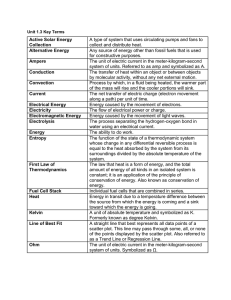
Unit 1.3 Key Terms Active Solar Energy Collection A type of system
... A general statement of the idea that there is a preferred direction for any process. A property of an object which determines the direction of heat flow when the object is placed in thermal contact with another object. Refers to the property of a thermodynamic system in which all parts of the system ...
... A general statement of the idea that there is a preferred direction for any process. A property of an object which determines the direction of heat flow when the object is placed in thermal contact with another object. Refers to the property of a thermodynamic system in which all parts of the system ...
Chapter 1 Thermodynamics
... engine. Heat engine is a system which undergoes a cyclic transformation that takes heat Q1 from a warmer reservoir, converts some of it to work W and rejects the rest Q2 = Q1 ≠ W to a colder reservoir. In contrast, refrigerator, is a heat engine running backwards in time: use work to extract heat fr ...
... engine. Heat engine is a system which undergoes a cyclic transformation that takes heat Q1 from a warmer reservoir, converts some of it to work W and rejects the rest Q2 = Q1 ≠ W to a colder reservoir. In contrast, refrigerator, is a heat engine running backwards in time: use work to extract heat fr ...
The second law of thermodynamics states that energy has the
... inhibited from doing so. The reason the second law is essential to the understanding of entropy is because it explains its basics. However, entropy is loosely defined as the disorder (and order) in a particular system or process. It studies the fluctuation - slowing, cooling, heating, and exhaustion ...
... inhibited from doing so. The reason the second law is essential to the understanding of entropy is because it explains its basics. However, entropy is loosely defined as the disorder (and order) in a particular system or process. It studies the fluctuation - slowing, cooling, heating, and exhaustion ...
9. Entropy 2nd and 3rd laws/ Thermodynamic processes / Droplet
... 9.1 Entropy in second and third laws of thermodynamics (2pts) 1. Explain the statistical definition of entropy (4pts) 2. Consider a “thermodynamic system” of two dices and let the energy of a certain throw (state of the system) be the sum of the two values of the dices. Calculate the respective entr ...
... 9.1 Entropy in second and third laws of thermodynamics (2pts) 1. Explain the statistical definition of entropy (4pts) 2. Consider a “thermodynamic system” of two dices and let the energy of a certain throw (state of the system) be the sum of the two values of the dices. Calculate the respective entr ...
PS5, Thermo Thermodynamics Standards: 3. Energy cannot be
... 3. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, although in many processes energy is transferred to the environment as heat. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know heat flow and work are two forms of energy transfer between systems. b. Students know that the work done by a heat engine ...
... 3. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, although in many processes energy is transferred to the environment as heat. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know heat flow and work are two forms of energy transfer between systems. b. Students know that the work done by a heat engine ...
here
... A transformation whose only final result is to transform into work heat extracted from a source that is at the same temperature throughout is impossible. (Kelvin -Planck statement) It is not possible for any cyclical machine to convey heat continuously from one body to another at a higher temper ...
... A transformation whose only final result is to transform into work heat extracted from a source that is at the same temperature throughout is impossible. (Kelvin -Planck statement) It is not possible for any cyclical machine to convey heat continuously from one body to another at a higher temper ...