Electrons and Photons
... They are in an antibonding state. We could take silicon as an example. When two such free silicon atoms meet, they may bond together. They will do so because the bonding state is at a lower energy than what existed previously. The valence electrons have thus fallen into some kind of potential well, ...
... They are in an antibonding state. We could take silicon as an example. When two such free silicon atoms meet, they may bond together. They will do so because the bonding state is at a lower energy than what existed previously. The valence electrons have thus fallen into some kind of potential well, ...
报告海报
... physics for applications to astrophysics, light science, and ultra-low temperature collisions; Calculations of long-range forces between pairs of atoms, and between atoms and conducting walls; Quantum electro dynamical studies of energy shifts arising from two transverse photon exchange leading to e ...
... physics for applications to astrophysics, light science, and ultra-low temperature collisions; Calculations of long-range forces between pairs of atoms, and between atoms and conducting walls; Quantum electro dynamical studies of energy shifts arising from two transverse photon exchange leading to e ...
Class15
... • Energy levels of nearby atoms are slightly shifted from each other, producing bands of allowed energies • Electrons move from the locality of one atom to the next only if an energy state is available within the same band ...
... • Energy levels of nearby atoms are slightly shifted from each other, producing bands of allowed energies • Electrons move from the locality of one atom to the next only if an energy state is available within the same band ...
λ - Chemistry 7
... with electromagnetic radiation (light), only specific frequencies eject electrons from the surface of the light sensitive plate to generate current. Einstein finds that light acts like a particle. He calls the light particles “photons” and each photon has an energy = hν. ...
... with electromagnetic radiation (light), only specific frequencies eject electrons from the surface of the light sensitive plate to generate current. Einstein finds that light acts like a particle. He calls the light particles “photons” and each photon has an energy = hν. ...
introduction - 123seminarsonly.com
... of light with a metal surface. Under certain conditions the energy carried by photons of light is transferred to packets of electrons, called plasmons, on a metal’s surface. Energy transfer occurs only at a specific resonance wavelength of light. That is, the wavelength where the quantum energy carr ...
... of light with a metal surface. Under certain conditions the energy carried by photons of light is transferred to packets of electrons, called plasmons, on a metal’s surface. Energy transfer occurs only at a specific resonance wavelength of light. That is, the wavelength where the quantum energy carr ...
departmentofmaterials scienceandengineering
... hydrides, silicates and all organic solids), an efficient atom displacement mechanism exists for removing atoms from their sites using only ionizing radiation, such as UV light, X-rays or γ-rays. This process is called radiolysis and in halides can be surprisingly efficient (up to ~50% of the ionizi ...
... hydrides, silicates and all organic solids), an efficient atom displacement mechanism exists for removing atoms from their sites using only ionizing radiation, such as UV light, X-rays or γ-rays. This process is called radiolysis and in halides can be surprisingly efficient (up to ~50% of the ionizi ...
PPTX
... light, light is emitted in the same polarized plane, provided that the molecule remains stationary throughout the excited state (which has a duration of 4 nanoseconds for fluorescein). If the molecule rotates and tumbles out of this plane during the excited state, light is emitted in a different pla ...
... light, light is emitted in the same polarized plane, provided that the molecule remains stationary throughout the excited state (which has a duration of 4 nanoseconds for fluorescein). If the molecule rotates and tumbles out of this plane during the excited state, light is emitted in a different pla ...
Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Topic 6, Worksheet 2
... electrons but the current only depends on the number of electrons emitted per second not their speed. ...
... electrons but the current only depends on the number of electrons emitted per second not their speed. ...
Problem Set 1 (due 2/21/06)
... 2. How do you collect a fluorescence emission spectrum? A fluorescence excitation spectrum? An absorption spectrum? Which two most closely resemble each other? A fluorescence emission spectrum is collected by illuminating the sample with a single wavelength and collecting a scan of the intensities o ...
... 2. How do you collect a fluorescence emission spectrum? A fluorescence excitation spectrum? An absorption spectrum? Which two most closely resemble each other? A fluorescence emission spectrum is collected by illuminating the sample with a single wavelength and collecting a scan of the intensities o ...
Visible Spectroscopy
... Part 1: The electron energy levels in atoms and ions are key to the production and detection of light. Energy levels or "shells" exist for electrons in atoms and molecules. The colors of dyes and other compounds results from electron jumps between these shells or levels. The colors of fireworks resu ...
... Part 1: The electron energy levels in atoms and ions are key to the production and detection of light. Energy levels or "shells" exist for electrons in atoms and molecules. The colors of dyes and other compounds results from electron jumps between these shells or levels. The colors of fireworks resu ...
Part 1
... Part 1: The electron energy levels in atoms and ions are key to the production and detection of light. Energy levels or "shells" exist for electrons in atoms and molecules. The colors of dyes and other compounds results from electron jumps between these shells or levels. The colors of fireworks resu ...
... Part 1: The electron energy levels in atoms and ions are key to the production and detection of light. Energy levels or "shells" exist for electrons in atoms and molecules. The colors of dyes and other compounds results from electron jumps between these shells or levels. The colors of fireworks resu ...
Topic 16: Geometric Optics
... Then, by using phonetics, Young gave sound values to each of the symbols. Applying this strategy to another inscription confirmed he was on the right track. However, after cracking the code, he ceased further work, calling his achievement the amusement of a few hours’ work. Young often left work unf ...
