The diffraction of light by sound waves of high
... other hand, the optical length of C'D' is greater than that of CD, for the refractive index is minimum along CD. A simple consideration of the above shows that the difference between the optical lengths of A'B' and C'D' is less than that between those of AB and CD. As this difference gives twice the ...
... other hand, the optical length of C'D' is greater than that of CD, for the refractive index is minimum along CD. A simple consideration of the above shows that the difference between the optical lengths of A'B' and C'D' is less than that between those of AB and CD. As this difference gives twice the ...
CHAPTER 4 REFLECTED LIGHT OPTICS
... as a stream of particles (photons). These are not conflicting theories but rather complementary ways of describing light; in different circumstances. either one may be the more appropriate. For most aspects of microscope optics. the "classical" approach ofdescribing light as waves is more applicable ...
... as a stream of particles (photons). These are not conflicting theories but rather complementary ways of describing light; in different circumstances. either one may be the more appropriate. For most aspects of microscope optics. the "classical" approach ofdescribing light as waves is more applicable ...
Mimicking celestial mechanics in metamaterials ARTICLES *
... linear source with width w = 6λ and wavelength λ = 1.55 µm is used. d–f, Poincaŕe maps (PT ) corresponding to all possible photon trajectories for linear (d) and nonlinear (e,f) refractive indices. In the linear case, the photon motion follows stable periodic and quasi-periodic trajectories for all ...
... linear source with width w = 6λ and wavelength λ = 1.55 µm is used. d–f, Poincaŕe maps (PT ) corresponding to all possible photon trajectories for linear (d) and nonlinear (e,f) refractive indices. In the linear case, the photon motion follows stable periodic and quasi-periodic trajectories for all ...
Sagnac-loop phase shifter with polarization
... block of photonic technologies, in particular in optical communications [1], [2]. For most typical applications, the devices work for only one particular polarization and can tolerate large insertion losses. The situation is very different in quantum information science. Here, losses are much more i ...
... block of photonic technologies, in particular in optical communications [1], [2]. For most typical applications, the devices work for only one particular polarization and can tolerate large insertion losses. The situation is very different in quantum information science. Here, losses are much more i ...
Multiband perfect absorbers using metal
... Figure 1(c) shows the calculated dispersion curves of the MDM structure with a lower-n dielectric core medium. The incident angle corresponding to the in-plane wavevector kx is determined by kx = (2π/λ)(sinθ), where λ represents the peak wavelength. The first order modes (m = 1) for each polarizatio ...
... Figure 1(c) shows the calculated dispersion curves of the MDM structure with a lower-n dielectric core medium. The incident angle corresponding to the in-plane wavevector kx is determined by kx = (2π/λ)(sinθ), where λ represents the peak wavelength. The first order modes (m = 1) for each polarizatio ...
lecture 3 Introduction to Laser
... Active Mode Locking The most common active mode-locking technique places a standing wave acousto-optic modulator into the laser cavity. This device, when placed in a laser cavity and driven with an electrical signal, induces a small, sinusoidally varying frequency shift in the light passing through ...
... Active Mode Locking The most common active mode-locking technique places a standing wave acousto-optic modulator into the laser cavity. This device, when placed in a laser cavity and driven with an electrical signal, induces a small, sinusoidally varying frequency shift in the light passing through ...
50 GHz Velocity-matched, Broad Wavelength LiNbO3
... Improved velocity matching in LiNb0 3 modulators has been achieved by several workers [l4] , using a combination of relatively thick (~ 1 p.m) Si0 2 buffer layers and thick (typically ~ 10 p.m) plated electrodes. Alternatively, a shielded ground plane above the substrate is used in place of the thic ...
... Improved velocity matching in LiNb0 3 modulators has been achieved by several workers [l4] , using a combination of relatively thick (~ 1 p.m) Si0 2 buffer layers and thick (typically ~ 10 p.m) plated electrodes. Alternatively, a shielded ground plane above the substrate is used in place of the thic ...
