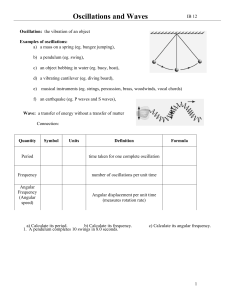
Physics Quest- Waves, wave-like behavior, and
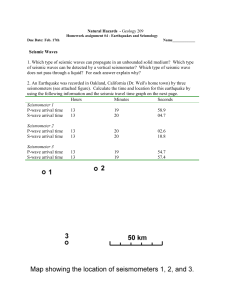
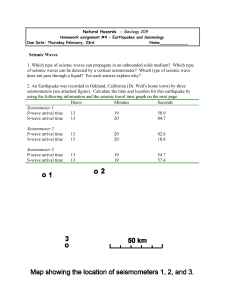
... 10. How fast do P-waves move in the crust? 11. How fast do S-waves move in the crust? 12. What happens to S-waves approximately 2900 km below Earth’s surface? Why? 13. Using only data on P-waves, how could you determine the depth of the boundary between the mantle and the outer core? 14. How does P- ...
... 10. How fast do P-waves move in the crust? 11. How fast do S-waves move in the crust? 12. What happens to S-waves approximately 2900 km below Earth’s surface? Why? 13. Using only data on P-waves, how could you determine the depth of the boundary between the mantle and the outer core? 14. How does P- ...
Part51
... apart (phase difference of 585o which is the same as 225o). 1. The blue is the incident wave arriving at the right end with a phase of 180o and is reflected. 2. The red is the first reflected wave from the right end starting with a phase of 180o+180o = 360o which is the same as 0o. The red wave reac ...
... apart (phase difference of 585o which is the same as 225o). 1. The blue is the incident wave arriving at the right end with a phase of 180o and is reflected. 2. The red is the first reflected wave from the right end starting with a phase of 180o+180o = 360o which is the same as 0o. The red wave reac ...
Faults - cloudfront.net
... Body waves that shake particles at right angles to the direction the waves travel. ...
... Body waves that shake particles at right angles to the direction the waves travel. ...
pkt 9 SHM and waves
... provide accurate clocks for microprocessors and to produce and detect sound waves in a medical test known as ultrasound. d) Greenhouse Effect: The natural frequency of oscillation of the molecules of the greenhouse gases (water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide) is in the infrared region ...
... provide accurate clocks for microprocessors and to produce and detect sound waves in a medical test known as ultrasound. d) Greenhouse Effect: The natural frequency of oscillation of the molecules of the greenhouse gases (water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide) is in the infrared region ...
Document
... distance that this station is from the epicenter of an earthquake if the difference between first P and first S waves arrivals is 5 minutes. a. 700 miles b. 1000 miles c. 1500 miles d. 2000 miles Using the chart and calculated distance from the previous question, if the first P wave arrived at 10:28 ...
... distance that this station is from the epicenter of an earthquake if the difference between first P and first S waves arrivals is 5 minutes. a. 700 miles b. 1000 miles c. 1500 miles d. 2000 miles Using the chart and calculated distance from the previous question, if the first P wave arrived at 10:28 ...
Non-Linear Static Analysis of Multi-Storied Building
... Design Seismic Base Shear- The total design lateral force or design seismic base shear (Vb) along any principal direction of the building shall be determined by the following expression VB= Ah W Where ...
... Design Seismic Base Shear- The total design lateral force or design seismic base shear (Vb) along any principal direction of the building shall be determined by the following expression VB= Ah W Where ...
Properties of Waves
... (b) The diagram shows circles drawn around two research stations, M and N. The stations are for detecting earthquakes. Each circle shows the distance of the earthquake from that station. ...
... (b) The diagram shows circles drawn around two research stations, M and N. The stations are for detecting earthquakes. Each circle shows the distance of the earthquake from that station. ...
Mechanical Waves
... traveling through the water. This starts the transformation of the tsunami. The topography of the seafloor and shape of the shore begins to affect the tsunami's appearance and behavior. As the velocity of the wave diminishes, the wave height increases considerably -- the compressed energy forces the ...
... traveling through the water. This starts the transformation of the tsunami. The topography of the seafloor and shape of the shore begins to affect the tsunami's appearance and behavior. As the velocity of the wave diminishes, the wave height increases considerably -- the compressed energy forces the ...
Earthquakes 1
... lengthen an object or pull it apart. 3. Shear/Transform: Stress that acts parallel to a surface. It can cause one object to slide over another. The most general definition is that shear acts to change the angles in an object. ...
... lengthen an object or pull it apart. 3. Shear/Transform: Stress that acts parallel to a surface. It can cause one object to slide over another. The most general definition is that shear acts to change the angles in an object. ...
ReMi Report - The Nevada Seismological Laboratory
... geophones collected several thirty second records measuring the relative amplitude of surface waves. The seismic records were processed using ReMiVspect and ReMiDipsert. Through Rayleigh phasevelocity dispersion picking (Louie, 2001), a shear-velocity model, shown in Figure 2, was made to approximat ...
... geophones collected several thirty second records measuring the relative amplitude of surface waves. The seismic records were processed using ReMiVspect and ReMiDipsert. Through Rayleigh phasevelocity dispersion picking (Louie, 2001), a shear-velocity model, shown in Figure 2, was made to approximat ...
Chapter 5: Earthquakes
... the energy builds so high, an earthquake occurs. • Seismic waves are vibrations that are similar to sound waves. They travel through Earth carrying energy released by an earthquake. ...
... the energy builds so high, an earthquake occurs. • Seismic waves are vibrations that are similar to sound waves. They travel through Earth carrying energy released by an earthquake. ...
bokelmannAbstract_5p..
... splitting among all shield regions on Earth which confirms the strong deformation in the lithosphere under stable North America and a relatively strong coupling with the deeper mantle. An open question, however, is in which direction the basal stresses operate, that is whether the deeper mantle is r ...
... splitting among all shield regions on Earth which confirms the strong deformation in the lithosphere under stable North America and a relatively strong coupling with the deeper mantle. An open question, however, is in which direction the basal stresses operate, that is whether the deeper mantle is r ...
Section 19.1 Forces within Earth
... What three things about the Earths interior do we now know thanks to all of the information we have from studying the seismic waves? From this information we can determine the density, thickness, and composition of the various layers of the Earth’s interior. ...
... What three things about the Earths interior do we now know thanks to all of the information we have from studying the seismic waves? From this information we can determine the density, thickness, and composition of the various layers of the Earth’s interior. ...
Shear wave splitting

Shear wave splitting, also called seismic birefringence, is the phenomenon that occurs when a polarized shear wave enters an anisotropic medium (Fig. 1). The incident shear wave splits into two polarized shear waves (Fig. 2). Shear wave splitting is typically used as a tool for testing the anisotropy of an area of interest. These measurements reflect the degree of anisotropy and lead to a better understanding of the area’s crack density and orientation or crystal alignment.We can think of the anisotropy of a particular area as a black box and the shear wave splitting measurements as a way of looking at what is in the box.