Ingen lysbildetittel - Department of Telematics
... State changed though phase shifts or by switching in space. Linear optical elements can be used without major problems (determinsitic), but loss and noise will destroy the system ...
... State changed though phase shifts or by switching in space. Linear optical elements can be used without major problems (determinsitic), but loss and noise will destroy the system ...
Optical Networks
... 2. Siva Ram Moorthy and Mohan Gurusamy, “WDM Optical Networks : Concept, Design and Algorithms”, Prentice Hall of India, 2002. 3. John M. Senior, "Optical Fiber Communications" 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall, 2009 4. Paul Eliot Green, "Fiber Optic Networks", Prentice Hall, 1993. ...
... 2. Siva Ram Moorthy and Mohan Gurusamy, “WDM Optical Networks : Concept, Design and Algorithms”, Prentice Hall of India, 2002. 3. John M. Senior, "Optical Fiber Communications" 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall, 2009 4. Paul Eliot Green, "Fiber Optic Networks", Prentice Hall, 1993. ...
1 - Capanina
... spectrum allocations, while optical systems can be designed on the basis of preferred wavelengths and readily obtainable hardware without consideration of spectrum availability, interference with other users etc. Optical hardware is small and compact and economic in power consumption by comparison w ...
... spectrum allocations, while optical systems can be designed on the basis of preferred wavelengths and readily obtainable hardware without consideration of spectrum availability, interference with other users etc. Optical hardware is small and compact and economic in power consumption by comparison w ...
Optical Storage Overview
... medium, and the grooves are separated by lands. But, the lands could be also used as a storage medium, instead of or together with the grooves. The groove depth is based on the laser wavelength and, typically, equals 1/8 of the wavelength of the laser beam. Another way to define tracks and provide s ...
... medium, and the grooves are separated by lands. But, the lands could be also used as a storage medium, instead of or together with the grooves. The groove depth is based on the laser wavelength and, typically, equals 1/8 of the wavelength of the laser beam. Another way to define tracks and provide s ...
Entangled states of light in classical polarization theory
... Here perfect organization means that orthogonality conditions apply in both vector spaces at the same time: hfi |fj i = hui |uj i = δij , and since intensity has been factored out, the three κs are normalized on the surface of a unit sphere: κ21 + κ22 + κ23 = 1. This Schmidt decomposition of the fie ...
... Here perfect organization means that orthogonality conditions apply in both vector spaces at the same time: hfi |fj i = hui |uj i = δij , and since intensity has been factored out, the three κs are normalized on the surface of a unit sphere: κ21 + κ22 + κ23 = 1. This Schmidt decomposition of the fie ...
The Critical Angle and Beyond - The Society of Vacuum Coaters
... form a right-handed set. In s-polarization the electric field of the wave is normal to the plane of incidence while in p-polarization it is parallel to the plane of incidence. In that article we showed that provided we define the amplitude reflection coefficient (and the transmission coefficient) in ...
... form a right-handed set. In s-polarization the electric field of the wave is normal to the plane of incidence while in p-polarization it is parallel to the plane of incidence. In that article we showed that provided we define the amplitude reflection coefficient (and the transmission coefficient) in ...
Conference title, upper and lower case, bolded, 18 point type
... collimated beam then passes through a Glan-Thompson polarizer (Thorlabs GTH10) and a quarter waveplate (achromatic (Thorlabs AQWP05M-600) or zero-order (Thorlabs WPQ05M-405) waveplate are selectively used depending on the bandwidth of the illumination source) to generate circularly polarized light. ...
... collimated beam then passes through a Glan-Thompson polarizer (Thorlabs GTH10) and a quarter waveplate (achromatic (Thorlabs AQWP05M-600) or zero-order (Thorlabs WPQ05M-405) waveplate are selectively used depending on the bandwidth of the illumination source) to generate circularly polarized light. ...
22-5 Polarized Light
... Polarizing film consists of linear molecules aligned with one another. When an electromagnetic wave is incident on the film, electric field components that are parallel to the molecules cause electrons to oscillate back and forth along the molecules. This transfers energy from the wave to the molecu ...
... Polarizing film consists of linear molecules aligned with one another. When an electromagnetic wave is incident on the film, electric field components that are parallel to the molecules cause electrons to oscillate back and forth along the molecules. This transfers energy from the wave to the molecu ...
