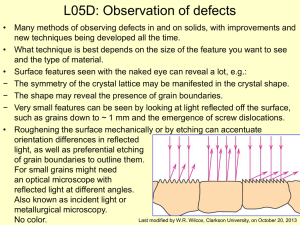
Light Microscopy
... Light as electromagnetic wave with mutually perpendicular E, B components characterized by wavelength,λ, and frequency, ν, in cycles/s. Wave velocity = ν x λ. [λ=500nm--> ν=6x1014 cycles/s] ...
... Light as electromagnetic wave with mutually perpendicular E, B components characterized by wavelength,λ, and frequency, ν, in cycles/s. Wave velocity = ν x λ. [λ=500nm--> ν=6x1014 cycles/s] ...
JC2315121515
... measurement speed is much higher, they can measure surfaces through transparent medium such as glass or plastic film. It can be used on soft materials like lenses, floppy discs. Disadvantages are it requires specimens must be small enough in order to fit into the specimen cell of the microscope, the ...
... measurement speed is much higher, they can measure surfaces through transparent medium such as glass or plastic film. It can be used on soft materials like lenses, floppy discs. Disadvantages are it requires specimens must be small enough in order to fit into the specimen cell of the microscope, the ...
Stellar Activity with SONG
... A wave plate (or retarder) works by shifting the phase of the light wave between two perpendicular polarization components. A typical wave plate is simply a birefringent crystal with a carefully chosen thickness. The wave plate is characterized by the amount of relative phase that it imparts on the ...
... A wave plate (or retarder) works by shifting the phase of the light wave between two perpendicular polarization components. A typical wave plate is simply a birefringent crystal with a carefully chosen thickness. The wave plate is characterized by the amount of relative phase that it imparts on the ...
The coherence length of black
... (|m| = 0, 1, 2, 3, . . .) of the superposed light. However, if black-body radiation is used, the coherence length is slightly less than the mean or effective wavelength. That is why no fringes (modulation of intensity) of order |m| � 1 occur. So, in the case of unfiltered black-body radiation, interf ...
... (|m| = 0, 1, 2, 3, . . .) of the superposed light. However, if black-body radiation is used, the coherence length is slightly less than the mean or effective wavelength. That is why no fringes (modulation of intensity) of order |m| � 1 occur. So, in the case of unfiltered black-body radiation, interf ...
a collection of problems about light rays, refraction and rainbows
... and rainbows get their colour. (i) Estimate the angular width of a rainbow. (ii) Why is a rainbow darkest just outside the blue band? (b) We have considered a drop in the sky at an angle χm to the direction of the Sun’s rays. Drops anywhere on a circle subtending χm to the eye with the Sun shining p ...
... and rainbows get their colour. (i) Estimate the angular width of a rainbow. (ii) Why is a rainbow darkest just outside the blue band? (b) We have considered a drop in the sky at an angle χm to the direction of the Sun’s rays. Drops anywhere on a circle subtending χm to the eye with the Sun shining p ...
Spectral lines, wavelength of light, Rydberg constant
... 1) With either a diffraction grating or a hand held spectrometer, observe the spectra of the following gases: argon, helium, hydrogen, mercury, neon, sodium. Identify them, by writing the tube number next to each gas, and a short description of the lines. Record these on table attached. ...
... 1) With either a diffraction grating or a hand held spectrometer, observe the spectra of the following gases: argon, helium, hydrogen, mercury, neon, sodium. Identify them, by writing the tube number next to each gas, and a short description of the lines. Record these on table attached. ...
Lecture 24
... An EM wave that is off the optic axis of a calcite crystal splits into two waves called ordinary and extraordinary waves. These waves have orthogonal polarizations and travel with different velocities. The o-wave has a polarization that is always perpendicular to the optical axis. ...
... An EM wave that is off the optic axis of a calcite crystal splits into two waves called ordinary and extraordinary waves. These waves have orthogonal polarizations and travel with different velocities. The o-wave has a polarization that is always perpendicular to the optical axis. ...
Acknowledgments
... In mechanical engineering, a primary motivation for studying optics is to learn how to use optical techniques for making measurements. Optical techniques are widely used in many areas of the thermal sciences for measuring system temperatures, velocities, and species on a time- and space-resolved bas ...
... In mechanical engineering, a primary motivation for studying optics is to learn how to use optical techniques for making measurements. Optical techniques are widely used in many areas of the thermal sciences for measuring system temperatures, velocities, and species on a time- and space-resolved bas ...
Diffusion-controlled optical elements for
... the guiding and cladding elements are both liquids 共L2 waveguides兲1 flowing at low Reynolds numbers through poly共dimethylsiloxane兲 共PDMS兲 microchannels. The optical properties of the liquid optical devices are controlled using the rate of flow and the composition of the fluids. We applied this capab ...
... the guiding and cladding elements are both liquids 共L2 waveguides兲1 flowing at low Reynolds numbers through poly共dimethylsiloxane兲 共PDMS兲 microchannels. The optical properties of the liquid optical devices are controlled using the rate of flow and the composition of the fluids. We applied this capab ...
the zeeman effect 161114
... in Figure A1-1, in some earlier course. In many cases the reflectance of the surfaces is low and one need only to take the first two rays into account. However, if the reflectance is high we must sum the contribution from (very) many rays, a phenomenon called multiple beam interference. This is the ...
