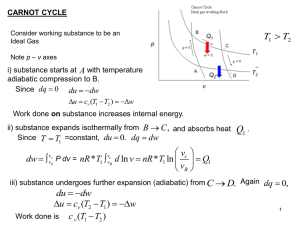
JIF 314 Thermodynamics - comsics
... Unless specified, when the word work is referred, it shall refer to external work Internal work is due to forces acting among the particles within a system As the internal net force is always summed to zero, there shall be no net change to the internal energy of the system due to the work done by th ...
... Unless specified, when the word work is referred, it shall refer to external work Internal work is due to forces acting among the particles within a system As the internal net force is always summed to zero, there shall be no net change to the internal energy of the system due to the work done by th ...
Isentropic Efficiency in Engineering Thermodynamics Introduction
... Examples are also given in the text for the isentropic efficiencies of nozzles and compressors, but they are all similar to the turbine example shown. Once you accept that a flowing fluid can have the properties of an equilibrium state, the rest follows. We see that the isentropic approximation is p ...
... Examples are also given in the text for the isentropic efficiencies of nozzles and compressors, but they are all similar to the turbine example shown. Once you accept that a flowing fluid can have the properties of an equilibrium state, the rest follows. We see that the isentropic approximation is p ...
Document
... and temperature that it had aper the cycle has been completed 1. The engine sucks in heat from the hot reservoir but, by expanding, keeps the temperature constant 2. The gas con]nues expanding adiaba]cally, lowering the temperature 3. The gas exhausts heat and compresses, keeping the temperat ...
... and temperature that it had aper the cycle has been completed 1. The engine sucks in heat from the hot reservoir but, by expanding, keeps the temperature constant 2. The gas con]nues expanding adiaba]cally, lowering the temperature 3. The gas exhausts heat and compresses, keeping the temperat ...
Basic Thermodynamics - CERN Accelerator School
... Thermodynamics provides macroscopic descriptions of the states of complex systems and of their behaviours when they interact or are constrained under various circumstances. A thermodynamic system is a precisely specified macroscopic region of the Universe. It is limited by boundaries of a particular ...
... Thermodynamics provides macroscopic descriptions of the states of complex systems and of their behaviours when they interact or are constrained under various circumstances. A thermodynamic system is a precisely specified macroscopic region of the Universe. It is limited by boundaries of a particular ...
2. Laws of thermodynamics
... 1.) Relate the heat absorbed by a gas, the work performed by the gas, and the internal energy change of the gas for any of the processes above. 2.) Relate the work performed by a gas in a cyclic process to the area enclosed by a curve on a PV diagram. b. Students should understand the second law of ...
... 1.) Relate the heat absorbed by a gas, the work performed by the gas, and the internal energy change of the gas for any of the processes above. 2.) Relate the work performed by a gas in a cyclic process to the area enclosed by a curve on a PV diagram. b. Students should understand the second law of ...
Chapter 1
... The study of thermodynamics is concerned with the ways energy is stored within a body and how energy transformations, which involve heat and work, may take place. One of the most fundamental laws of nature is the conservation of energy principle. It simply states that during an energy interaction, e ...
... The study of thermodynamics is concerned with the ways energy is stored within a body and how energy transformations, which involve heat and work, may take place. One of the most fundamental laws of nature is the conservation of energy principle. It simply states that during an energy interaction, e ...
lecture1 - Unaab.edu.ng
... Thermodynamics: This is the study of energy changes in chemical and physical processes and of the laws and relationships which govern them. Some terms are commonly used: (a) System; A system in thermodynamics is defined as collection of matter i.e that part of the universe under study. The rest of t ...
... Thermodynamics: This is the study of energy changes in chemical and physical processes and of the laws and relationships which govern them. Some terms are commonly used: (a) System; A system in thermodynamics is defined as collection of matter i.e that part of the universe under study. The rest of t ...
UNIT I PART B 1). (i). A spherical balloon of diameter
... friction of the piston on the walls is insignificant. The atmospheric pressure is 1.0135 bar. The latch holding the piston in position is suddenly removed and the gas is allowed to expand. The expansion is arrested when the volume is double the original volume. Determine the work done in the surroun ...