Experiment 3 1 The Michelson Interferometer and the He
... With a population inversion, incident photons of energy E2 – E1 from some other atom can cause stimulated emission from state 2 to state 1. With stimulated emission, the incident photon will trigger ...
... With a population inversion, incident photons of energy E2 – E1 from some other atom can cause stimulated emission from state 2 to state 1. With stimulated emission, the incident photon will trigger ...
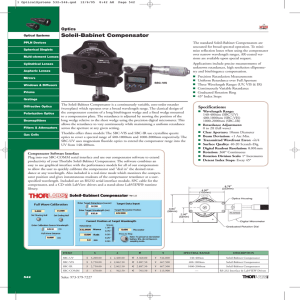
Soleil-Babinet Compensator
... The Soleil-Babinet Compensator is a continuously variable, zero-order retarder (waveplate) which operates over a broad wavelength range. The classical design of the compensator consists of a long birefringent wedge and a fixed wedge mounted Polarization Optics to a compensator plate. The retardance ...
... The Soleil-Babinet Compensator is a continuously variable, zero-order retarder (waveplate) which operates over a broad wavelength range. The classical design of the compensator consists of a long birefringent wedge and a fixed wedge mounted Polarization Optics to a compensator plate. The retardance ...
Optical Maser Action of Nd^{+3} in a Barium Crown Glass
... 0.012 in. and 32 mierons in diameter. The cladding was an ordinary soda-lime-silicate with an index of refraction of 1.52. The samples were ...
... 0.012 in. and 32 mierons in diameter. The cladding was an ordinary soda-lime-silicate with an index of refraction of 1.52. The samples were ...
Full Paper
... shown in fig. 4, LCTF cell consists of an initial linear polarizer followed by a birefringent quartz element of fixed retardance, then a liquid crystal waveplate which permits to obtain a variable retardance with the help of two transparent electrodes placed on each side of the plate. These electrod ...
... shown in fig. 4, LCTF cell consists of an initial linear polarizer followed by a birefringent quartz element of fixed retardance, then a liquid crystal waveplate which permits to obtain a variable retardance with the help of two transparent electrodes placed on each side of the plate. These electrod ...
4 Lab 1: Scattering and Reflection of Polarized Light
... In contrast, in a smooth piece of a transparent solid (the characteristic dimension of which, L, is much larger than the wavelength of light λ, i.e., L >> λ) where the atoms are very close to each other (i.e., λ >> interatomic spacing) and are arranged in an orderly pattern, the superposition of sca ...
... In contrast, in a smooth piece of a transparent solid (the characteristic dimension of which, L, is much larger than the wavelength of light λ, i.e., L >> λ) where the atoms are very close to each other (i.e., λ >> interatomic spacing) and are arranged in an orderly pattern, the superposition of sca ...
Isolated hexaphenyl nanofibers as optical waveguides
... Quantitative understanding and improved control of the waveguiding properties require an analytical theory for optical waveguiding in nanometer-scaled aggregates. Motivated by the force microscopy images, we assume the nanofiber to have a rectangular cross section and to be an optically uniaxial med ...
... Quantitative understanding and improved control of the waveguiding properties require an analytical theory for optical waveguiding in nanometer-scaled aggregates. Motivated by the force microscopy images, we assume the nanofiber to have a rectangular cross section and to be an optically uniaxial med ...
Quasi-3D plasmonic coupling scheme for near-field optical lithography and imaging Y W
... light intensity profile is obtained at the middle between the pin and the silicon wafer. In the above PPL design, aluminum is chosen as the PPL material for its low loss at 355 nm and sapphire is chosen as the substrate material where the PPL structure is placed on. The width of the grating slits is ...
... light intensity profile is obtained at the middle between the pin and the silicon wafer. In the above PPL design, aluminum is chosen as the PPL material for its low loss at 355 nm and sapphire is chosen as the substrate material where the PPL structure is placed on. The width of the grating slits is ...
File
... 3. A bi convex lens is made of glass of ref index 1.5.The radius of curvature of each face is 30 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens in air. 4. Explain why white light is dispersed when passing through a prism? 5. For the same angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three different me ...
... 3. A bi convex lens is made of glass of ref index 1.5.The radius of curvature of each face is 30 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens in air. 4. Explain why white light is dispersed when passing through a prism? 5. For the same angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three different me ...
