ppt file - Angelfire
... Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures Enact building codes to design and build earthquake-resistant structures in high seismic risk areas. wood, steel and reinforced concrete are preferred as they tend to move with the shaking ground (unreinforced concrete and heavy masonry tend to move independ ...
... Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures Enact building codes to design and build earthquake-resistant structures in high seismic risk areas. wood, steel and reinforced concrete are preferred as they tend to move with the shaking ground (unreinforced concrete and heavy masonry tend to move independ ...
Introduction to Engineering Seismology
... Earthquake foci are described as: Shallow: less than 70 km depth Intermediate: 70 - 300 km depth Deep: 300 - 700 km depth 90% of earthquake foci are less than 100 km deep Large earthquakes are mostly at < 60 km depth No earthquakes occur deeper than 700 km ...
... Earthquake foci are described as: Shallow: less than 70 km depth Intermediate: 70 - 300 km depth Deep: 300 - 700 km depth 90% of earthquake foci are less than 100 km deep Large earthquakes are mostly at < 60 km depth No earthquakes occur deeper than 700 km ...
Waves
... • An echo is reflected sound. Sound reflects from all surfaces. • You see your face in a mirror because of reflection. Light waves produced by a source of light bounce off your face, strike the mirror, and reflect back to your eyes. ...
... • An echo is reflected sound. Sound reflects from all surfaces. • You see your face in a mirror because of reflection. Light waves produced by a source of light bounce off your face, strike the mirror, and reflect back to your eyes. ...
Energy and Power
... • Actual value of v = /k is determined by the medium • as wave passes, the “particles” in the medium oscillate • medium has both inertia (KE) and elasticity (PE) • dimensional argument: v= length/time LT-1 • inertia is the mass of an element =mass/length ML-1 • tension F is the elastic character ( ...
... • Actual value of v = /k is determined by the medium • as wave passes, the “particles” in the medium oscillate • medium has both inertia (KE) and elasticity (PE) • dimensional argument: v= length/time LT-1 • inertia is the mass of an element =mass/length ML-1 • tension F is the elastic character ( ...
Earthquake
... Surface Waves (slowest travel speeds) • R-waves – (Rayleigh, named for a physicist) surface shear waves that make the ground move up and down in a retrograde elliptical pattern. • L-waves – (Love, named for a seismologist) surface shear waves that cause the ground to move horizontally back and forth ...
... Surface Waves (slowest travel speeds) • R-waves – (Rayleigh, named for a physicist) surface shear waves that make the ground move up and down in a retrograde elliptical pattern. • L-waves – (Love, named for a seismologist) surface shear waves that cause the ground to move horizontally back and forth ...
Chapter 1: Basic Seismology and Earthquake Terminology
... then rushes away to find a level surface. This motion creates seismic sea waves (also known as Tsunami, Surface Sea wave, or Tidal Wave). Seismic sea waves can also result if the seafloor drops. Water rushes in an enormous amount and a complex sloshing occurs back and forth. In deep ocean, the sei ...
... then rushes away to find a level surface. This motion creates seismic sea waves (also known as Tsunami, Surface Sea wave, or Tidal Wave). Seismic sea waves can also result if the seafloor drops. Water rushes in an enormous amount and a complex sloshing occurs back and forth. In deep ocean, the sei ...
20051215163017006-149555
... Cnjlm 0 only if the resonant conditions are held: n j l m, n 2 j 2 l 2 m 2 ...
... Cnjlm 0 only if the resonant conditions are held: n j l m, n 2 j 2 l 2 m 2 ...
Part42
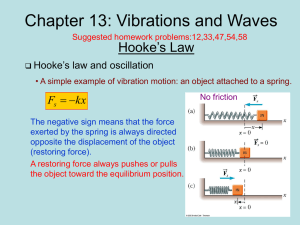
... This says that if y is negative (spring stretched), the force is positive and hence the acceleration is positive. This will produce a velocity that, if initially zero, will become positive, tending to reduce the negative y. As y approaches the equilibrium position, the force approaches zero and the ...
... This says that if y is negative (spring stretched), the force is positive and hence the acceleration is positive. This will produce a velocity that, if initially zero, will become positive, tending to reduce the negative y. As y approaches the equilibrium position, the force approaches zero and the ...
Why do we have earthquakes?
... vibrations travels outwards from the focus, we call these seismic waves. Epicentre ...
... vibrations travels outwards from the focus, we call these seismic waves. Epicentre ...
Shear wave splitting

Shear wave splitting, also called seismic birefringence, is the phenomenon that occurs when a polarized shear wave enters an anisotropic medium (Fig. 1). The incident shear wave splits into two polarized shear waves (Fig. 2). Shear wave splitting is typically used as a tool for testing the anisotropy of an area of interest. These measurements reflect the degree of anisotropy and lead to a better understanding of the area’s crack density and orientation or crystal alignment.We can think of the anisotropy of a particular area as a black box and the shear wave splitting measurements as a way of looking at what is in the box.