Cl Cl and
... Too much energy is needed to remove 4 electrons from an atom. Too much energy is needed to insert 4 electrons into an atom in order to overcome the repulsive forces between like charges. 28. Why do elements of groups 6 and 7 form ions of charge –2 and –1 respectively? By gaining electrons they achie ...
... Too much energy is needed to remove 4 electrons from an atom. Too much energy is needed to insert 4 electrons into an atom in order to overcome the repulsive forces between like charges. 28. Why do elements of groups 6 and 7 form ions of charge –2 and –1 respectively? By gaining electrons they achie ...
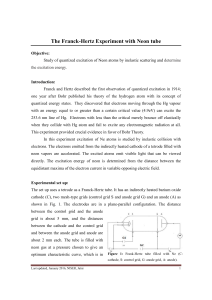
The Franck-Hertz Experiment with Neon tube
... one year after Bohr published his theory of the hydrogen atom with its concept of ...
... one year after Bohr published his theory of the hydrogen atom with its concept of ...
probability = ψ 2
... atom. Almost all of the mass in an atom is made up from the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the orbiting electrons. The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 1.6 fm (1.6 × 10−15 m) (for a proton in light hydrogen) to about 15 fm (for the heaviest atoms, ...
... atom. Almost all of the mass in an atom is made up from the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the orbiting electrons. The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 1.6 fm (1.6 × 10−15 m) (for a proton in light hydrogen) to about 15 fm (for the heaviest atoms, ...
CHEM1411,chapter 1-2-3 exercises 1. In 1828, the diameter of the
... 20. Commonly used gases in the laboratory are generally obtained from pressurized metal gas cylinders, but for small amounts of occasionally used gases, it is sometimes easier just to prepare them chemically as needed. For example, nitrogen monoxide, NO(g), can be prepared in the lab by the followin ...
... 20. Commonly used gases in the laboratory are generally obtained from pressurized metal gas cylinders, but for small amounts of occasionally used gases, it is sometimes easier just to prepare them chemically as needed. For example, nitrogen monoxide, NO(g), can be prepared in the lab by the followin ...
Grade 9 Chemistry Unit Test Name: Part A: Multiple Choice (15
... _____ 1. Which scientist is responsible for developing the scientific method? a) Francis Bacon b) Joseph Proust c) The Alchemists d) Antoine Lavoisier _____ 2. Which group of “scientists” was very hands-on, but also very secretive? a) Francis Bacon b) Joseph Proust c) The Alchemists d) Antoine Lavoi ...
... _____ 1. Which scientist is responsible for developing the scientific method? a) Francis Bacon b) Joseph Proust c) The Alchemists d) Antoine Lavoisier _____ 2. Which group of “scientists” was very hands-on, but also very secretive? a) Francis Bacon b) Joseph Proust c) The Alchemists d) Antoine Lavoi ...
Ionic bonding - Nidderdale High School
... move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up during the reaction. Different reactions need different catalysts. Catalysts are important in ...
... move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up during the reaction. Different reactions need different catalysts. Catalysts are important in ...
Document
... ii. Many of these symbols consist of the first letter or the first two letters of the element name. c. 3.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory i. In the early 1800’s English scientist John Dalton came up with an explanation of how atoms combine to form compounds. ii. Dalton’s atomic theory has five main points: ...
... ii. Many of these symbols consist of the first letter or the first two letters of the element name. c. 3.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory i. In the early 1800’s English scientist John Dalton came up with an explanation of how atoms combine to form compounds. ii. Dalton’s atomic theory has five main points: ...
PHYS150-Ch28
... intrinsic spin. It is useful to compare this to the Earth spinning on its axis. This cannot be truly what is happening since the surface of the electron would be traveling faster than the speed of light. ...
... intrinsic spin. It is useful to compare this to the Earth spinning on its axis. This cannot be truly what is happening since the surface of the electron would be traveling faster than the speed of light. ...
Honors Midterm - Stamford High School
... How much does a proton weigh? A neutron weigh? A electron weigh? ...
... How much does a proton weigh? A neutron weigh? A electron weigh? ...
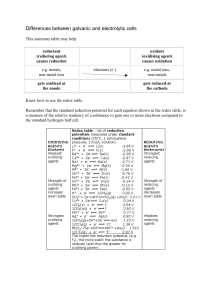
Differences between galvanic and electrolytic cells
... e.g. metal ions, non-metals gets reduced at the cathode ...
... e.g. metal ions, non-metals gets reduced at the cathode ...
