Chap 7 - College of Science | Oregon State University
... Instead of moving thermal energy around to output work (motion), we put in the work (a motor drives a compressor for example) and thus move thermal energy around. Form 3: Entropy is increasing. (In any physical process within some system, the total entropy of the system either stays constant or incr ...
... Instead of moving thermal energy around to output work (motion), we put in the work (a motor drives a compressor for example) and thus move thermal energy around. Form 3: Entropy is increasing. (In any physical process within some system, the total entropy of the system either stays constant or incr ...
Construction of microcanonical entropy on
... Before we proceed it is important to explain the meaning of Q within the microcanonical formalism. The idea behind the microcanonical ensemble is that E and λ are controllable parameters.1 Accordingly, if the system is on an energy surface identified by (E,λ), the idea is that the experimentalist is ...
... Before we proceed it is important to explain the meaning of Q within the microcanonical formalism. The idea behind the microcanonical ensemble is that E and λ are controllable parameters.1 Accordingly, if the system is on an energy surface identified by (E,λ), the idea is that the experimentalist is ...
The Four Laws of Thermodynamics
... universe), through the concept of free energy, and to the brink, and then beyond the brink, of absolute zero. C.P. Snow once remarked that not knowing the second law of thermodynamics is like never having read a work by Shakespeare. This brief but brilliant book introduces general readers to one of ...
... universe), through the concept of free energy, and to the brink, and then beyond the brink, of absolute zero. C.P. Snow once remarked that not knowing the second law of thermodynamics is like never having read a work by Shakespeare. This brief but brilliant book introduces general readers to one of ...
any physical system, whether or not it can exchange energy and
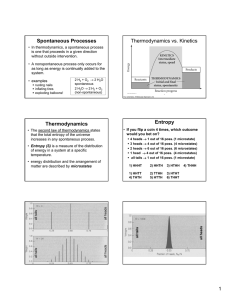
... The first law states that energy can not be destroyed nor created. The second law (often referred to as the 'entropy' law) states that the quality of energy is degraded in each spontaneous change. ...
... The first law states that energy can not be destroyed nor created. The second law (often referred to as the 'entropy' law) states that the quality of energy is degraded in each spontaneous change. ...
Lecture 1
... directly related to the increase in disorder of the gas. Since there is more space to occupy, there are more ways which the molecules can exist where the gas has the same state. ...
... directly related to the increase in disorder of the gas. Since there is more space to occupy, there are more ways which the molecules can exist where the gas has the same state. ...
+ p
... Maxwell and Boltzmann developed a statistical model of thermodynamics in which the entropy appeared as a measure of “uncertainty”. Uncertainty should be interpreted as “uniformity” or “lack of differentiation”. ...
... Maxwell and Boltzmann developed a statistical model of thermodynamics in which the entropy appeared as a measure of “uncertainty”. Uncertainty should be interpreted as “uniformity” or “lack of differentiation”. ...
Free Energy Examples
... Suppose an isolated box of volume 2V is divided into two equal compartments. An ideal gas occupies half of the container and the other half is empty. When the partition separating the two halves of the box is removed and the system reaches equilibrium again, how does the new internal energy of the ...
... Suppose an isolated box of volume 2V is divided into two equal compartments. An ideal gas occupies half of the container and the other half is empty. When the partition separating the two halves of the box is removed and the system reaches equilibrium again, how does the new internal energy of the ...
Entropy change of an ideal gas determination with no reversible
... all processes considered are equivalent. The simulations showed that entropy change can indeed be calculated without considering any auxiliary reversible process, and they are also of didactical and pedagogical value, since they can be used to follow the evolution of the gas under a variety of diffe ...
... all processes considered are equivalent. The simulations showed that entropy change can indeed be calculated without considering any auxiliary reversible process, and they are also of didactical and pedagogical value, since they can be used to follow the evolution of the gas under a variety of diffe ...
Chapter 18 - Evangel University
... Energy can be converted from one form to another but energy cannot be created or destroyed. Second Law of __________________ The entropy of the universe increases in a spontaneous process and remains unchanged in an equilibrium process. ...
... Energy can be converted from one form to another but energy cannot be created or destroyed. Second Law of __________________ The entropy of the universe increases in a spontaneous process and remains unchanged in an equilibrium process. ...
IB 3.2 Gases Feb 16 Agenda
... is algebra derivation of formulas types. So know these two fundamental relationships. (Only the first is in the IB packet.) ...
... is algebra derivation of formulas types. So know these two fundamental relationships. (Only the first is in the IB packet.) ...
BOLTZMANN ENTROPY: PROBABILITY AND INFORMATION The
... We have presented a rigorous axiomatic derivation of Boltzmann entropy on the basis of the axioms of additivity and increasing law of entropy consistent with two basic properties of thermodynamic entropy [11]. The method is superior, both mathematically and physically, to the existing methods (excep ...
... We have presented a rigorous axiomatic derivation of Boltzmann entropy on the basis of the axioms of additivity and increasing law of entropy consistent with two basic properties of thermodynamic entropy [11]. The method is superior, both mathematically and physically, to the existing methods (excep ...
Chemistry Entropy Notes 1. What is entropy? How many ways can
... Entropy is the key variable that helps us understand if chemicals will react completely, or if they will react partially, or of they will fail to react. What we call the “system” is the process that we’re interested in – something like the mixing of HCl and NaOH solutions in a single beaker. What we ...
... Entropy is the key variable that helps us understand if chemicals will react completely, or if they will react partially, or of they will fail to react. What we call the “system” is the process that we’re interested in – something like the mixing of HCl and NaOH solutions in a single beaker. What we ...
The “Second Law” of Probability: Entropy Growth in the Central Limit
... Joule and Carnot studied ways to improve the efficiency of steam engines. Is it possible for a thermodynamic system to move from state A to state B without any net energy being put into the system from outside? A single experimental quantity, dubbed entropy, made it possible to decide the direction ...
... Joule and Carnot studied ways to improve the efficiency of steam engines. Is it possible for a thermodynamic system to move from state A to state B without any net energy being put into the system from outside? A single experimental quantity, dubbed entropy, made it possible to decide the direction ...
H-theorem

In classical statistical mechanics, the H-theorem, introduced by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872, describes the tendency to increase in the quantity H (defined below) in a nearly-ideal gas of molecules. As this quantity H was meant to represent the entropy of thermodynamics, the H-theorem was an early demonstration of the power of statistical mechanics as it claimed to derive the second law of thermodynamics—a statement about fundamentally irreversible processes—from reversible microscopic mechanics.The H-theorem is a natural consequence of the kinetic equation derived by Boltzmann that has come to be known as Boltzmann's equation. The H-theorem has led to considerable discussion about its actual implications, with major themes being: What is entropy? In what sense does Boltzmann's quantity H correspond to the thermodynamic entropy? Are the assumptions (such as the Stosszahlansatz described below) behind Boltzmann's equation too strong? When are these assumptions violated?↑