Digestion Fizz
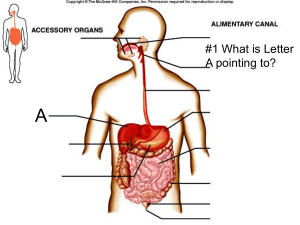
... picture of the stomach and small intestine. B Which letter is closest to the esophageal sphincter? ...
... picture of the stomach and small intestine. B Which letter is closest to the esophageal sphincter? ...
Anatomy of Root of the Neck
... right/left hepatic ductscommon hepatic duct +cystic ductbile duct gallbladder (store) cystic, bile ductsduodenum spaces b/t anterior part of liver, diaphragm (Morison’s pouch) –deep recess on right side, when supinefluid from omental bursa drains in, communicates w/ right subphrenic recess ante ...
... right/left hepatic ductscommon hepatic duct +cystic ductbile duct gallbladder (store) cystic, bile ductsduodenum spaces b/t anterior part of liver, diaphragm (Morison’s pouch) –deep recess on right side, when supinefluid from omental bursa drains in, communicates w/ right subphrenic recess ante ...
Essential Functional Hepatic and Biliary Anatomy for the
... of the internal anatomy of the liver have been proffered over the last century, Couinaud’s (1957) segmental anatomy of the liver is the most useful for the surgeon. Couinaud’s classification system divides the liver into four unique sectors based upon the course of the three major hepatic veins. Eac ...
... of the internal anatomy of the liver have been proffered over the last century, Couinaud’s (1957) segmental anatomy of the liver is the most useful for the surgeon. Couinaud’s classification system divides the liver into four unique sectors based upon the course of the three major hepatic veins. Eac ...
3 - ANATOMY The Small Intestine.notebook
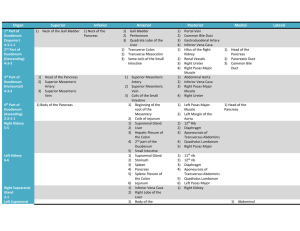
... receives secretions from the pancreas and liver via the Duodenum: the first section of the small intestines which is a short section that pancreatic and common bile ducts. receives secretions from the pancreas and liver via the pancreatic and common The food is a highly acidic mush and needs to ...
... receives secretions from the pancreas and liver via the Duodenum: the first section of the small intestines which is a short section that pancreatic and common bile ducts. receives secretions from the pancreas and liver via the pancreatic and common The food is a highly acidic mush and needs to ...
ST120 Digestive System_BB
... the digestive system including signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options. Demonstrate knowledge of medical terminology related to the digestive system verbally and in the written form. ...
... the digestive system including signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options. Demonstrate knowledge of medical terminology related to the digestive system verbally and in the written form. ...
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Obstruction
... (BLOCKAGE OF THE EXTRAHEPATIC OR COMMON BILE DUCT) BASICS OVERVIEW ...
... (BLOCKAGE OF THE EXTRAHEPATIC OR COMMON BILE DUCT) BASICS OVERVIEW ...
Chapter 24new
... Histology of the Stomach • Rugae = folds of empty stomach • Muscularis mucosa and externa contain extra oblique layers of smooth muscle • Simple columnar epithelium lines all portions of stomach, is a secretory sheet: produces mucus that covers interior surface of stomach ...
... Histology of the Stomach • Rugae = folds of empty stomach • Muscularis mucosa and externa contain extra oblique layers of smooth muscle • Simple columnar epithelium lines all portions of stomach, is a secretory sheet: produces mucus that covers interior surface of stomach ...
Chapter 17
... The cecum is a dilated, pouch like structure that hangs slightly below the ileocecal opening. This represents the beginning of the large intestine. The colon is divided into four parts. The ascending colon begins at the cecum and travels upward against the posterior abdominal wall to a point just be ...
... The cecum is a dilated, pouch like structure that hangs slightly below the ileocecal opening. This represents the beginning of the large intestine. The colon is divided into four parts. The ascending colon begins at the cecum and travels upward against the posterior abdominal wall to a point just be ...
Chapter 23 outline
... Endocrine cells – secrete ghrelin – a hormone that stimulates the hypothalamus to increase appetite and gastrin which ...
... Endocrine cells – secrete ghrelin – a hormone that stimulates the hypothalamus to increase appetite and gastrin which ...
