Introduction into thermodynamics Thermodynamic variables
... Because we do not know the absolute values of those energies, this equation can be actually used in the form ∆G = ∆H − T ∆S ...
... Because we do not know the absolute values of those energies, this equation can be actually used in the form ∆G = ∆H − T ∆S ...
Some useful Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Introduction
... The second law states that the number of accessible micro-states of an isolated system, Ω, never decreases. If we consider subsystem A to contain and ideal atomic gas, then the number of accessible micro-states of A is simply the number of places in space that may be occupied by the gas atoms. Thus, ...
... The second law states that the number of accessible micro-states of an isolated system, Ω, never decreases. If we consider subsystem A to contain and ideal atomic gas, then the number of accessible micro-states of A is simply the number of places in space that may be occupied by the gas atoms. Thus, ...
about entropy in psoup
... The motion of each bug is pseudodeterministic. Due to the very large random, being driven by a pseudonumber of particles, statistical methods random number generator, and are used to discuss average behaviour moderated (biased) by the effects of the and/or probability distributions. Palmiter genes. ...
... The motion of each bug is pseudodeterministic. Due to the very large random, being driven by a pseudonumber of particles, statistical methods random number generator, and are used to discuss average behaviour moderated (biased) by the effects of the and/or probability distributions. Palmiter genes. ...
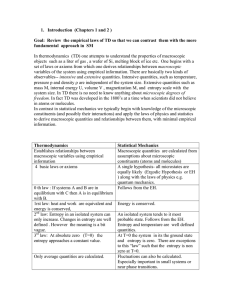
1. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2 ) Goal: Review the empirical laws
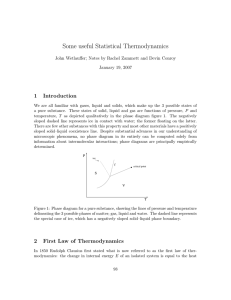
... 1. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2 ) Goal: Review the empirical laws of TD so that we can contrast them with the more fundamental approach in SM In thermodynamics (TD) one attempts to understand the properties of macroscopic objects such as a liter of gas , a wafer of Si, melting block of ice etc. On ...
... 1. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2 ) Goal: Review the empirical laws of TD so that we can contrast them with the more fundamental approach in SM In thermodynamics (TD) one attempts to understand the properties of macroscopic objects such as a liter of gas , a wafer of Si, melting block of ice etc. On ...
On Clausius, Boltzmann and Shannon Notions of Entropy
... rigorous, particularly in what concerns the cases of inverse-power law intermolecular potentials with p > 2 . For the former Boltmann’s equation, recently has been proved that it has classical solutions holding some relevant additional conditions (see [7] and [8]) which has been an open and very dif ...
... rigorous, particularly in what concerns the cases of inverse-power law intermolecular potentials with p > 2 . For the former Boltmann’s equation, recently has been proved that it has classical solutions holding some relevant additional conditions (see [7] and [8]) which has been an open and very dif ...
H-theorem

In classical statistical mechanics, the H-theorem, introduced by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872, describes the tendency to increase in the quantity H (defined below) in a nearly-ideal gas of molecules. As this quantity H was meant to represent the entropy of thermodynamics, the H-theorem was an early demonstration of the power of statistical mechanics as it claimed to derive the second law of thermodynamics—a statement about fundamentally irreversible processes—from reversible microscopic mechanics.The H-theorem is a natural consequence of the kinetic equation derived by Boltzmann that has come to be known as Boltzmann's equation. The H-theorem has led to considerable discussion about its actual implications, with major themes being: What is entropy? In what sense does Boltzmann's quantity H correspond to the thermodynamic entropy? Are the assumptions (such as the Stosszahlansatz described below) behind Boltzmann's equation too strong? When are these assumptions violated?↑