Optical pulse generation using a low-voltage electro-optic
... photonics links [1]. In particular, ultra-wide-bandwidth (UWB) pulse technology is currently considered in order to fully exploit the advantages provided by optics. This technology allows wide bandwidth operation especially for antenna remoting applications. To this end, some configurations to gener ...
... photonics links [1]. In particular, ultra-wide-bandwidth (UWB) pulse technology is currently considered in order to fully exploit the advantages provided by optics. This technology allows wide bandwidth operation especially for antenna remoting applications. To this end, some configurations to gener ...
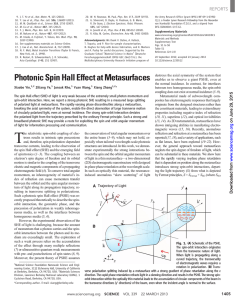
Supporting Information For the discussion of the optical absorption
... carried out by the authors [Figure S6] and Forker [18]. This result indicates that the ex-situ measurement reveals the QT HOMO level drops to a lower level or the optical band-gap expands after exposure to air. In any case, this ex-situ effect is not ignored in estimating and evaluating the realisti ...
... carried out by the authors [Figure S6] and Forker [18]. This result indicates that the ex-situ measurement reveals the QT HOMO level drops to a lower level or the optical band-gap expands after exposure to air. In any case, this ex-situ effect is not ignored in estimating and evaluating the realisti ...
New imaging modes for lenslet-array tandem scanning microscopes
... incoherent light to be introduced to a lenslet array TSM. The optical sectioning characteristics of the instrument are not dramatically affected by using incoherent illumination. However, there is a very significant reduction in the fluorescence image signal level when compared with laser illuminati ...
... incoherent light to be introduced to a lenslet array TSM. The optical sectioning characteristics of the instrument are not dramatically affected by using incoherent illumination. However, there is a very significant reduction in the fluorescence image signal level when compared with laser illuminati ...
The Michelson Interferometer and Its Applications
... constructed an optical interferometer with which he presumed he would then be able to detect the relative motion of Earth against the static aether. That is, since Earth’s orbital velocity is approximately ...
... constructed an optical interferometer with which he presumed he would then be able to detect the relative motion of Earth against the static aether. That is, since Earth’s orbital velocity is approximately ...
(Digital Micro-Mirror Device) Based Multi-Object
... mask that allows several spectrally different objects in the scene to be rapidly measured in sequence. We will focus on spectral measurements in the visual and near-infrared part of the spectrum, as there are several applications in this wavelength region where such a system is of interest. ...
... mask that allows several spectrally different objects in the scene to be rapidly measured in sequence. We will focus on spectral measurements in the visual and near-infrared part of the spectrum, as there are several applications in this wavelength region where such a system is of interest. ...
What are Fiber Optics
... Single-mode fibers – in single mode fiber only one mode can propagate through the fiber. This type of fiber has small core diameter(5um) and high cladding diameter(70um) and the difference between the refractive index of core and cladding is very small. There is no dispersion i.e. no degradation of ...
... Single-mode fibers – in single mode fiber only one mode can propagate through the fiber. This type of fiber has small core diameter(5um) and high cladding diameter(70um) and the difference between the refractive index of core and cladding is very small. There is no dispersion i.e. no degradation of ...
1 Introduction 2 Theory of Optical Trapping
... 2 Theory of Optical Trapping 2.1 Simple explanation of optical trapping A basic and intuitive explanation of optical trapping can be given by a ray description. Consider a transparent bead (whose index of refraction is larger than that of surrounding medium), placed in an intensity gradient (Figure ...
... 2 Theory of Optical Trapping 2.1 Simple explanation of optical trapping A basic and intuitive explanation of optical trapping can be given by a ray description. Consider a transparent bead (whose index of refraction is larger than that of surrounding medium), placed in an intensity gradient (Figure ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester
... Examples: • Transmission through an optically inactive material: ...
... Examples: • Transmission through an optically inactive material: ...