Chapter 26-Part 2-Digestive System
... lobes and secures liver to anterior abdominal wall • inferior edge is round ligament of the liver (AKA ligamentum teres) is remnant of umbilical vein ...
... lobes and secures liver to anterior abdominal wall • inferior edge is round ligament of the liver (AKA ligamentum teres) is remnant of umbilical vein ...
Gallbladder Disease: Imaging and Treatment
... which join to form the common hepatic duct (see Figure 1). This duct then connects to the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. 5 The pancreatic duct joins the common bile duct and empties into the duodenum. The gallbladder and ducts that carry bile and other digestiv ...
... which join to form the common hepatic duct (see Figure 1). This duct then connects to the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. 5 The pancreatic duct joins the common bile duct and empties into the duodenum. The gallbladder and ducts that carry bile and other digestiv ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 25 Martini lecture Outline
... between the left and right lobes The inferior portion of the falciform ligament becomes thick and round and is called the round ligament The round ligament used to be the fetal umbilical vein The falciform ligament spreads on the surface of the liver attaching to the inferior side of the diaphragm T ...
... between the left and right lobes The inferior portion of the falciform ligament becomes thick and round and is called the round ligament The round ligament used to be the fetal umbilical vein The falciform ligament spreads on the surface of the liver attaching to the inferior side of the diaphragm T ...
Poisonous mushrooms
... Bile salts and their circulation • Bile salts are produced in the liver and enter the duodenum • Most of the bile salts are reabsorbed in the lower part of the small intestine • These bile salts are returned to the liver in the blood 3 (a) ...
... Bile salts and their circulation • Bile salts are produced in the liver and enter the duodenum • Most of the bile salts are reabsorbed in the lower part of the small intestine • These bile salts are returned to the liver in the blood 3 (a) ...
Infrahepatic space
... Anterior-lesser omentum, peritoneum of posterior wall of stomach, and anterior two layers of greater omentum ...
... Anterior-lesser omentum, peritoneum of posterior wall of stomach, and anterior two layers of greater omentum ...
1. The stomach: a. Lies anterior to the greater sac. b. Receives all its
... 1. The ilioinguinal nerve: (a) Is a branch from L1 spinal nerve (b) It descends behind the kidney (c) It passes through the deep inguinal ring (d) It is entirely sensory (e) It is sensory to the scrotum or labium majus 2. The external oblique muscle: (a) Is attached posteriorly to the lumbar fascia ...
... 1. The ilioinguinal nerve: (a) Is a branch from L1 spinal nerve (b) It descends behind the kidney (c) It passes through the deep inguinal ring (d) It is entirely sensory (e) It is sensory to the scrotum or labium majus 2. The external oblique muscle: (a) Is attached posteriorly to the lumbar fascia ...
Relationships
... 1) Transitions from the renal pelvis and descends as a retroperitoneal structure along the anterior surface of the psoas major muscle. It passes posterior to the testicular/ovarian vessels. The left ureter is also crossed by the inferior mesenteric artery and vein. Then, it courses anterior to the b ...
... 1) Transitions from the renal pelvis and descends as a retroperitoneal structure along the anterior surface of the psoas major muscle. It passes posterior to the testicular/ovarian vessels. The left ureter is also crossed by the inferior mesenteric artery and vein. Then, it courses anterior to the b ...
The peritoneum 腹膜
... Hepatoduodenal ligament 肝十二指肠韧带 extends from porta hepatis to superior part of duodenum, it contains common bile duct, proper hepatic a. hepatic portal v. ...
... Hepatoduodenal ligament 肝十二指肠韧带 extends from porta hepatis to superior part of duodenum, it contains common bile duct, proper hepatic a. hepatic portal v. ...
Major Concepts of Anatomy and Physiology
... Epithelium: Comes in direct contact with the GI tract contents – made up of nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium that serves a protective function, with simple columnar epithelium functions in secretion & absorption & lines the stomach & intestines. Lamina Propia: Layer of connective tissue ...
... Epithelium: Comes in direct contact with the GI tract contents – made up of nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium that serves a protective function, with simple columnar epithelium functions in secretion & absorption & lines the stomach & intestines. Lamina Propia: Layer of connective tissue ...
