Ling 8700: Lecture Notes 1 A Model of Neural Activation
... Over time (e.g. during sentence processing), the activation of neurons/clusters changes. These changes can be modeled with Recurrent Neural Networks [Elman, 1991]: • the model is defined in terms of a ‘context’ vector of neural units, as shown above; • activation of the context vector defines a ment ...
... Over time (e.g. during sentence processing), the activation of neurons/clusters changes. These changes can be modeled with Recurrent Neural Networks [Elman, 1991]: • the model is defined in terms of a ‘context’ vector of neural units, as shown above; • activation of the context vector defines a ment ...
In What Sense, if Any, do Hippocampal “Time Cells” Represent or
... There is good evidence that the auditory input travels along many parallel patways before reaching the primary auditory cortex. It is prima facie plausible that these different signals do not take the same time to reach their target. So one can describe the auditory cortex as equipped with incoming ...
... There is good evidence that the auditory input travels along many parallel patways before reaching the primary auditory cortex. It is prima facie plausible that these different signals do not take the same time to reach their target. So one can describe the auditory cortex as equipped with incoming ...
**** 1
... number of target they must select by either direct arm motion or neural signals. Interfaces based on selection of a small number of states can be cumbersome to use. ...
... number of target they must select by either direct arm motion or neural signals. Interfaces based on selection of a small number of states can be cumbersome to use. ...
Physiological bases of mental and physical work
... The prefrontal association area is essential to carrying out thought processes in the mind. This presumably results from some of the same capabilities of the prefrontal cortex that allow it to plan motor activities. The prefrontal association area is frequently described as important for elabora ...
... The prefrontal association area is essential to carrying out thought processes in the mind. This presumably results from some of the same capabilities of the prefrontal cortex that allow it to plan motor activities. The prefrontal association area is frequently described as important for elabora ...
Endocrine System: Overview
... Somatic Motor Pathways 9. What two main somatic motor pathways convey action potentials to skeletal muscles? ...
... Somatic Motor Pathways 9. What two main somatic motor pathways convey action potentials to skeletal muscles? ...
ARIEL LEVINE Postdoctoral Associate, The Salk Institute for
... These molecularly-defined “motor synergy encoder” (MSE) neurons represent a central node in neural pathways for volitional and reflexive movement. Direct optical stimulation of MSE neurons is sufficient to drive reliable patterns of activity in multiple motor groups, and we found that the evoked mot ...
... These molecularly-defined “motor synergy encoder” (MSE) neurons represent a central node in neural pathways for volitional and reflexive movement. Direct optical stimulation of MSE neurons is sufficient to drive reliable patterns of activity in multiple motor groups, and we found that the evoked mot ...
Modelling the Development of Mirror Neurons for Auditory
... around those motor-sound pairs that co-vary reliably. These are pairs where the mapping from parameter to sound is nearlinear: a certain motor parameter set corresponds to a certain sound, and small variations in the parameters will only lead to small changes in the produced sound. This relationship ...
... around those motor-sound pairs that co-vary reliably. These are pairs where the mapping from parameter to sound is nearlinear: a certain motor parameter set corresponds to a certain sound, and small variations in the parameters will only lead to small changes in the produced sound. This relationship ...
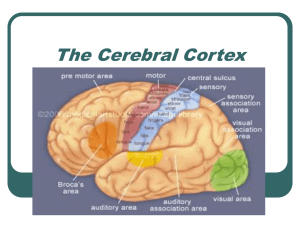
The Cerebral Cortex
... parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
... parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... Cerebral nuclei do not exert direct control over lower motor neurons; instead, they adjust the motor commands issued in other nuclei and provide a background pattern and rhythm once a movement is under way. The cerebral nuclei also play a key role in cognition and in emotions. The cerebellum influen ...
... Cerebral nuclei do not exert direct control over lower motor neurons; instead, they adjust the motor commands issued in other nuclei and provide a background pattern and rhythm once a movement is under way. The cerebral nuclei also play a key role in cognition and in emotions. The cerebellum influen ...
