www.laney.edu
... 1.Mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors •Respond to stretch, changes in osmolarity and pH, and presence of substrate and end products of digestion •Initiate reflexes that –Activate or inhibit digestive glands –Stimulate smooth muscle to mix and move lumen contents ...
... 1.Mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors •Respond to stretch, changes in osmolarity and pH, and presence of substrate and end products of digestion •Initiate reflexes that –Activate or inhibit digestive glands –Stimulate smooth muscle to mix and move lumen contents ...
Ch 14 Review
... 2. Discuss at least four essential activities that take place in the alimentary canal. ...
... 2. Discuss at least four essential activities that take place in the alimentary canal. ...
The Journey of a Cupcake
... They enter the small intestine through the pancreatic duct ( Pancreas ) ...
... They enter the small intestine through the pancreatic duct ( Pancreas ) ...
Frog Dissection Procedure: adapted from http://www.biologyjunction
... 6. Lift and cut through the muscles and breast bone to open up the body cavity. If your frog is a female, the abdominal cavity may be filled with dark-colored eggs. If so, remove the eggs on one side so you can see the organs underlying them. 7. Identify the following organs below Fat Bodies --Spag ...
... 6. Lift and cut through the muscles and breast bone to open up the body cavity. If your frog is a female, the abdominal cavity may be filled with dark-colored eggs. If so, remove the eggs on one side so you can see the organs underlying them. 7. Identify the following organs below Fat Bodies --Spag ...
Ventral Cavity
... form the common bile duct, which should be traced to the duodenum. Also in this ligament, to the right and dorsal to the cystic and common bile ducts, lies the large hepatic portal vein. Try not to injure this vessel, but trace it to its branch into the right lateral lobe of the liver. S. HEPATIC LI ...
... form the common bile duct, which should be traced to the duodenum. Also in this ligament, to the right and dorsal to the cystic and common bile ducts, lies the large hepatic portal vein. Try not to injure this vessel, but trace it to its branch into the right lateral lobe of the liver. S. HEPATIC LI ...
anatomy of the digestive system - Yeditepe University Pharma
... The liver is the largest gland in the body and, after the skin, the largest single organ. It weighs approximately 1500 g and accounts for approximately 2.5% of adult body weight. Except for fat, all nutrients absorbed from the digestive tract are initially conveyed to the liver by the portal venous ...
... The liver is the largest gland in the body and, after the skin, the largest single organ. It weighs approximately 1500 g and accounts for approximately 2.5% of adult body weight. Except for fat, all nutrients absorbed from the digestive tract are initially conveyed to the liver by the portal venous ...
Replaced Common Hepatic Artery From Superior Mesenteric Artery
... a RCHA, which can also be applied to a replaced right hepatic artery (RRHA)(7). A RCHA that courses through the pancreatic parenchyma can be preserved by dividing the pancreas. With this strategy, there is a risk of not achieving tumorfree margins because the division line of the pancreas is likely ...
... a RCHA, which can also be applied to a replaced right hepatic artery (RRHA)(7). A RCHA that courses through the pancreatic parenchyma can be preserved by dividing the pancreas. With this strategy, there is a risk of not achieving tumorfree margins because the division line of the pancreas is likely ...
04 Overview of internal organs. Phylogenesis of the digestive
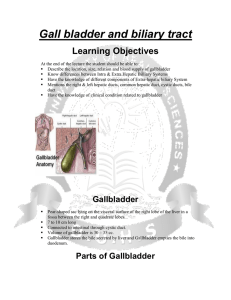
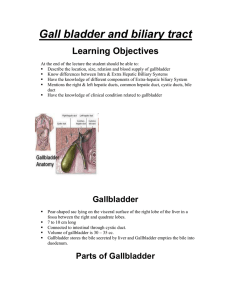
... concentrates bile produced by the liver and stores this concentrate until it is needed for digestion cystic duct connects the gallbladder to the common bile duct can hold approximately 40 to 60 milliliters of concentrated bile ...
... concentrates bile produced by the liver and stores this concentrate until it is needed for digestion cystic duct connects the gallbladder to the common bile duct can hold approximately 40 to 60 milliliters of concentrated bile ...