C-Point singularities in Poincare beams
... a field of ellipses whose semi-major axis rotates about the C-point. This divides the C-points into two classes: those that rotate with the angular coordinate about the C-point, and those that rotate counter to it. An index representing this rotation about the C-point is IC . Since ellipses’ axes ar ...
... a field of ellipses whose semi-major axis rotates about the C-point. This divides the C-points into two classes: those that rotate with the angular coordinate about the C-point, and those that rotate counter to it. An index representing this rotation about the C-point is IC . Since ellipses’ axes ar ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... (a) Linearly polarized light with Eyo = 2Exo and = 0. (b) When = /4 (45), the light is right elliptically polarized with a tilted major axis. (c) When = /2 (90), the light is right elliptically polarized. If Exo and Eyo were equal, this would be right circularly polarized light. © 1999 S.O ...
... (a) Linearly polarized light with Eyo = 2Exo and = 0. (b) When = /4 (45), the light is right elliptically polarized with a tilted major axis. (c) When = /2 (90), the light is right elliptically polarized. If Exo and Eyo were equal, this would be right circularly polarized light. © 1999 S.O ...
Optical properties of Al2O3 thin films grown by
... 25 mm and the optical properties of the Al2 O3 films were investigated by measuring the reflection spectra at five different positions on each sample 5 mm apart from each other. MATLAB curve fitting tools were used for analysis of the reflection spectrum data. The experimentally measured reflection ...
... 25 mm and the optical properties of the Al2 O3 films were investigated by measuring the reflection spectra at five different positions on each sample 5 mm apart from each other. MATLAB curve fitting tools were used for analysis of the reflection spectrum data. The experimentally measured reflection ...
... is a correction to the light trajectory raised from the metasurface-induced spin-orbit interaction). The PSHE or the spin-orbit interaction arises from the noncolinear momentum and velocity (the change of trajectory) of light. When light is propagating along a curved trajectory (Fig. 1A), the time-v ...
Optical measurement of the axial eye length by laser Doppler
... can be achieved if the center of the signal peak is determined instead of the position of the signal maximum, since the overall shape of the signal is less influenced by statistical noise than the position of the maximum. Therefore, the center of the peak was determined throughout all the optical me ...
... can be achieved if the center of the signal peak is determined instead of the position of the signal maximum, since the overall shape of the signal is less influenced by statistical noise than the position of the maximum. Therefore, the center of the peak was determined throughout all the optical me ...
wavelength dependence of the light-induced index
... optical path length and thus the optical phase of light propagating through the irradiated arm. The change in optical phase is readily determined from the experimental data by using the fact that a change in the coupling ratio from 0% to 100% corresponds to an optical phase change of 7r. Thus the me ...
... optical path length and thus the optical phase of light propagating through the irradiated arm. The change in optical phase is readily determined from the experimental data by using the fact that a change in the coupling ratio from 0% to 100% corresponds to an optical phase change of 7r. Thus the me ...
Course code: EE412 Course title: Optical
... Learning Objective: To understand the principle of EM waves propagation in fiber cables and also about different types of optical fibers. Overview of Optical Networks including PDH, SDH/SONET and DWDM . To learn the various optical source materials, LED structures, quantum efficiency, Laser diodes ...
... Learning Objective: To understand the principle of EM waves propagation in fiber cables and also about different types of optical fibers. Overview of Optical Networks including PDH, SDH/SONET and DWDM . To learn the various optical source materials, LED structures, quantum efficiency, Laser diodes ...
Theory of relativistic harmonic generation
... shows discrete and well resolved harmonics up to 160 eV. The number of photons per pump pulse in the 50-150 eV spectral range is -7 x lo6, which corresponds to a conversion efficiency of -3 x As shown in the inset of Fig. 1, which displays an enlarged portion of the harmonic spectrum on a logarithmi ...
... shows discrete and well resolved harmonics up to 160 eV. The number of photons per pump pulse in the 50-150 eV spectral range is -7 x lo6, which corresponds to a conversion efficiency of -3 x As shown in the inset of Fig. 1, which displays an enlarged portion of the harmonic spectrum on a logarithmi ...