From the Archives - Oxford Academic
... lacked grammar; he could not complete a list of vowels or the alphabet; conversely, ‘tests with writing, recognition of colours, clock-reading, word-building with cards, typing, and reading were executed pretty well . . . calculations were carried out with some difficulty’. Was this merely a dactylo ...
... lacked grammar; he could not complete a list of vowels or the alphabet; conversely, ‘tests with writing, recognition of colours, clock-reading, word-building with cards, typing, and reading were executed pretty well . . . calculations were carried out with some difficulty’. Was this merely a dactylo ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... 1. Sensory (afferent) neurons sends information from sensory receptors (e.g. skin, eyes, ears) 2. Motor (efferent) neurons sends information AWAY from the CNS to muscles or organs. 3. Inter-neurons: send information between sensory and motor neuron; most are located in CNS. ...
... 1. Sensory (afferent) neurons sends information from sensory receptors (e.g. skin, eyes, ears) 2. Motor (efferent) neurons sends information AWAY from the CNS to muscles or organs. 3. Inter-neurons: send information between sensory and motor neuron; most are located in CNS. ...
Artificial Neural Networks - Introduction -
... Artificial neural networks Tasks to be solved by artificial neural networks: • controlling the movements of a robot based on selfperception and other information (e.g., visual information); • deciding the category of potential food items (e.g., edible or non-edible) in an artificial world; ...
... Artificial neural networks Tasks to be solved by artificial neural networks: • controlling the movements of a robot based on selfperception and other information (e.g., visual information); • deciding the category of potential food items (e.g., edible or non-edible) in an artificial world; ...
Cortical interactions underlying the production of speech sounds
... As the model repeatedly produces a speech sound, it learns a somatosensory target region for the sound, analogous to the auditory target region mentioned above. This target represents the expected tactile and proprioceptive sensations associated with the sound and is used in the somatosensory feedba ...
... As the model repeatedly produces a speech sound, it learns a somatosensory target region for the sound, analogous to the auditory target region mentioned above. This target represents the expected tactile and proprioceptive sensations associated with the sound and is used in the somatosensory feedba ...
Parkinson`s - Personal Web Pages
... Is a chronic, progressive disorder of the central nervous system that belongs to a group of conditions called motor system disorders. Direct result of the loss of cells in a section of the brain called the substantia nigra. Those cells produce dopamine, which is a chemical messenger responsible for ...
... Is a chronic, progressive disorder of the central nervous system that belongs to a group of conditions called motor system disorders. Direct result of the loss of cells in a section of the brain called the substantia nigra. Those cells produce dopamine, which is a chemical messenger responsible for ...
Background: Classical fear conditioning is a phenomenon in which
... fear of the conditioned danger cue (CS+) can also be observed when a subject is presented a stimulus that shares similar characteristics with the CS+. This is known as fear generalization. Although some amount of generalization is normal, over generalizing to the CS+ has been implicated as a marker ...
... fear of the conditioned danger cue (CS+) can also be observed when a subject is presented a stimulus that shares similar characteristics with the CS+. This is known as fear generalization. Although some amount of generalization is normal, over generalizing to the CS+ has been implicated as a marker ...
Introduction to Anatomy
... Indirect (extrapyramidal) pathways for coordination and control of movement cerebral cortex ...
... Indirect (extrapyramidal) pathways for coordination and control of movement cerebral cortex ...
Slide ()
... neuromuscular junction ensures that each muscle fiber innervated by the same neuron will generate an action potential and contract in response to an action potential in the motor neuron. Activation of one or a few motor neurons produces a simple extracellular voltage signal and a small contraction ( ...
... neuromuscular junction ensures that each muscle fiber innervated by the same neuron will generate an action potential and contract in response to an action potential in the motor neuron. Activation of one or a few motor neurons produces a simple extracellular voltage signal and a small contraction ( ...
Slide ()
... neuromuscular junction ensures that each muscle fiber innervated by the same neuron will generate an action potential and contract in response to an action potential in the motor neuron. Activation of one or a few motor neurons produces a simple extracellular voltage signal and a small contraction ( ...