Digestive System
... concentrates bile produced by the liver and stores this concentrate until it is needed for digestion cystic duct connects the gallbladder to the common bile duct can hold approximately 40 to 60 milliliters of concentrated bile ...
... concentrates bile produced by the liver and stores this concentrate until it is needed for digestion cystic duct connects the gallbladder to the common bile duct can hold approximately 40 to 60 milliliters of concentrated bile ...
Lecture 18 - Missouri State University
... Activates sensory neurons of _________ and produces an inhibitory neural reflex: Inhibits gastric motility and secretion. In the presence of fat, enterogasterone inhibits gastric motility and secretion. ...
... Activates sensory neurons of _________ and produces an inhibitory neural reflex: Inhibits gastric motility and secretion. In the presence of fat, enterogasterone inhibits gastric motility and secretion. ...
Frog External Anatomy
... • Peritoneum A spider web like membrane that covers many of the organs, you may have to carefully pick it off to get a clear view • Liver--The largest structure of the body cavity. This brown colored organ is composed of three parts, or lobes. The right lobe, the left anterior lobe, and the left pos ...
... • Peritoneum A spider web like membrane that covers many of the organs, you may have to carefully pick it off to get a clear view • Liver--The largest structure of the body cavity. This brown colored organ is composed of three parts, or lobes. The right lobe, the left anterior lobe, and the left pos ...
Unit 24: Abdominal and Peritoneal Cavities
... descending colons are called the right (hepatic) and left (splenic) colic flexures respectfully. In the left iliac fossa, the descending colon becomes the sigmoid colon, which has a mesentery. The attachment of the sigmoid mesocolon is variable, but it usually crosses from abdominal to pelvic caviti ...
... descending colons are called the right (hepatic) and left (splenic) colic flexures respectfully. In the left iliac fossa, the descending colon becomes the sigmoid colon, which has a mesentery. The attachment of the sigmoid mesocolon is variable, but it usually crosses from abdominal to pelvic caviti ...
Organology II – Digestive tract and accessory organs
... acids, carbohydrates, and fatty acids). The large intestine is named for its large diameter and it passes to the cloaca or anus. It’s mucosa is rich in goblet cells and its enterocytes absorb water and metabolic ions. II. ...
... acids, carbohydrates, and fatty acids). The large intestine is named for its large diameter and it passes to the cloaca or anus. It’s mucosa is rich in goblet cells and its enterocytes absorb water and metabolic ions. II. ...
Biliary Anatomy and Physiology
... Seeing a small diverticulum in the neck of the gall bladder (Hartman’s pouch) is could be sign of a pathological problem such as impacted stone. There is a significant association between the presence of Hartmann's pouch and stones (p < 0.05). Adhesions between the cystic duct and the neck of the ga ...
... Seeing a small diverticulum in the neck of the gall bladder (Hartman’s pouch) is could be sign of a pathological problem such as impacted stone. There is a significant association between the presence of Hartmann's pouch and stones (p < 0.05). Adhesions between the cystic duct and the neck of the ga ...
Relations of Gallbladder
... Bile Duct is formed by the junction of the cystic and hepatic ducts About 7.5 cm. long. Bile Duct is accompanied by the hepatic artery and portal vein in the right free margin of lesser omentum and descends downwards and passing behind the first part of duodenum and opens by piercing the mid point o ...
... Bile Duct is formed by the junction of the cystic and hepatic ducts About 7.5 cm. long. Bile Duct is accompanied by the hepatic artery and portal vein in the right free margin of lesser omentum and descends downwards and passing behind the first part of duodenum and opens by piercing the mid point o ...
The Digestive System
... At the end of the small intestine most nutrients have been ____________________________. What remains is mostly _______________________, ___________________________ and other indigestible matter. This mass passes into the large intestine or ___________________________. In the colon, most of the ___ ...
... At the end of the small intestine most nutrients have been ____________________________. What remains is mostly _______________________, ___________________________ and other indigestible matter. This mass passes into the large intestine or ___________________________. In the colon, most of the ___ ...
