Atomic Theory Review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Both Rutherford’s and Bohr’s models of the atom have a nucleus, which is an extremely small, dense region in the center of the atom, that contains most of the atom’s mass and all of its positive charge. Both models have negatively charged electrons orbiting the nucleus. The difference is that Bohr’s ...
... Both Rutherford’s and Bohr’s models of the atom have a nucleus, which is an extremely small, dense region in the center of the atom, that contains most of the atom’s mass and all of its positive charge. Both models have negatively charged electrons orbiting the nucleus. The difference is that Bohr’s ...
Atomic Theory Review
... Both Rutherford’s and Bohr’s models of the atom have a nucleus, which is an extremely small, dense region in the center of the atom, that contains most of the atom’s mass and all of its positive charge. Both models have negatively charged electrons orbiting the nucleus. The difference is that Bohr’s ...
... Both Rutherford’s and Bohr’s models of the atom have a nucleus, which is an extremely small, dense region in the center of the atom, that contains most of the atom’s mass and all of its positive charge. Both models have negatively charged electrons orbiting the nucleus. The difference is that Bohr’s ...
Reactions I Can..
... 10. Explain why some atomic nuclei are unstable 11. Predict the type of nuclear decay that will occur given the composition of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. 12. Balance a nuclear equation for both charge and mass. 13. Identify the source of energy in nuclear reactions. 14. Compare and contras ...
... 10. Explain why some atomic nuclei are unstable 11. Predict the type of nuclear decay that will occur given the composition of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. 12. Balance a nuclear equation for both charge and mass. 13. Identify the source of energy in nuclear reactions. 14. Compare and contras ...
Atoms
... 10. Explain why some atomic nuclei are unstable 11. Predict the type of nuclear decay that will occur given the composition of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. 12. Balance a nuclear equation for both charge and mass. 13. Identify the source of energy in nuclear reactions. 14. Compare and contras ...
... 10. Explain why some atomic nuclei are unstable 11. Predict the type of nuclear decay that will occur given the composition of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. 12. Balance a nuclear equation for both charge and mass. 13. Identify the source of energy in nuclear reactions. 14. Compare and contras ...
Excitations
... faster due to their higher energy E=ћ. The center of a wave packet moves with the group velocity vg . That determines how fast a signal pulse propagates. Solitons In a non-linear medium, the phase velocity depends on the amplitude. The spread of a wave packet due to dispersion can be compensated by ...
... faster due to their higher energy E=ћ. The center of a wave packet moves with the group velocity vg . That determines how fast a signal pulse propagates. Solitons In a non-linear medium, the phase velocity depends on the amplitude. The spread of a wave packet due to dispersion can be compensated by ...
Particle-Wave Duality
... Light as a Particle • We can now understand why electrons are ONLY emitted in the photoelectric effect * If the frequency of the light EXCEEDS some critical energy • Electrons are emitted from the metal surface by ABSORBING the energy of photons * A FINITE amount of energy must be absorbed to remov ...
... Light as a Particle • We can now understand why electrons are ONLY emitted in the photoelectric effect * If the frequency of the light EXCEEDS some critical energy • Electrons are emitted from the metal surface by ABSORBING the energy of photons * A FINITE amount of energy must be absorbed to remov ...
Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... Monatomic Ions: Ions formed from a single atom -Followed by the name “ion” -Cation combined with anion Binary Compounds: Compounds composed of 2 different elements -Drop ending of element name and add “ide” ...
... Monatomic Ions: Ions formed from a single atom -Followed by the name “ion” -Cation combined with anion Binary Compounds: Compounds composed of 2 different elements -Drop ending of element name and add “ide” ...
The de Broglie-Bohr Model for the Hydrogen Atom
... This figure shows that atomic stability involves a balance between potential and kinetic energy. The electron is drawn toward the nucleus by the attractive potential energy interaction (~ -1/R), but is prevented from collapsing into the nucleus by the extremely large kinetic energy (~1/R 2) associa ...
... This figure shows that atomic stability involves a balance between potential and kinetic energy. The electron is drawn toward the nucleus by the attractive potential energy interaction (~ -1/R), but is prevented from collapsing into the nucleus by the extremely large kinetic energy (~1/R 2) associa ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 2. An electron carries one unit of negative charge and its mass is about 1/1840 the mass of a hydrogen atom or 9.11 x 10-28g (more precisely, 9.10939 × 10–28 g); charge and mass of electron determined by Robert Millikan in 1916 B. Protons and Neutrons 1. Protons have a positive charge, cathode ray t ...
... 2. An electron carries one unit of negative charge and its mass is about 1/1840 the mass of a hydrogen atom or 9.11 x 10-28g (more precisely, 9.10939 × 10–28 g); charge and mass of electron determined by Robert Millikan in 1916 B. Protons and Neutrons 1. Protons have a positive charge, cathode ray t ...
