Physical Chemistry for the Biosciences I (Ch 416 )
... in temperature. Similarly he passed current through resistor and measured the rise in temperature. Now we know that in a closed system, energy can flow in either as work done on the system or as heat flow. If the energy flows into the system it must be provided by surroundings. Otherwise we will hav ...
... in temperature. Similarly he passed current through resistor and measured the rise in temperature. Now we know that in a closed system, energy can flow in either as work done on the system or as heat flow. If the energy flows into the system it must be provided by surroundings. Otherwise we will hav ...
Chemistry and the material world
... the adiabatic path and w for the non-adiabatic path. q = wad – w Finally, from the first law of thermodynamics also follows that the internal energy of an isolated system cannot change. Because for an isolated system there is w = 0 and q = 0 and with ΔU = q + w it follows that ΔU = 0. The state of a ...
... the adiabatic path and w for the non-adiabatic path. q = wad – w Finally, from the first law of thermodynamics also follows that the internal energy of an isolated system cannot change. Because for an isolated system there is w = 0 and q = 0 and with ΔU = q + w it follows that ΔU = 0. The state of a ...
Chapter 6:
... d. The equivalence of internal energy and work. Answer: A 4. The statement, the internal work of an isolated system is constant, is also known as what? a. The first law of thermodynamics. b. The law of conservation of energy. c. The law of conservation of mass. d. None of the above. Answer: D 5. Upo ...
... d. The equivalence of internal energy and work. Answer: A 4. The statement, the internal work of an isolated system is constant, is also known as what? a. The first law of thermodynamics. b. The law of conservation of energy. c. The law of conservation of mass. d. None of the above. Answer: D 5. Upo ...
Thermodynamics - StrikerPhysics
... • System – a definite quantity of matter enclosed by boundaries or surfaces. Boundaries need not have definite shape or volume. • Thermally Isolated System – system in which no heat is transferred into or out of the system. • Heat Reservoir – a large separate system with unlimited heat capacity (any ...
... • System – a definite quantity of matter enclosed by boundaries or surfaces. Boundaries need not have definite shape or volume. • Thermally Isolated System – system in which no heat is transferred into or out of the system. • Heat Reservoir – a large separate system with unlimited heat capacity (any ...
1. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2 ) Goal: Review the empirical laws
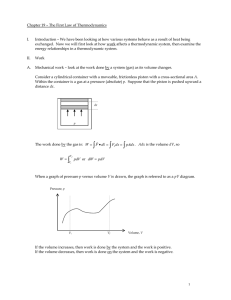
... basically energy conservation. Note W and Q are not state functions since they are not functions of state variables (e.g. p, V for a gas with NA kmoles ). In differential form the first law of TD is: dU Q pdV For example one can move the system from points A to C through different paths (throug ...
... basically energy conservation. Note W and Q are not state functions since they are not functions of state variables (e.g. p, V for a gas with NA kmoles ). In differential form the first law of TD is: dU Q pdV For example one can move the system from points A to C through different paths (throug ...
Ch 14.3 PPT - Using Heat
... • The disorder of a system tends to increase. – Over time, in any given system left to itself, the entropy of that system will tend to increase. • entropy: a measure of the randomness or disorder of a system • Usable energy decreases in all energy transfers. – As entropy increases – usable energy de ...
... • The disorder of a system tends to increase. – Over time, in any given system left to itself, the entropy of that system will tend to increase. • entropy: a measure of the randomness or disorder of a system • Usable energy decreases in all energy transfers. – As entropy increases – usable energy de ...
Internal Energy
... The first law of thermodynamics states that the internal energy of a system is conserved. Q is the heat that is added to the system • If heat is lost, Q is negative. W is the work done by the system. • If work is done on the system, W is negative ...
... The first law of thermodynamics states that the internal energy of a system is conserved. Q is the heat that is added to the system • If heat is lost, Q is negative. W is the work done by the system. • If work is done on the system, W is negative ...
Chapter 19 – The First Law of Thermodynamics
... Interesting Note: If a system changes from an initial state i to a final state f along different paths (e.g., Path A and Path B), the change in internal energy will be the same along those paths. And, in fact, all paths that go from i to f. That is, U = Uf - Ui . From the first law, that means that ...
... Interesting Note: If a system changes from an initial state i to a final state f along different paths (e.g., Path A and Path B), the change in internal energy will be the same along those paths. And, in fact, all paths that go from i to f. That is, U = Uf - Ui . From the first law, that means that ...
Heat and Thermodynamics
... as the energy required to create a system in the absence of changes in temperature or volume. But if the process changes the volume, as in a chemical reaction which produces a gaseous product, then work must be done to produce the change in volume. For a constant pressure process the work you must d ...
... as the energy required to create a system in the absence of changes in temperature or volume. But if the process changes the volume, as in a chemical reaction which produces a gaseous product, then work must be done to produce the change in volume. For a constant pressure process the work you must d ...
12276_61180_First Law of Thermodynamics for a
... net heat transferred from the system regardless of work interaction. Based on this experimental evidence Joule stated that, “When a system (closed system) is undergoing a cyclic process, the net heat transfer to thesystem is directly proportional to the net work done by the system”. This statement ...
... net heat transferred from the system regardless of work interaction. Based on this experimental evidence Joule stated that, “When a system (closed system) is undergoing a cyclic process, the net heat transfer to thesystem is directly proportional to the net work done by the system”. This statement ...
Section 10.2 The Flow of Energy
... • How much energy is there in a substance? 2. To understand how heat is measured • What are the units of energy? 3. To understand how the flow of heat changes temperature • How does an amount of heat gained or lost relate to a change in temperature? ...
... • How much energy is there in a substance? 2. To understand how heat is measured • What are the units of energy? 3. To understand how the flow of heat changes temperature • How does an amount of heat gained or lost relate to a change in temperature? ...
Chapter 12 Laws of Thermodynamics
... because in the water the molecules are not organized into a regular crystal lattice. • 2nd Law of TD stated as entropy. The total entropy of a system in any physical process cannot decrease, but it can increase. (also can stay the same, but need to be very careful to do so.) ...
... because in the water the molecules are not organized into a regular crystal lattice. • 2nd Law of TD stated as entropy. The total entropy of a system in any physical process cannot decrease, but it can increase. (also can stay the same, but need to be very careful to do so.) ...