VII. Earthquake Mitigation
... If survivability is the goal, then engineering approaches and building codes are the main solution Reinforced buildings and bridges in earthquake prone areas Identify problem soils and avoid them, anchor foundations in bedrock or use foundation isolators Avoid building sites in areas prone to ...
... If survivability is the goal, then engineering approaches and building codes are the main solution Reinforced buildings and bridges in earthquake prone areas Identify problem soils and avoid them, anchor foundations in bedrock or use foundation isolators Avoid building sites in areas prone to ...
(Kyoshin Monitor) with earthquake early warning
... latest forecast, with the Kyoshin Monitor as the real observation is much important in mitigating earthquake damage. We have developed a new Kyoshin Monitor that can provide the combined information (hereafter referred to as the “Trial Version Kyoshin Monitor”). In this research, a social experiment ...
... latest forecast, with the Kyoshin Monitor as the real observation is much important in mitigating earthquake damage. We have developed a new Kyoshin Monitor that can provide the combined information (hereafter referred to as the “Trial Version Kyoshin Monitor”). In this research, a social experiment ...
3.0 Earthquake Resistant Structural Systems
... of transverse waves, therefore longitudinal waves are often called the primary waves (P-waves) and transverse waves are called the secondary waves (Swaves). Some typical values of the wave propagation velocities are shown in Table 2.1 (Tomaževič, 1999). The effects of earthquake ground motions on th ...
... of transverse waves, therefore longitudinal waves are often called the primary waves (P-waves) and transverse waves are called the secondary waves (Swaves). Some typical values of the wave propagation velocities are shown in Table 2.1 (Tomaževič, 1999). The effects of earthquake ground motions on th ...
Section 1 Review
... earthquake a mo~emen~ortrerT!bling of the the directi.on ·inwhich.the wave .i~traverini: .....•... :. ground that is caused.bya sudden release of energy when rocks along afault move shadow. zone an area on EarthrssUffacew~ere.;\: no. direct seismic wave~ frQm~. partkul~r ',:'.' ,.:.:. ...
... earthquake a mo~emen~ortrerT!bling of the the directi.on ·inwhich.the wave .i~traverini: .....•... :. ground that is caused.bya sudden release of energy when rocks along afault move shadow. zone an area on EarthrssUffacew~ere.;\: no. direct seismic wave~ frQm~. partkul~r ',:'.' ,.:.:. ...
File
... or pulling away from each other. This stress builds until the plates themselves break. When they break large amounts of energy is released in the form of waves. This release of energy from the stress built up in the crust is what we call Earthquakes. Earthquakes are caused by the release of stress t ...
... or pulling away from each other. This stress builds until the plates themselves break. When they break large amounts of energy is released in the form of waves. This release of energy from the stress built up in the crust is what we call Earthquakes. Earthquakes are caused by the release of stress t ...
Rare Video: Japan Tsunami
... This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. ...
... This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. ...
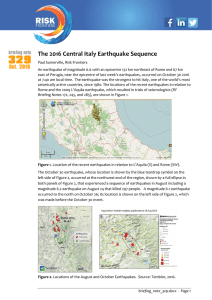
The 2016 Central Italy Earthquake Sequence
... in Italy’s southern toe, in 1783 when there were five major earthquakes of magnitude 6.5 or larger in less than two months. More recently, there were three earthquakes around Assisi in central Italy in 1997, the first one of magnitude 6.4 which killed 11 people, another the following day, and anothe ...
... in Italy’s southern toe, in 1783 when there were five major earthquakes of magnitude 6.5 or larger in less than two months. More recently, there were three earthquakes around Assisi in central Italy in 1997, the first one of magnitude 6.4 which killed 11 people, another the following day, and anothe ...
We used results of other geophysical surveys (shallow seismic
... cross a sandstone layer about 60–80 m thick and extract water from a confined aquifer in fractured zones between basalt flow layers (Cretaceous Serra Geral Formation of the intracratonic Paraná Basin); the basalt pack in this region is about ~500m thick. The activity occurs as swarms of events mostl ...
... cross a sandstone layer about 60–80 m thick and extract water from a confined aquifer in fractured zones between basalt flow layers (Cretaceous Serra Geral Formation of the intracratonic Paraná Basin); the basalt pack in this region is about ~500m thick. The activity occurs as swarms of events mostl ...
