Abdominal Exam
... occur from every other second to every 12 seconds. Note: During the abdominal exam auscultation is done before palpation ...
... occur from every other second to every 12 seconds. Note: During the abdominal exam auscultation is done before palpation ...
Introduction to Abdominal Radiology
... – Can displace stomach cranially and small intestines in various direction depending on location ...
... – Can displace stomach cranially and small intestines in various direction depending on location ...
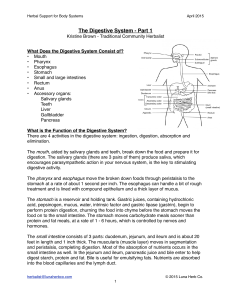
The Digestive System - Part 1
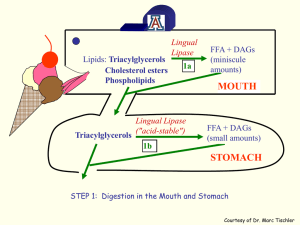
... and peristalsis, completing digestion. Most of the absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine as well. In the jejunum and ileum, pancreatic juice and bile enter to help digest starch, protein and fat. Bile is useful for emulsifying fats. Nutrients are absorbed into the blood capillaries a ...
... and peristalsis, completing digestion. Most of the absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine as well. In the jejunum and ileum, pancreatic juice and bile enter to help digest starch, protein and fat. Bile is useful for emulsifying fats. Nutrients are absorbed into the blood capillaries a ...
Digestion And Absorption
... 4. The liver also performs several roles in lipid metabolism: 5. The liver produces coagulation factors I (fibrinogen), II (prothrombin), V, VII, IX, X and XI, as well as protein C, protein S and antithrombin. 6. In the first trimester of foetus, the liver is the main site of red blood cell producti ...
... 4. The liver also performs several roles in lipid metabolism: 5. The liver produces coagulation factors I (fibrinogen), II (prothrombin), V, VII, IX, X and XI, as well as protein C, protein S and antithrombin. 6. In the first trimester of foetus, the liver is the main site of red blood cell producti ...
Jose
... of digestion occurs, being (in humans and many mammals) a pear-shaped enlargement of the... ...
... of digestion occurs, being (in humans and many mammals) a pear-shaped enlargement of the... ...
Investigation of the abdomen
... • The cecum forms a softer, wider tube in the right lower quadrant, • The lower margin of the liver is often palpable, • The lower pole of the right kidney is occasionally palpable, especially in thin individuals with relaxed abdominal muscles, • Pulsation of the abdominal aorta usually palpable in ...
... • The cecum forms a softer, wider tube in the right lower quadrant, • The lower margin of the liver is often palpable, • The lower pole of the right kidney is occasionally palpable, especially in thin individuals with relaxed abdominal muscles, • Pulsation of the abdominal aorta usually palpable in ...
Document
... A lateral view of the upper GI tract following a barium swallow This image demonstrates normal anatomy of the esophagus ...
... A lateral view of the upper GI tract following a barium swallow This image demonstrates normal anatomy of the esophagus ...
File
... Located in the upper right part of the abdomen. Plays an essential role in the normal metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. ...
... Located in the upper right part of the abdomen. Plays an essential role in the normal metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. ...
Amino Acids: From Ingestion To Excretion.
... procarboxypeptidase are also secreted by the pancreas and activated by other enzymes, like enteropeptidase. These activated enzymes further hydrolyze the incoming peptides from the stomach. Other enzymes in the small intestine complete the degradation of the ingested proteins into their free amino a ...
... procarboxypeptidase are also secreted by the pancreas and activated by other enzymes, like enteropeptidase. These activated enzymes further hydrolyze the incoming peptides from the stomach. Other enzymes in the small intestine complete the degradation of the ingested proteins into their free amino a ...
McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition
... 42. The intestinal tract is sterile at birth and becomes totally colonized within 3 to 4 weeks. 43. Endogenous infections of the gastrointestinal tract occur by excessive proliferation of bacteria, perforation of the intestine, or contamination from neighboring structures. ...
... 42. The intestinal tract is sterile at birth and becomes totally colonized within 3 to 4 weeks. 43. Endogenous infections of the gastrointestinal tract occur by excessive proliferation of bacteria, perforation of the intestine, or contamination from neighboring structures. ...
Digestive Quiz17studyquide
... There are two main groups of organs in the digestive system (the alimentary canal and accessory organs What organ is involved with the creation of bolus? Where does chemical digestion begin? What part of the G.I. tract allows the passage of food, drink and air? Know the correct order of the G.I. tr ...
... There are two main groups of organs in the digestive system (the alimentary canal and accessory organs What organ is involved with the creation of bolus? Where does chemical digestion begin? What part of the G.I. tract allows the passage of food, drink and air? Know the correct order of the G.I. tr ...
Pharynx
... Separates the right and left lobes anteriorly Suspends the liver from the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall ...
... Separates the right and left lobes anteriorly Suspends the liver from the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall ...
Accessory Organs of the Digestive System
... partly digested food expelled by the stomach into the duodenum. ...
