A Michelson Interferometer-Based Method For Measuring The Angle
... The angle of rotation of a surface about its axis can be measured in a number of ways based on optical interferometry, internal-reflection of optical elements and fringe projectiont'° Each method has its advantages and limitations. For example, the method ofpoint-of-light triangulation is easy to pe ...
... The angle of rotation of a surface about its axis can be measured in a number of ways based on optical interferometry, internal-reflection of optical elements and fringe projectiont'° Each method has its advantages and limitations. For example, the method ofpoint-of-light triangulation is easy to pe ...
Interference 1 - schoolphysics
... beam reflects from the near end and part from the far end. When the two beams combine they show interference due to the path difference formed by travelling along the rod and back. The rod is now heated gently, the end nearest the laser being fixed and the other end being allowed to expand. It is fo ...
... beam reflects from the near end and part from the far end. When the two beams combine they show interference due to the path difference formed by travelling along the rod and back. The rod is now heated gently, the end nearest the laser being fixed and the other end being allowed to expand. It is fo ...
20170327_AH_Interference
... You’ll have met Young’s double slit experiment – landmark experiment proving light was a wave. You will also seen time when your image has been reflected in some glass and not in other, picture framers and opticians often sell their products as no reflective. This also uses interference and we’ll ex ...
... You’ll have met Young’s double slit experiment – landmark experiment proving light was a wave. You will also seen time when your image has been reflected in some glass and not in other, picture framers and opticians often sell their products as no reflective. This also uses interference and we’ll ex ...
HP unit 12 - wave optics student handout
... The camera on a spy satellite has a lens with a diameter of 1.5m. This satellite is in low earth orbit about 2.9x105m above the surface of the Earth. Determine the approximate size of the smallest feature the camera can resolve when taking a picture of something on the Earth's surface (assume blue ...
... The camera on a spy satellite has a lens with a diameter of 1.5m. This satellite is in low earth orbit about 2.9x105m above the surface of the Earth. Determine the approximate size of the smallest feature the camera can resolve when taking a picture of something on the Earth's surface (assume blue ...
Final Exam
... c) Now consider that a 1-mm glass slide (n = 1.52) is inserted behind the top slit. How much will the fringe pattern move along the y-axis? Is it going to move up or down? y ...
... c) Now consider that a 1-mm glass slide (n = 1.52) is inserted behind the top slit. How much will the fringe pattern move along the y-axis? Is it going to move up or down? y ...
Surface Plasmon Resonance
... - plasmons confined to surface (interface) and interact with light resulting in polaritons. - propagating electron density waves occurring at the interface between metal and dielectric. Surface Plasmon Resonance: - light () in resonance with surface plasmon oscillation ...
... - plasmons confined to surface (interface) and interact with light resulting in polaritons. - propagating electron density waves occurring at the interface between metal and dielectric. Surface Plasmon Resonance: - light () in resonance with surface plasmon oscillation ...
Michelson Interferometer
... diameter changes are observed. Similarly, move your eye left and right, and adjust the left-lower screw. Finally, perfectly ...
... diameter changes are observed. Similarly, move your eye left and right, and adjust the left-lower screw. Finally, perfectly ...
Optics and Optoelectronics
... ray and wave optics, physical optics phenomena, as well as raise understanding about the close connection between optics and electronics (1) Understanding of ray and and wave approximation used for description of optical phenomenon (2) Ability to solve problems in optics and optoelectronics using ma ...
... ray and wave optics, physical optics phenomena, as well as raise understanding about the close connection between optics and electronics (1) Understanding of ray and and wave approximation used for description of optical phenomenon (2) Ability to solve problems in optics and optoelectronics using ma ...
Michelson Interferometer
... 4. Turn the laser on and adjust the laser beam height using lab jack lifting knob until the beam is approximately parallel with the top of the interferometer and strikes the mirror at the centre. 5. Set the viewing screen opposite of the adjustable mirror M2. Note that the viewing screen should be p ...
... 4. Turn the laser on and adjust the laser beam height using lab jack lifting knob until the beam is approximately parallel with the top of the interferometer and strikes the mirror at the centre. 5. Set the viewing screen opposite of the adjustable mirror M2. Note that the viewing screen should be p ...
Diffraction and Interference * Learning Outcomes
... passing between the lines behaves as if it passed through slits (i.e. it diffracts). Gratings are usually described as having some number of lines per mm (e.g. 400 lines per mm). The distance between adjacent gaps, d is the ...
... passing between the lines behaves as if it passed through slits (i.e. it diffracts). Gratings are usually described as having some number of lines per mm (e.g. 400 lines per mm). The distance between adjacent gaps, d is the ...
Physics 116 Interference in gratings and thin films
... •! Ray reflected from top surface (air to glass): phase flip •! Ray reflected from 2nd surface (glass to air): no flip (Ray 1) •! Ray reflected from 3rd surface (air to glass): phase flip again (Ray 2) •! Suppose angle of incidence is nearly vertical –! so neglect the angle shown in drawing: Ray 2 t ...