... in Figure A1-1, in some earlier course. In many cases the reflectance of the surfaces is low and one need only to take the first two rays into account. However, if the reflectance is high we must sum the contribution from (very) many rays, a phenomenon called multiple beam interference. This is the ...
Evanescent-field optical microscopy: effects of polarization, tip
... the grating lines. The p-polarization image displays a grating with steps 4.3/xm wide and 1.5 high, while the s-polarization image only vaguely reveals the grating with 0.9 /xm step height. Fig. 4a displays steep slopes on the grating edges which are the result of abrupt changes in feedback action. ...
... the grating lines. The p-polarization image displays a grating with steps 4.3/xm wide and 1.5 high, while the s-polarization image only vaguely reveals the grating with 0.9 /xm step height. Fig. 4a displays steep slopes on the grating edges which are the result of abrupt changes in feedback action. ...
Full-field refractive index measurement with simultaneous phase
... Therefore, according to Eqs. (12) and (13), when the phase difference is accurately measured, the refractive index of the tested specimen n2 can be obtained using Eq. (7). 3. Experimental setup and results To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed method, various mixtures of the tested specimen ...
... Therefore, according to Eqs. (12) and (13), when the phase difference is accurately measured, the refractive index of the tested specimen n2 can be obtained using Eq. (7). 3. Experimental setup and results To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed method, various mixtures of the tested specimen ...
Multiple-wavelength operation of electroabsorption intensity
... 共channel 7兲, respectively. Note that the band edge of channel 9 could not be determined due to the limitation of the tunable laser source. It is observed from this figure that the photocurrent absorption curves have been blueshifted as a function of SiO2 thickness. This implies that the different de ...
... 共channel 7兲, respectively. Note that the band edge of channel 9 could not be determined due to the limitation of the tunable laser source. It is observed from this figure that the photocurrent absorption curves have been blueshifted as a function of SiO2 thickness. This implies that the different de ...
optical computer - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... switching-intensity. Both incident beams are aimed at the same spot on the first mirror. Only if both incident beams have an intensity. If both incident beams, or one of them, has an intensity below its highlevel, the transmitted beam will be of lowlevel intensity. This is exactly like an ...
... switching-intensity. Both incident beams are aimed at the same spot on the first mirror. Only if both incident beams have an intensity. If both incident beams, or one of them, has an intensity below its highlevel, the transmitted beam will be of lowlevel intensity. This is exactly like an ...
Imaging properties of supercritical angle
... A fundamental goal of physical optics is the characterization of the imaging properties of a given optical system. When dealing with imaging of non-coherent fluorescent sources, this is equivalent to calculating the image of single dipole emitters as a function of their position in sample space. For ...
... A fundamental goal of physical optics is the characterization of the imaging properties of a given optical system. When dealing with imaging of non-coherent fluorescent sources, this is equivalent to calculating the image of single dipole emitters as a function of their position in sample space. For ...
Trapping and destruction of long range high intensity optical/plasma
... The spatio-temporally varying refractive index of the wake of molecular alignment causes predictable spectral modulation and broadening of the probe filament. ...
... The spatio-temporally varying refractive index of the wake of molecular alignment causes predictable spectral modulation and broadening of the probe filament. ...
ZnO/SiO2 microcavity modulator on silicon Abstract - Paul
... of a λ/2 cavity spacer (C) of thickness dc and refractive index nc inserted between two Bragg mirror (BM) stacks of dielectric and simultaneously, piezoelectric λ/4 layers. A surface acoustic wave (SAW) generated on the structure by an interdigitated transducer (IDT) creates an optical superlattice ...
... of a λ/2 cavity spacer (C) of thickness dc and refractive index nc inserted between two Bragg mirror (BM) stacks of dielectric and simultaneously, piezoelectric λ/4 layers. A surface acoustic wave (SAW) generated on the structure by an interdigitated transducer (IDT) creates an optical superlattice ...
Chapter 2 Optical fibers
... Optical fiber losses have been reduced from about 1000 dB/km before 1970, to around 20 dB/km in 1970, and 0.2 dB/km at 1.55-µm region in 1979. ...
... Optical fiber losses have been reduced from about 1000 dB/km before 1970, to around 20 dB/km in 1970, and 0.2 dB/km at 1.55-µm region in 1979. ...
optics(conceptuals)
... Q.46 Draw ray diagrams to show how a right angled isosceles prism can be used to (i) deviate the ray through 180 (ii) deviate the ray through 90 (iii) invert the rays. Q.47 What is the nature and size of the image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed between its pole and focus? Dra ...
... Q.46 Draw ray diagrams to show how a right angled isosceles prism can be used to (i) deviate the ray through 180 (ii) deviate the ray through 90 (iii) invert the rays. Q.47 What is the nature and size of the image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed between its pole and focus? Dra ...
Optical Sources and Detectors
... computer chips, high-resolution microscopes, infrared sensors and highly efficient lighting sources. The invention of laser has led to majority of its applications. It is, of course, the unique properties of the laser – monochromaticity, directionality, coherency, and brightness – that account for i ...
... computer chips, high-resolution microscopes, infrared sensors and highly efficient lighting sources. The invention of laser has led to majority of its applications. It is, of course, the unique properties of the laser – monochromaticity, directionality, coherency, and brightness – that account for i ...