VII-I
... angle of incidence is equal the angle of reflection. By convention in optics we measure these angles from the normal to the reflecting surface. • This is valid for any element of the surface. • If a surface of a reasonable size is smooth the reflection is specular and from P we can see the image of ...
... angle of incidence is equal the angle of reflection. By convention in optics we measure these angles from the normal to the reflecting surface. • This is valid for any element of the surface. • If a surface of a reasonable size is smooth the reflection is specular and from P we can see the image of ...
THE FARADAY EFFECT AND DISPERSION IN LIQUIDS
... Revised September 4, 2014. The Faraday effect, which is the rotation of the polarization of light due to an applied magnetic field, and dispersion, which is the variation in refractive index as a function of wavelength of light, are related to each other through their basis in the phenomenon of abso ...
... Revised September 4, 2014. The Faraday effect, which is the rotation of the polarization of light due to an applied magnetic field, and dispersion, which is the variation in refractive index as a function of wavelength of light, are related to each other through their basis in the phenomenon of abso ...
Gyrotropic response in the absence of a bias field
... in a gyrotropic medium do not revert to their initial incident polarization states; this implies broken local time-reversal symmetry and nonreciprocal propagation. In slightly more complicated geometries, Faraday rotation can also enable nonreciprocal amplitude and phase response (24), or even more ...
... in a gyrotropic medium do not revert to their initial incident polarization states; this implies broken local time-reversal symmetry and nonreciprocal propagation. In slightly more complicated geometries, Faraday rotation can also enable nonreciprocal amplitude and phase response (24), or even more ...
Gain-Flattening Filters Using Dielectric Multilayer Thin Film
... layer being deposited can be represented as a function of the physical thickness alone. If the rate of deposition and the refractive index within the layer being deposited are constant, the physical thickness will be directly proportional to the deposition time, so that the change in transmittance c ...
... layer being deposited can be represented as a function of the physical thickness alone. If the rate of deposition and the refractive index within the layer being deposited are constant, the physical thickness will be directly proportional to the deposition time, so that the change in transmittance c ...
Ultrafast holographic Stokesmeter for polarization imaging in real time Mark Kleinschmit
... splitter. The f irst beam is diffracted into two beams by use of two multiplexed holographic gratings. The second beam passes through a quarter-wave plate before diffracting from a similar set of multiplexed holographic gratings. The diffracted beams are projected onto four CCD arrays. Their intensi ...
... splitter. The f irst beam is diffracted into two beams by use of two multiplexed holographic gratings. The second beam passes through a quarter-wave plate before diffracting from a similar set of multiplexed holographic gratings. The diffracted beams are projected onto four CCD arrays. Their intensi ...
Spatially resolved measurement of femtosecond
... materials. Based on an iterative Fourier transform algorithm, this technique spatially resolves the refractive index of complex structures by combining the dimensions of the modified region with the corresponding phase change extracted from far-field intensity measurements. This approach is used to ...
... materials. Based on an iterative Fourier transform algorithm, this technique spatially resolves the refractive index of complex structures by combining the dimensions of the modified region with the corresponding phase change extracted from far-field intensity measurements. This approach is used to ...
Study of optical characteristics of tin oxide thin film prepared by sol
... Abstract. In this paper, we present details of preparation of tin oxide (SnO2 ) thin film by sol–gel process. The film was synthesized on a glass (Corning 7059) plate by dip coating method. Here, we used tin (II) chloride as precursor and methanol as solvent. Optical characteristics and physical pro ...
... Abstract. In this paper, we present details of preparation of tin oxide (SnO2 ) thin film by sol–gel process. The film was synthesized on a glass (Corning 7059) plate by dip coating method. Here, we used tin (II) chloride as precursor and methanol as solvent. Optical characteristics and physical pro ...
High-speed spectral-domain optical coherence tomography at 1.3
... nm (w = 0.5). The y-offset of 109.25 dB represents the sensitivity at zero depth and agrees well with the theoretically expected value of 110.3 dB based on Eq. (1). The fit value of 0.104 nm was larger than the predicted value by diffraction theory (0.063 nm). We attribute the discrepancy to aberra ...
... nm (w = 0.5). The y-offset of 109.25 dB represents the sensitivity at zero depth and agrees well with the theoretically expected value of 110.3 dB based on Eq. (1). The fit value of 0.104 nm was larger than the predicted value by diffraction theory (0.063 nm). We attribute the discrepancy to aberra ...