Principles of Geology
... The major branches of the travel-time curves carry the same descriptions as for shallow-focus events. Waves leaving the focus in an upward direction, and reflected at the surface are described by the letters p, s, as follows: ...
... The major branches of the travel-time curves carry the same descriptions as for shallow-focus events. Waves leaving the focus in an upward direction, and reflected at the surface are described by the letters p, s, as follows: ...
Plate tectonics NB Name
... statement best explains why this occurred? A. S waves are much weaker than P waves. B. S waves travel faster that P waves. C. The liquid outer core prevents the S waves from travelling to seismic stations C and D. D. The solid outer core prevents the S waves from travelling to seismic stations C and ...
... statement best explains why this occurred? A. S waves are much weaker than P waves. B. S waves travel faster that P waves. C. The liquid outer core prevents the S waves from travelling to seismic stations C and D. D. The solid outer core prevents the S waves from travelling to seismic stations C and ...
Seismic Waves and Earth`s Interior
... – The composition data obtained from seismic waves is supported by studies of meteorites. – Meteorites are pieces of asteroids, which are thought to have formed in much the same way and at the same time as the planets in our solar system. – Meteorites consist mostly of iron, nickel, and chunks of ro ...
... – The composition data obtained from seismic waves is supported by studies of meteorites. – Meteorites are pieces of asteroids, which are thought to have formed in much the same way and at the same time as the planets in our solar system. – Meteorites consist mostly of iron, nickel, and chunks of ro ...
hazards and threats: earthquakes terms and definitions
... An earthquake is the vibration, sometimes violent, of the Earth's surface that follows a release of energy in the Earth's crust. This energy can be generated by a sudden dislocation of segments of the crust, by a volcanic eruption, or event by manmade explosions. Most destructive quakes, however, ar ...
... An earthquake is the vibration, sometimes violent, of the Earth's surface that follows a release of energy in the Earth's crust. This energy can be generated by a sudden dislocation of segments of the crust, by a volcanic eruption, or event by manmade explosions. Most destructive quakes, however, ar ...
earthquakes
... and expands the ground • The first wave to arrive at an earthquake http://daphne.meccahosting.com/~a0000e89/insideearth2.htm ...
... and expands the ground • The first wave to arrive at an earthquake http://daphne.meccahosting.com/~a0000e89/insideearth2.htm ...
Earthquakes - Blountstown Middle School
... and expands the ground • The first wave to arrive at an earthquake http://daphne.meccahosting.com/~a0000e89/insideearth2.htm ...
... and expands the ground • The first wave to arrive at an earthquake http://daphne.meccahosting.com/~a0000e89/insideearth2.htm ...
HOUSING REPORT Uncoursed rubble stone masonry walls with
... The walls are constructed in a random uncoursed manner by using irregular stones bound with mud mortar. The stones are collected from quarries, riverbeds or fields, and are sometimes partially dressed. Space between the interior and exterior wythes is filled with stone rubble and mud. The joists and ...
... The walls are constructed in a random uncoursed manner by using irregular stones bound with mud mortar. The stones are collected from quarries, riverbeds or fields, and are sometimes partially dressed. Space between the interior and exterior wythes is filled with stone rubble and mud. The joists and ...
Baku forum Fuad - New Challenges in the European Area
... One of the most important aspects of seismic hazard estimation is the calculation of earthquake occurrence possibility with different intensity values in any place without indication of time, whenever any seismic event may take place (Riznichenko Yu. V., 1979). Such analyzes and calculations for Aze ...
... One of the most important aspects of seismic hazard estimation is the calculation of earthquake occurrence possibility with different intensity values in any place without indication of time, whenever any seismic event may take place (Riznichenko Yu. V., 1979). Such analyzes and calculations for Aze ...
Research Poster 36 x 48 - Western Oregon University
... •In efforts to reduce destruction, programs to augment public awareness are being implemented. ...
... •In efforts to reduce destruction, programs to augment public awareness are being implemented. ...
December 26, 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake & Tsunami
... This is the fourth largest earthquake in the world since 1900 and is the largest since the 1964 Prince William Sound, Alaska earthquake. The earthquake had a depth of 10 km ...