2. Essential Chemistry
... o Element: a substance composed of only one type of atom (all the atoms have the same number of protons). o Molecule: a unit composed of two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds o Compound: a substance composed of 2 or more elements that have been joined by chemical bonds o Mixture: a com ...
... o Element: a substance composed of only one type of atom (all the atoms have the same number of protons). o Molecule: a unit composed of two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds o Compound: a substance composed of 2 or more elements that have been joined by chemical bonds o Mixture: a com ...
BONDS AND LEWIS STRUCTURES
... Polarity of Bonds Differences in electronegativity can be used to determine how polar a bond is between two atoms. If the difference in the electronegativities of the atoms is 0.5 or less, the bond is considered to be nonpolar covalent and the electron sharing is more or less equal. If the differenc ...
... Polarity of Bonds Differences in electronegativity can be used to determine how polar a bond is between two atoms. If the difference in the electronegativities of the atoms is 0.5 or less, the bond is considered to be nonpolar covalent and the electron sharing is more or less equal. If the differenc ...
Materials Science for Chemical Engineers
... The Electronic Structure of the Atom Electrons occupy discrete energy levels within the atom. The energy level to which each electron belongs is determined by 4 quantum numbers: The principal quantum number n (1, 2, 3, …) The azimuthal quantum number l The magnetic quantum number ml The spin quantu ...
... The Electronic Structure of the Atom Electrons occupy discrete energy levels within the atom. The energy level to which each electron belongs is determined by 4 quantum numbers: The principal quantum number n (1, 2, 3, …) The azimuthal quantum number l The magnetic quantum number ml The spin quantu ...
Chemistry (CP) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 7. a physical blend of two or more components ____ 8. part of a sample having uniform composition and properties ____ 9. not uniform in composition ____ 10. a substance formed in a chemical reaction ____ 11. starting substance in a chemical reaction Match each item with the correct statement be ...
... ____ 7. a physical blend of two or more components ____ 8. part of a sample having uniform composition and properties ____ 9. not uniform in composition ____ 10. a substance formed in a chemical reaction ____ 11. starting substance in a chemical reaction Match each item with the correct statement be ...
Electron-Config
... Subshell (l), s-p-d-f (Shapes) Within each principal energy level there are a certain number of sublevels Energy level 1 has 1 sublevel; energy level 2 has 2 sublevels; energy level 3 has 3 sublevels, etc. ...
... Subshell (l), s-p-d-f (Shapes) Within each principal energy level there are a certain number of sublevels Energy level 1 has 1 sublevel; energy level 2 has 2 sublevels; energy level 3 has 3 sublevels, etc. ...
- Department of Chemistry, York University
... - Electron density is thought to determine the rate of cloud collapse, and therefore of star formation. Molecular ion measurements can provide an assay of the degree of ionization and the electron density (and so insight into the rate of star formation). ...
... - Electron density is thought to determine the rate of cloud collapse, and therefore of star formation. Molecular ion measurements can provide an assay of the degree of ionization and the electron density (and so insight into the rate of star formation). ...
Covalent Bonds - WordPress.com
... • A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of only one pair of valence electrons • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons • The double bonds are stronger than s ...
... • A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of only one pair of valence electrons • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons • The double bonds are stronger than s ...
Note 1.1 Chemistry of Life
... Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are not found within the nucleus and do not contribute to the ...
... Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are not found within the nucleus and do not contribute to the ...
Electron Configuration
... Subshell (l), s-p-d-f (Shapes) Within each principal energy level there are a certain number of sublevels Energy level 1 has 1 sublevel; energy level 2 has 2 sublevels; energy level 3 has 3 sublevels, etc. ...
... Subshell (l), s-p-d-f (Shapes) Within each principal energy level there are a certain number of sublevels Energy level 1 has 1 sublevel; energy level 2 has 2 sublevels; energy level 3 has 3 sublevels, etc. ...
Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final
... 2. How many moles of sulfur dioxide will be produced when 6 moles of oxygen react completely? 3. What is the mole to mole ratio of… a. Dihydrogen sulfide to oxygen? b. Oxygen to water? c. Dihydrogen sulfide to sulfur dioxide? ...
... 2. How many moles of sulfur dioxide will be produced when 6 moles of oxygen react completely? 3. What is the mole to mole ratio of… a. Dihydrogen sulfide to oxygen? b. Oxygen to water? c. Dihydrogen sulfide to sulfur dioxide? ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.