... partly digested food expelled by the stomach into the duodenum. ...
diet and your liver - Dr. Imtiaz Alam, MD
... intestinal enzymes and absorbed. Bile is also essential for the absorption of vitamins A, D, E, and K, the fat soluble vitamins. After digestion, bile acids are reabsorbed by the intestine, returned to the liver, and recycled as bile once again. Can poor nutrition cause liver disease? There are many ...
... intestinal enzymes and absorbed. Bile is also essential for the absorption of vitamins A, D, E, and K, the fat soluble vitamins. After digestion, bile acids are reabsorbed by the intestine, returned to the liver, and recycled as bile once again. Can poor nutrition cause liver disease? There are many ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... • Large, continuous sheet of serous membrane • Membrane covering the surfaces of organs – allows movement of each and helps prevent strangulation of the GI tract ...
... • Large, continuous sheet of serous membrane • Membrane covering the surfaces of organs – allows movement of each and helps prevent strangulation of the GI tract ...
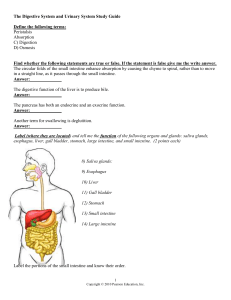
NAME: DATE: BLOCK: ____ Look at the diagram of the digestive
... ______lymphatic vessel in each villus that helps carries nutrients to the body ______a tube that carries pancreatic juice from pancreas to duodenum ______wavelike movements that moves food down the canal ______mixture of food particles and gastric juice ______undigested and unabsorbed materials; als ...
... ______lymphatic vessel in each villus that helps carries nutrients to the body ______a tube that carries pancreatic juice from pancreas to duodenum ______wavelike movements that moves food down the canal ______mixture of food particles and gastric juice ______undigested and unabsorbed materials; als ...
lecture 13 gastrointestinal pathophysiology
... itself (volvulus). A volvulus not only obstructs the bowel but can twist the mesenteric blood vessels (strangulation) and result in death of intestinal tissue. ...
... itself (volvulus). A volvulus not only obstructs the bowel but can twist the mesenteric blood vessels (strangulation) and result in death of intestinal tissue. ...
ileum
... ileocecal valve-consists of two folds, probably delays flow of ileal contents into large intestine A opening of appendix ...
... ileocecal valve-consists of two folds, probably delays flow of ileal contents into large intestine A opening of appendix ...
The Digestive System
... Bile (produced by hepatocytes) drains into the bile duct after passing through portal triad Bile then shipped to gallbladder for storage ...
... Bile (produced by hepatocytes) drains into the bile duct after passing through portal triad Bile then shipped to gallbladder for storage ...
Digestive system outcomes assignment #3
... Enzymes that need to be described according to source, target area, substrate & product and conditions of optimal function: o Salivary amylase, Pesinogen/pepsin, Panreatic amylase, Lipase, Trypsin, Maltase, Peptidases, and nucleases o **Other secretions that need to described & included in similar m ...
... Enzymes that need to be described according to source, target area, substrate & product and conditions of optimal function: o Salivary amylase, Pesinogen/pepsin, Panreatic amylase, Lipase, Trypsin, Maltase, Peptidases, and nucleases o **Other secretions that need to described & included in similar m ...
liver, ultrasound scan, topographic anatomical section, meridian
... On ultrasound scans on the right anterior medial meridian (M11) defined the contours of a large vessel in the longitudinal section of the upper and lower parts of the scan. Comparison of scans with topographic anatomical section allows to conclude that a large vessel on scan is unfilled by contrast ...
... On ultrasound scans on the right anterior medial meridian (M11) defined the contours of a large vessel in the longitudinal section of the upper and lower parts of the scan. Comparison of scans with topographic anatomical section allows to conclude that a large vessel on scan is unfilled by contrast ...
C23/v2/5: Accessory Organs of the Digestive System
... – visible in the triangular areas where three or more lobules meet – branches of proper hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein • both supply blood to sinusoids which receive a mixture of nutrientladen venous blood from the intestines, and freshly oxygenated arterial blood from the celiac trunk • aft ...
... – visible in the triangular areas where three or more lobules meet – branches of proper hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein • both supply blood to sinusoids which receive a mixture of nutrientladen venous blood from the intestines, and freshly oxygenated arterial blood from the celiac trunk • aft ...
Liver

The liver is a vital organ of vertebrates and some other animals. In the human it is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm. The liver has a wide range of functions, including detoxification of various metabolites, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.The liver is a gland and plays a major role in metabolism with numerous functions in the human body, including regulation of glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, plasma protein synthesis, hormone production, and detoxification. It is an accessory digestive gland and produces bile, an alkaline compound which aids in digestion via the emulsification of lipids. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver. The liver's highly specialized tissue consisting of mostly hepatocytes regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions, including the synthesis and breakdown of small and complex molecules, many of which are necessary for normal vital functions. Estimates regarding the organ's total number of functions vary, but textbooks generally cite it being around 500.Terminology related to the liver often starts in hepar- or hepat- from the Greek word for liver, hēpar (ἧπαρ, root hepat-, ἡπατ-).There is currently no way to compensate for the absence of liver function in the long term, although liver dialysis techniques can be used in the short term. Liver transplantation is the only option for complete liver failure.