... friction of the piston on the walls is insignificant. The atmospheric pressure is 1.0135 bar. The latch holding the piston in position is suddenly removed and the gas is allowed to expand. The expansion is arrested when the volume is double the original volume. Determine the work done in the surroun ...
Chapter 6 lecture notes
... The system is described by a set of variables that represent the state of the system—these are called state variable. Common state variables are temperature, pressure, and volume. The distinguishing feature of state variables is that when a change of state occurs, the path taken in the change does n ...
... The system is described by a set of variables that represent the state of the system—these are called state variable. Common state variables are temperature, pressure, and volume. The distinguishing feature of state variables is that when a change of state occurs, the path taken in the change does n ...
Chapter 01 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... The study of thermodynamics is concerned with the ways energy is stored within a body and how energy transformations, which involve heat and work, may take place. One of the most fundamental laws of nature is the conservation of energy principle. It simply states that during an energy interaction, e ...
... The study of thermodynamics is concerned with the ways energy is stored within a body and how energy transformations, which involve heat and work, may take place. One of the most fundamental laws of nature is the conservation of energy principle. It simply states that during an energy interaction, e ...
HEALTH, AGEING AND ENTROPY
... constant temperature and it means that on one said we receive energy in form of fats, carbohydrates and proteins and on the other side we transfer it to the surroundings as heat. Thermodynamically it means that ordered organic molecules are changed to totally unordered form of energy – heat. Highly ...
... constant temperature and it means that on one said we receive energy in form of fats, carbohydrates and proteins and on the other side we transfer it to the surroundings as heat. Thermodynamically it means that ordered organic molecules are changed to totally unordered form of energy – heat. Highly ...
Lecture 2: Energy, Exergy, and Thermodynamics
... can be obtained from a given quantity of a certain substance in a given initial state, without increasing its total volume or allowing heat to pass to or from external bodies, except such as at the close of the processes are left in their initial condition. ...
... can be obtained from a given quantity of a certain substance in a given initial state, without increasing its total volume or allowing heat to pass to or from external bodies, except such as at the close of the processes are left in their initial condition. ...
Class01 Intro Units
... • 1st Law of Thermo [Conservation of energy]: Total work is same in all adiabatic processes between any two equilibrium states having same kinetic and potential energy. – Introduces idea of stored or internal energy E – dE = dQ - dW • dW = Work done by system [+]=dWout= - pdV • Some books have dE=dQ ...
... • 1st Law of Thermo [Conservation of energy]: Total work is same in all adiabatic processes between any two equilibrium states having same kinetic and potential energy. – Introduces idea of stored or internal energy E – dE = dQ - dW • dW = Work done by system [+]=dWout= - pdV • Some books have dE=dQ ...
Chapter 1 Classical Thermodynamics: The First Law 1.1 Introduction
... 2. TD variables (parameters): measurable macroscopic quantities associated with the system and are defined experimentally, e.g., P, V, T, Ha etc., where Ha is an applied field. These quantities are either intensive or extensive, i.e., either independent or linearly dependent on the amount of matter. ...
... 2. TD variables (parameters): measurable macroscopic quantities associated with the system and are defined experimentally, e.g., P, V, T, Ha etc., where Ha is an applied field. These quantities are either intensive or extensive, i.e., either independent or linearly dependent on the amount of matter. ...
PPT
... We need to generalize the definition of entropy since real systems are typically spontaneous and irreversible, moving from a state of non-equilibrium to a state of equilibrium. Second law can be formulated as 4 postulates: 1. There exists a STATE VARIABLE for any substance called the ENTROPY. 2. Ent ...
... We need to generalize the definition of entropy since real systems are typically spontaneous and irreversible, moving from a state of non-equilibrium to a state of equilibrium. Second law can be formulated as 4 postulates: 1. There exists a STATE VARIABLE for any substance called the ENTROPY. 2. Ent ...