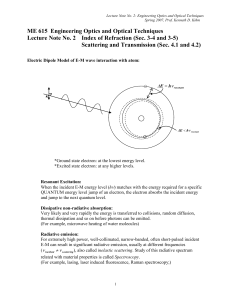
ME 615 Engineering Optics and Optical Techniques
... atoms/molecules at high altitude absorb most of UV coming from the outer space including the sun. This will make the survival of living cells on the earth ever possible. … What a God’s trick! The atom or molecules are called submicroscopic scatterers. No scattering exists in free space, because of ...
... atoms/molecules at high altitude absorb most of UV coming from the outer space including the sun. This will make the survival of living cells on the earth ever possible. … What a God’s trick! The atom or molecules are called submicroscopic scatterers. No scattering exists in free space, because of ...
Text S1.
... optimized at the HF/6-31G level of Quantum Mechanics (QM). All QM calculations were done by using the Gaussian simulation package 032. Molecular electrostatic potential for each conformer was calculated by using density functional theory (DFT) method B3LYP with the ccpVTZ basis set. The IEFPCM conti ...
... optimized at the HF/6-31G level of Quantum Mechanics (QM). All QM calculations were done by using the Gaussian simulation package 032. Molecular electrostatic potential for each conformer was calculated by using density functional theory (DFT) method B3LYP with the ccpVTZ basis set. The IEFPCM conti ...
BACH, the Beamline for Advanced diCHroic and scattering
... tool to study the electronic and magnetic properties of matter. These techniques have been applied to investigate the interplay between spin-orbit interaction, hybridization, exchange coupling and crystal field in a variety of systems showing exotic behaviors such as oscillatory coupling in multilay ...
... tool to study the electronic and magnetic properties of matter. These techniques have been applied to investigate the interplay between spin-orbit interaction, hybridization, exchange coupling and crystal field in a variety of systems showing exotic behaviors such as oscillatory coupling in multilay ...
Ch. 9
... • Most names end in –ite or –ate but some end in –ium or –ide • Some begin with a H so we say Hydrogen Phosphate for HPO4. The biprefix means: add H+ ions to the anion until its charge is -1, So H2PO4 is biphosphate and HCO3 is bicarbonate. • *9.1 sect. assessment pg. 258 ...
... • Most names end in –ite or –ate but some end in –ium or –ide • Some begin with a H so we say Hydrogen Phosphate for HPO4. The biprefix means: add H+ ions to the anion until its charge is -1, So H2PO4 is biphosphate and HCO3 is bicarbonate. • *9.1 sect. assessment pg. 258 ...
Polarization and Optical Properties of n-Layer Doped with Au Nanoparticles
... wavelength range and angle of incidence. In this paper, this subject is investigated. Multilayer structures that are periodical in their optical properties in one direction, have been known for a long time and represents more than a century old subject of investigation [1]. Most common applications ...
... wavelength range and angle of incidence. In this paper, this subject is investigated. Multilayer structures that are periodical in their optical properties in one direction, have been known for a long time and represents more than a century old subject of investigation [1]. Most common applications ...
BORH`S DERIVATION OF BALMER
... charged particles and was recognized as a remarkable triumph of the human intellect. However, the transition from one orbit to another, the quantum jump in zero time, as a necessary condition for radiation of energy, is a drawback on Bohr’s quantum theory. So also is the failure to relate the freque ...
... charged particles and was recognized as a remarkable triumph of the human intellect. However, the transition from one orbit to another, the quantum jump in zero time, as a necessary condition for radiation of energy, is a drawback on Bohr’s quantum theory. So also is the failure to relate the freque ...
Lecture 9 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... This was an enormous step towards the understanding of experimentally observed spectra of Hydrogen atom since it yielded the correct values for the energy levels (1/n2 dependence). In addition Bohr model correctly predicted the experimentally measured ionization energy (the energy which must be supp ...
... This was an enormous step towards the understanding of experimentally observed spectra of Hydrogen atom since it yielded the correct values for the energy levels (1/n2 dependence). In addition Bohr model correctly predicted the experimentally measured ionization energy (the energy which must be supp ...
Chapter 27
... The effect was first discovered by Hertz The successful explanation of the effect was given by Einstein in 1905 ...
... The effect was first discovered by Hertz The successful explanation of the effect was given by Einstein in 1905 ...
energy quantization
... Say we are given that y(x) satisfies y”(x) =2. This is called a second order differential equation as a second derivative enters the equation. What about this function y(x)? Also here there are many functions satisfying this requirement: e.g. y(x) =x2 , y(x) = x2+x+8 ,, y(x) = x2-5 etc. In general a ...
... Say we are given that y(x) satisfies y”(x) =2. This is called a second order differential equation as a second derivative enters the equation. What about this function y(x)? Also here there are many functions satisfying this requirement: e.g. y(x) =x2 , y(x) = x2+x+8 ,, y(x) = x2-5 etc. In general a ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.