DMS131 Abdominal Sonography I Multiple
... 4. What do the superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein join together to form? a. celiac axis b. portal vein c. inferior vena cava d. main hepatic vein 5. The celiac axis is _______ to the origin of the superior mesenteric artery. a. cephalad b. caudal c. medial d. lateral 6. Which vessel lies ...
... 4. What do the superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein join together to form? a. celiac axis b. portal vein c. inferior vena cava d. main hepatic vein 5. The celiac axis is _______ to the origin of the superior mesenteric artery. a. cephalad b. caudal c. medial d. lateral 6. Which vessel lies ...
1.Duedenum & Pancreas2008-02
... Pain from the pancreas is commonly referred to the back. Because the pancreas lies behind the stomach and transverse colon, disease of the gland can be confused with that of the stomach or transverse colon. Inflammation of the pancreas can spread to the peritoneum forming the posterior wall of the l ...
... Pain from the pancreas is commonly referred to the back. Because the pancreas lies behind the stomach and transverse colon, disease of the gland can be confused with that of the stomach or transverse colon. Inflammation of the pancreas can spread to the peritoneum forming the posterior wall of the l ...
AnatomyGIT - UMK CARNIVORES 3
... Its concave anterior border is infront of a transverse plane through the tuber coxae-branches on either side to form the dorsal and ventral coronary pillars –which separate the posterior blind sacs from the general cavity on the sides and ventrally.The ventral coronary pillar is complete-the dorsal ...
... Its concave anterior border is infront of a transverse plane through the tuber coxae-branches on either side to form the dorsal and ventral coronary pillars –which separate the posterior blind sacs from the general cavity on the sides and ventrally.The ventral coronary pillar is complete-the dorsal ...
Dissection 14: Abdominopelvic Cavity
... stomach and anastomose with the left gastric artery. c. Gastroduodenal artery: From the hepatic artery and descends posterior to the gastroduodenal junction to supply the stomach, pancreas, first part of the duodenum, and the distal part of the bile duct. It will anastomose with the inferior duodena ...
... stomach and anastomose with the left gastric artery. c. Gastroduodenal artery: From the hepatic artery and descends posterior to the gastroduodenal junction to supply the stomach, pancreas, first part of the duodenum, and the distal part of the bile duct. It will anastomose with the inferior duodena ...
The peritoneal cavity
... . The infection may spread into the peritoneal cavity and cause inflammation of the peritoneum which is called as peritonitis. The infected fluid may tend to collect in the most dependent area of the peritoneal cavity in supine position, these areas are pelvis and the right subphrenic space. In su ...
... . The infection may spread into the peritoneal cavity and cause inflammation of the peritoneum which is called as peritonitis. The infected fluid may tend to collect in the most dependent area of the peritoneal cavity in supine position, these areas are pelvis and the right subphrenic space. In su ...
Digestion - Sinoe Medical Association
... BILE SALTS, (formed in the liver from cholesterol) are the most essential part of bile. BILE PIGMENTS-The pigment bilirubin (red) and biliverdin (green), derived from hemoglobin, give bile its greenish color because it secretes bile into ducts. ...
... BILE SALTS, (formed in the liver from cholesterol) are the most essential part of bile. BILE PIGMENTS-The pigment bilirubin (red) and biliverdin (green), derived from hemoglobin, give bile its greenish color because it secretes bile into ducts. ...
Liver

The liver is a vital organ of vertebrates and some other animals. In the human it is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm. The liver has a wide range of functions, including detoxification of various metabolites, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.The liver is a gland and plays a major role in metabolism with numerous functions in the human body, including regulation of glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, plasma protein synthesis, hormone production, and detoxification. It is an accessory digestive gland and produces bile, an alkaline compound which aids in digestion via the emulsification of lipids. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver. The liver's highly specialized tissue consisting of mostly hepatocytes regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions, including the synthesis and breakdown of small and complex molecules, many of which are necessary for normal vital functions. Estimates regarding the organ's total number of functions vary, but textbooks generally cite it being around 500.Terminology related to the liver often starts in hepar- or hepat- from the Greek word for liver, hēpar (ἧπαρ, root hepat-, ἡπατ-).There is currently no way to compensate for the absence of liver function in the long term, although liver dialysis techniques can be used in the short term. Liver transplantation is the only option for complete liver failure.