Gall bladder and biliary tract
... Bile Duct is formed by the junction of the cystic and hepatic ducts About 7.5 cm. long. Bile Duct is accompanied by the hepatic artery and portal vein in the right free margin of lesser omentum and descends downwards and passing behind the first part of duodenum and opens by piercing the mid point o ...
... Bile Duct is formed by the junction of the cystic and hepatic ducts About 7.5 cm. long. Bile Duct is accompanied by the hepatic artery and portal vein in the right free margin of lesser omentum and descends downwards and passing behind the first part of duodenum and opens by piercing the mid point o ...
Chapter 15 The Digestion and Absorption of Food
... • The liver also processes and stores nutrients. • The liver also serves as a filter and functions in the removal of old red blood cells which leads to hemoglobin processing and the generation of bilirubin. ...
... • The liver also processes and stores nutrients. • The liver also serves as a filter and functions in the removal of old red blood cells which leads to hemoglobin processing and the generation of bilirubin. ...
Period 2 - Digestive System
... 1. Oral Cavity, PharynxThe oral cavity is where food is chewed and saliva is produced to help propel food toward the stomach. The upper portion of the oral cavity is where the hard and soft palates are located, with the tongue serving as the primary organ in the area.The Pharynx muscular walls funct ...
... 1. Oral Cavity, PharynxThe oral cavity is where food is chewed and saliva is produced to help propel food toward the stomach. The upper portion of the oral cavity is where the hard and soft palates are located, with the tongue serving as the primary organ in the area.The Pharynx muscular walls funct ...
SKELETAL SYSTEM LAB
... 5. Identify the major structures of the liver and pancreas on models (see list below). 6. Identify the three types of salivary glands on microscope slides and identify the serous and mucous acini in each. 7. Identify the major histological structures and layers of the esophagus, stomach, stomach, du ...
... 5. Identify the major structures of the liver and pancreas on models (see list below). 6. Identify the three types of salivary glands on microscope slides and identify the serous and mucous acini in each. 7. Identify the major histological structures and layers of the esophagus, stomach, stomach, du ...
1.Fecal pH test
... Two types of nerves help to control the action of the digestive system. Extrinsic (outside) nerves come to the digestive organs from the unconscious part of the brain or from the spinal cord. They release a chemical called acetylcholine and another called adrenaline. Acetylcholine causes the muscle ...
... Two types of nerves help to control the action of the digestive system. Extrinsic (outside) nerves come to the digestive organs from the unconscious part of the brain or from the spinal cord. They release a chemical called acetylcholine and another called adrenaline. Acetylcholine causes the muscle ...
File - Schrand Science
... Cholecystokinin from the wall of the small intestine stimulates the release of pancreatic juice with abundant digestive enzymes. ...
... Cholecystokinin from the wall of the small intestine stimulates the release of pancreatic juice with abundant digestive enzymes. ...
- Surgery (Journal)
... venous blood into the inferior vena cava allowing oxygenated blood to bypass the liver. The ductus venosus closes during the first week of life in term neonates but may take longer to close in pre-term babies. The remnant of the ductus is the ...
... venous blood into the inferior vena cava allowing oxygenated blood to bypass the liver. The ductus venosus closes during the first week of life in term neonates but may take longer to close in pre-term babies. The remnant of the ductus is the ...
Liver

The liver is a vital organ of vertebrates and some other animals. In the human it is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm. The liver has a wide range of functions, including detoxification of various metabolites, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.The liver is a gland and plays a major role in metabolism with numerous functions in the human body, including regulation of glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, plasma protein synthesis, hormone production, and detoxification. It is an accessory digestive gland and produces bile, an alkaline compound which aids in digestion via the emulsification of lipids. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver. The liver's highly specialized tissue consisting of mostly hepatocytes regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions, including the synthesis and breakdown of small and complex molecules, many of which are necessary for normal vital functions. Estimates regarding the organ's total number of functions vary, but textbooks generally cite it being around 500.Terminology related to the liver often starts in hepar- or hepat- from the Greek word for liver, hēpar (ἧπαρ, root hepat-, ἡπατ-).There is currently no way to compensate for the absence of liver function in the long term, although liver dialysis techniques can be used in the short term. Liver transplantation is the only option for complete liver failure.