... neuromuscular junction ensures that each muscle fiber innervated by the same neuron will generate an action potential and contract in response to an action potential in the motor neuron. Activation of one or a few motor neurons produces a simple extracellular voltage signal and a small contraction ( ...
CSD 5XXX Introduction to Research Methods in CSD
... to examine whether there are differences in listener perceptions of randomly selected TE and conventional esophageal speech. Williams and Watson (1987) found the naïve listeners rated esophageal and TE speakers differently on quality/extraneous noise, visual presentation, speaking rate, pitch, loudn ...
... to examine whether there are differences in listener perceptions of randomly selected TE and conventional esophageal speech. Williams and Watson (1987) found the naïve listeners rated esophageal and TE speakers differently on quality/extraneous noise, visual presentation, speaking rate, pitch, loudn ...
Chapter 3: The nerve cell Multiple Choice Questions (1
... 1. If the synapse between neurons is inhibitory, the probability of the next neuron firing is a. increased b. decreased c. unchanged d. dependent upon the type of neuron 2. If the synapse between neurons is excitatory, the probability of the next neuron firing is a. increased b. decreased c. unchang ...
... 1. If the synapse between neurons is inhibitory, the probability of the next neuron firing is a. increased b. decreased c. unchanged d. dependent upon the type of neuron 2. If the synapse between neurons is excitatory, the probability of the next neuron firing is a. increased b. decreased c. unchang ...
Nolte – Chapter 2 (Development of the Nervous System)
... an move under the ectoderm that got pinched, the cells on top get inhibited, while the other ones begin to express their calling of becoming neurons. The hinhibited ones become epidermis. The dorsal blastopore lip forms. o A full fusing results in the neural tube, that is separate from the ectoder ...
... an move under the ectoderm that got pinched, the cells on top get inhibited, while the other ones begin to express their calling of becoming neurons. The hinhibited ones become epidermis. The dorsal blastopore lip forms. o A full fusing results in the neural tube, that is separate from the ectoder ...
Central Nervous System Part 2
... Primary somatosensory cortex Visual association area Auditory association area primary visual cortex primary auditory cortex auditory association area olfactory cortex gustatory cortex ...
... Primary somatosensory cortex Visual association area Auditory association area primary visual cortex primary auditory cortex auditory association area olfactory cortex gustatory cortex ...
The Neural Optimal Control Hierarchy
... The basal ganglia has been characterized in several ways: 1) As a winner-take-all (WTA) circuit [5], 2) as responsible for scaling movements or providing an ‘energy vigor’ term [9], 3) and as performing dimension reduction [1]. Recently, spiking neuron implementations of the WTA circuit model have b ...
... The basal ganglia has been characterized in several ways: 1) As a winner-take-all (WTA) circuit [5], 2) as responsible for scaling movements or providing an ‘energy vigor’ term [9], 3) and as performing dimension reduction [1]. Recently, spiking neuron implementations of the WTA circuit model have b ...
PDF
... axonal projections of the sensory neurons in these embryos are abnormal. Because neurotrophin 3 (Ntf3) and its receptors are strongly expressed in motoneurons and sensory neurons, respectively, the researchers also investigate whether Ntf3 is one of the motoneuron-derived factors that regulate senso ...
... axonal projections of the sensory neurons in these embryos are abnormal. Because neurotrophin 3 (Ntf3) and its receptors are strongly expressed in motoneurons and sensory neurons, respectively, the researchers also investigate whether Ntf3 is one of the motoneuron-derived factors that regulate senso ...
Introduction My research focuses on the link between perception
... formation of new mappings between auditory and motor representations of sound sequences. I have previously argued that the temporary binding of auditory and motor representations of speech - as is required during tasks of phonological short-term memory -- is mediated by area Spt and the auditory dor ...
... formation of new mappings between auditory and motor representations of sound sequences. I have previously argued that the temporary binding of auditory and motor representations of speech - as is required during tasks of phonological short-term memory -- is mediated by area Spt and the auditory dor ...