... Then, by using phonetics, Young gave sound values to each of the symbols. Applying this strategy to another inscription confirmed he was on the right track. However, after cracking the code, he ceased further work, calling his achievement the amusement of a few hours’ work. Young often left work unf ...
Measuring threshold frequency
... Albert Einstein explained the photoelectric effect in a paper published in 1905. It was the second of five ground-breaking papers he wrote that year. In the first paper, Einstein explained the mysterious Brownian motion of particles contained in pollen grains as due to the random impact of much smal ...
... Albert Einstein explained the photoelectric effect in a paper published in 1905. It was the second of five ground-breaking papers he wrote that year. In the first paper, Einstein explained the mysterious Brownian motion of particles contained in pollen grains as due to the random impact of much smal ...
Click here to get the file
... nowhere in between 3. When electrons absorb a photon of the correct energy, the electron jumps to a higher energy level 4. When the electron falls to a lower energy level, a photon of only one certain energy is emitted The emitted photons have a discrete energy, frequency or wavelength that we obser ...
... nowhere in between 3. When electrons absorb a photon of the correct energy, the electron jumps to a higher energy level 4. When the electron falls to a lower energy level, a photon of only one certain energy is emitted The emitted photons have a discrete energy, frequency or wavelength that we obser ...
6.4 - Hockerill Students
... prove that the electron behaves like a wave it must have wave properties, such diffraction. To make an electron diffract around an obstacle of size d, its wavelength λ must be comparable to or bigger that d. electron of mass 9.1x10-31kg and speed of 105 m/s will have a wavelength λ = 7.2x10-9m. An ...
... prove that the electron behaves like a wave it must have wave properties, such diffraction. To make an electron diffract around an obstacle of size d, its wavelength λ must be comparable to or bigger that d. electron of mass 9.1x10-31kg and speed of 105 m/s will have a wavelength λ = 7.2x10-9m. An ...
Einstein`s paper is a “bold, not to say reckless, hypothesis…which
... even for intense light! This makes no sense classically. Increasing the electric field should have an effect. Lecture 7, p 12 ...
... even for intense light! This makes no sense classically. Increasing the electric field should have an effect. Lecture 7, p 12 ...
Slide - Journal of Vision
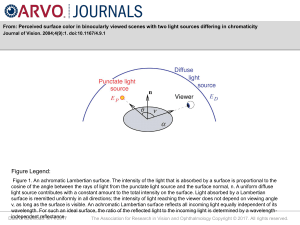
... Figure 1. An achromatic Lambertian surface. The intensity of the light that is absorbed by a surface is proportional to the cosine of the angle between the rays of light from the punctate light source and the surface normal, n. A uniform diffuse light source contributes with a constant amount to the ...
... Figure 1. An achromatic Lambertian surface. The intensity of the light that is absorbed by a surface is proportional to the cosine of the angle between the rays of light from the punctate light source and the surface normal, n. A uniform diffuse light source contributes with a constant amount to the ...
www.ck12.org Wave-Particle Theory Practice Worksheet Visit CK12
... Fill in the answer blanks with correct answer. 4. The electromagnetic waves consist of vibrating electric and _______ fields. Answer: 5. The amount of energy in a photon corresponds to the _____ of the electromagnetic wave. Answer: 6. A “packet” of light energy is called a(n) _____. Answer: 7. The f ...
... Fill in the answer blanks with correct answer. 4. The electromagnetic waves consist of vibrating electric and _______ fields. Answer: 5. The amount of energy in a photon corresponds to the _____ of the electromagnetic wave. Answer: 6. A “packet” of light energy is called a(n) _____. Answer: 7. The f ...
17588_lecture10-11_11795_laser-and-its-applications2
... the interaction of matter and radiative, it is necessary to include that process in which an excited atom may be induced by the presence of radiation emit a photon and decay to lower energy state. ...
... the interaction of matter and radiative, it is necessary to include that process in which an excited atom may be induced by the presence of radiation emit a photon and decay to lower energy state. ...
Chemistry 201/211 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... 7.061014 Hz is used to examine an object, what is the size of the smallest detail that can be seen? In the 1930’s, scientists built an electron microscope that uses electrons instead of light to probe matter. If the speed of the electrons (m = 9.1110-31 kg) used is 1.45107 m/s, what wavelength do ...
... 7.061014 Hz is used to examine an object, what is the size of the smallest detail that can be seen? In the 1930’s, scientists built an electron microscope that uses electrons instead of light to probe matter. If the speed of the electrons (m = 9.1110-31 kg) used is 1.45107 m/s, what wavelength do ...
Theoretical work in the CUA. Strongly correlated many
... Direct decay is not allowed by energy conservation ...
... Direct decay is not allowed by energy conservation ...
Slide 1
... Energy Levels in Atoms • The situation is not quite as simple as has been portrayed because there are sublevels within the main allowed levels and this makes them spectra significantly more complex, nevertheless they may still be used to determine the allowed energy levels for electrons within an a ...
... Energy Levels in Atoms • The situation is not quite as simple as has been portrayed because there are sublevels within the main allowed levels and this makes them spectra significantly more complex, nevertheless they may still be used to determine the allowed energy levels for electrons within an a ...