Ch 20 Thermodynamics
... Ch 20: Thermodynamics: First law of thermodynamics: Law of conservation of energy: Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. ∆E= q + w (q=heat, w=work, E=internal energy) E univ= E sys + E surr Heat gained by system is lost by surroundings and vice-versa. Total energy of Universe is constant ∆E s ...
... Ch 20: Thermodynamics: First law of thermodynamics: Law of conservation of energy: Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. ∆E= q + w (q=heat, w=work, E=internal energy) E univ= E sys + E surr Heat gained by system is lost by surroundings and vice-versa. Total energy of Universe is constant ∆E s ...
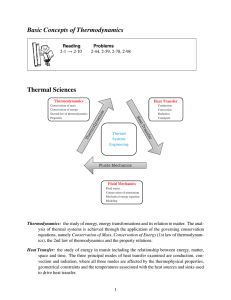
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Thermal Sciences
... space and time. The three principal modes of heat transfer examined are conduction, convection and radiation, where all three modes are affected by the thermophysical properties, geometrical constraints and the temperatures associated with the heat sources and sinks used to drive heat transfer. ...
... space and time. The three principal modes of heat transfer examined are conduction, convection and radiation, where all three modes are affected by the thermophysical properties, geometrical constraints and the temperatures associated with the heat sources and sinks used to drive heat transfer. ...
20. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
... properties of the system. Experimentally, however, it is observed that the quantity Q - W is the same for all processes. It depends only on the initial and final states and it does not matter at what path is followed to get from one to the other. The quantity Q - W is called the change in the intern ...
... properties of the system. Experimentally, however, it is observed that the quantity Q - W is the same for all processes. It depends only on the initial and final states and it does not matter at what path is followed to get from one to the other. The quantity Q - W is called the change in the intern ...
The Boltzmann distribution law and statistical thermodynamics
... where h 0 is an arbitrary fixed reference height. If the gas is a mixture of different species with differing molecular masses m, each has its own distribution (1.6) with its own m. This is the barometric distribution. Since the probability of finding any specified molecule at the height h is proportio ...
... where h 0 is an arbitrary fixed reference height. If the gas is a mixture of different species with differing molecular masses m, each has its own distribution (1.6) with its own m. This is the barometric distribution. Since the probability of finding any specified molecule at the height h is proportio ...
Chapter 22-1 - UCF College of Sciences
... mechanical energy of the gas is converted into random internal energy and the temperature of the gas rises. The gas still has the same total energy, but now all of the energy is associated with the random motion of the molecules about of center of the mass of the gas, which is now at rest. ...
... mechanical energy of the gas is converted into random internal energy and the temperature of the gas rises. The gas still has the same total energy, but now all of the energy is associated with the random motion of the molecules about of center of the mass of the gas, which is now at rest. ...
ENERGY CONSERVATION The Fisrt Law
... other non-reversible machines. A non-reversible machine includes all real machines. They are subjected to friction and other adverse factors that detriment their motion. Non-perpetual motion Let’s now consider the following hypothesis: There is not such a thing like perpetual motion. (This is basi ...
... other non-reversible machines. A non-reversible machine includes all real machines. They are subjected to friction and other adverse factors that detriment their motion. Non-perpetual motion Let’s now consider the following hypothesis: There is not such a thing like perpetual motion. (This is basi ...
1st Year Thermodynamic Lectures Dr Mark R. Wormald
... Spontaneous changes are those which, if carried out under the proper conditions, can be made to do work. If carried out reversibly they yield a maximum amount of work. In irreversible (spontaneous) processes the maximum work is never achieved. ...
... Spontaneous changes are those which, if carried out under the proper conditions, can be made to do work. If carried out reversibly they yield a maximum amount of work. In irreversible (spontaneous) processes the maximum work is never achieved. ...
File - Elements of Mechanical Engineering
... Q8. Is stored energy a property of system? If yes then name and define the same. Q9. Name the various processes to which we can apply first law of thermodynamics. Q10. What is a polytropic process? Q11. How can you say that a polytrophic process can represent all the reversible processes? Q12. What ...
... Q8. Is stored energy a property of system? If yes then name and define the same. Q9. Name the various processes to which we can apply first law of thermodynamics. Q10. What is a polytropic process? Q11. How can you say that a polytrophic process can represent all the reversible processes? Q12. What ...
Thermochemistry
... Two of the terms we use in thermodynamics are “internal energy” and "enthalpy”. They refer to the energy content of a substance in slightly different ways. This energy content changes by the general processes of heat transfer and work (q and w). Internal energy can be thought of as the thermal energ ...
... Two of the terms we use in thermodynamics are “internal energy” and "enthalpy”. They refer to the energy content of a substance in slightly different ways. This energy content changes by the general processes of heat transfer and work (q and w). Internal energy can be thought of as the thermal energ ...
Lecture August 28
... In this way ☛ we obtain isothermal curve (or isotherm) in (P, V ) plot Repeating this @ different temperatures of bath we obtain many isotherms For most of substances (except water near 4 C ) isotherms corresponding to different temperatures do not cross ...
... In this way ☛ we obtain isothermal curve (or isotherm) in (P, V ) plot Repeating this @ different temperatures of bath we obtain many isotherms For most of substances (except water near 4 C ) isotherms corresponding to different temperatures do not cross ...
A thermodynamic system is one that interacts and exchanges
... move from cooler to warmer areas, it is going against what is “natural”, so the system must put in some work for it to happen. ...
... move from cooler to warmer areas, it is going against what is “natural”, so the system must put in some work for it to happen. ...



![documentstyle[12pt]{article}](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010234315_1-392ad57a1bf5b2aaeca94206588a5307-300x300.png)