... This is the fourth largest earthquake in the world since 1900 and is the largest since the 1964 Prince William Sound, Alaska earthquake. The earthquake had a depth of 10 km ...
Earthquakes
... 3.5-5.4 Often felt, but rarely causes damage. Under 6.0 At most slight damage to well-designed buildings. Can cause major damage to poorly constructed buildings over small regions. 6.1-6.9 Can be destructive in areas up to about 100 kilometers across where people live. 7.0-7.9 Major earthquake. Can ...
... 3.5-5.4 Often felt, but rarely causes damage. Under 6.0 At most slight damage to well-designed buildings. Can cause major damage to poorly constructed buildings over small regions. 6.1-6.9 Can be destructive in areas up to about 100 kilometers across where people live. 7.0-7.9 Major earthquake. Can ...
Earthquakes
... plates could form. • The faults in the New Madrid Zone are remnants of this old event. Earthquakes occur because the North American Plate is still "settling down". The faults in the New Madrid Zone do not reach the Earth’s surface. They are buried beneath thousands of feet of rock and sediment depos ...
... plates could form. • The faults in the New Madrid Zone are remnants of this old event. Earthquakes occur because the North American Plate is still "settling down". The faults in the New Madrid Zone do not reach the Earth’s surface. They are buried beneath thousands of feet of rock and sediment depos ...
Answer the following questions. 1. What are Earthquakes
... The Pacific Ring of Fire is located around plate boundaries of moving plates in areas where major oceanic plates are undergoing subduction ( subduction is the process that takes ...
... The Pacific Ring of Fire is located around plate boundaries of moving plates in areas where major oceanic plates are undergoing subduction ( subduction is the process that takes ...
Earthquakes
... travel through the crust are called seismic waves. • A seismic wave starts with shaking caused by rocks scraping against each other. • This shaking results in several kinds of seismic waves. • The waves travel at different speeds. • Three kinds: – Primary Waves – P waves – Secondary Waves – S waves ...
... travel through the crust are called seismic waves. • A seismic wave starts with shaking caused by rocks scraping against each other. • This shaking results in several kinds of seismic waves. • The waves travel at different speeds. • Three kinds: – Primary Waves – P waves – Secondary Waves – S waves ...
Earthquakes
... cause devastation and kill thousands – mostly under collapsing buildings. By studying earthquake regions and damage, geoscientists help save lives – warning those at risk, showing them how to prepare and to protect themselves, and advising on the siting, design and construction of buildings. ...
... cause devastation and kill thousands – mostly under collapsing buildings. By studying earthquake regions and damage, geoscientists help save lives – warning those at risk, showing them how to prepare and to protect themselves, and advising on the siting, design and construction of buildings. ...
JANUARY 2013 — B.C. EARTHQUAKE SETTING THE STAGE On
... structural damage to water treatment plants and other major industries. It is also expected that a huge tsunami would be created by the earthquake, which would do further catastrophic damage of its own. ...
... structural damage to water treatment plants and other major industries. It is also expected that a huge tsunami would be created by the earthquake, which would do further catastrophic damage of its own. ...
Earthquake engineering

Earthquake engineering or Seismic engineering is a branch of engineering that searches for ways to make structures, such as buildings and bridges, resistant to earthquake damage. Earthquake engineer, better known as a seismic engineer aim to develop building techniques that will prevent any damage in a minor quake and avoid serious damage or collapse in a major shake. It is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural environment, and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels. Traditionally, it has been narrowly defined as the study of the behavior of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic loading; it is considered as a subset of both structural and geotechnical engineering. However, the tremendous costs experienced in recent earthquakes have led to an expansion of its scope to encompass disciplines from the wider field of civil engineering, mechanical engineering and from the social sciences, especially sociology, political science, economics and finance. The main objectives of earthquake engineering are: Foresee the potential consequences of strong earthquakes on urban areas and civil infrastructure. Design, construct and maintain structures to perform at earthquake exposure up to the expectations and in compliance with building codes.A properly engineered structure does not necessarily have to be extremely strong or expensive. It has to be properly designed to withstand the seismic effects while sustaining an acceptable level of damage.