... •! Ray reflected from top surface (air to glass): phase flip •! Ray reflected from 2nd surface (glass to air): no flip (Ray 1) •! Ray reflected from 3rd surface (air to glass): phase flip again (Ray 2) •! Suppose angle of incidence is nearly vertical –! so neglect the angle shown in drawing: Ray 2 t ...
Particles: Newton Waves: Huygens, Young, Fresnel
... Academie des Sciences for 1819, which was awarded for the best work on diffraction ; -- established the theory that light is a transverse wave; -- invented the Fresnel lens for lighthouses. ...
... Academie des Sciences for 1819, which was awarded for the best work on diffraction ; -- established the theory that light is a transverse wave; -- invented the Fresnel lens for lighthouses. ...
Ch14 Review
... Recognize how additive colors affect the color of light. Recognize how pigments affect the color of reflected light. Explain how linearly polarized light is formed and detected. Chapter 14 Key Ideas Light is electromagnetic radiation that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields ...
... Recognize how additive colors affect the color of light. Recognize how pigments affect the color of reflected light. Explain how linearly polarized light is formed and detected. Chapter 14 Key Ideas Light is electromagnetic radiation that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields ...
Solutions #2
... bottom edges. We must determine if it strikes a vertical face or the bottom face. We will calculate the lateral distance travelled when the vertical distance is equal to the length of one edge of the cube. The lateral displacement will be larger than half the length of one side = distance from the c ...
... bottom edges. We must determine if it strikes a vertical face or the bottom face. We will calculate the lateral distance travelled when the vertical distance is equal to the length of one edge of the cube. The lateral displacement will be larger than half the length of one side = distance from the c ...
PHE-09 (2007
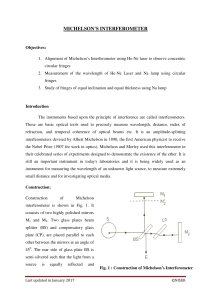
... ii) With the help of a diagram, explain the working of Michelson interferometer. State the conditions for obtaining (a) circular, and (b) localised fringes. Explain how Michelson interferometer can be used for determining the refractive index of a thin plate. ...
... ii) With the help of a diagram, explain the working of Michelson interferometer. State the conditions for obtaining (a) circular, and (b) localised fringes. Explain how Michelson interferometer can be used for determining the refractive index of a thin plate. ...
Michelson Interferometer
... small amount ∆λ, such as the orange-yellow sodium D lines, there will be two fringe systems superimposed which are very similar but not identical. For some mirror positions, where 2d is an integer number of wavelengths for both components, the fringes will coincide over a good range of θ and will lo ...
... small amount ∆λ, such as the orange-yellow sodium D lines, there will be two fringe systems superimposed which are very similar but not identical. For some mirror positions, where 2d is an integer number of wavelengths for both components, the fringes will coincide over a good range of θ and will lo ...
Surface waves
... Propagation of the wave requires k 2 > 0 thus, being ε1 ε2 < 0, we get the additional condition ε1 + ε2 < 0. g) Since ε2 < −ε1 = −1 must hold, we may choose a metal√(a free electron gas, or an ideal plasma) for which ε2 = 1 − ωp2 /ω 2 , and a frequency such that ωp > 2ω. The above described EM modes ...
... Propagation of the wave requires k 2 > 0 thus, being ε1 ε2 < 0, we get the additional condition ε1 + ε2 < 0. g) Since ε2 < −ε1 = −1 must hold, we may choose a metal√(a free electron gas, or an ideal plasma) for which ε2 = 1 − ωp2 /ω 2 , and a frequency such that ωp > 2ω. The above described EM modes ...
Ray Box Lab - Iona Physics
... To locate the focus and measure the focal length several optical components. ...
... To locate the focus and measure the focal length several optical components. ...
Youngs Double Slit
... The double slit slide has several sets of slits. Use black tape to leave one set of slits only. Set up the white light or white LED source on the optical bench. Bring the slit up close to the eye and view the light source. What do you see? The interference pattern can only occur when the light diffr ...
... The double slit slide has several sets of slits. Use black tape to leave one set of slits only. Set up the white light or white LED source on the optical bench. Bring the slit up close to the eye and view the light source. What do you see? The interference pattern can only occur when the light diffr ...
Wave Picture
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
Experiment 3 1 The Michelson Interferometer and the He
... The basic idea of a laser is illustrated in Fig. 3 where the energy levels of an atom are pictured. In the normal state, almost all of the atoms would be in their ground state, E1. If, on ...
... The basic idea of a laser is illustrated in Fig. 3 where the energy levels of an atom are pictured. In the normal state, almost all of the atoms would be in their ground state, E1. If, on ...
Unit 7 Lab Review - Harrison High School
... 6. Name the optical device that causes reflected light rays to converge. 7. Describe the image of an object far away when viewed through a convex lens. 8. In the index of refraction lab which test tube was hardest to see? Why? 9. How did the size of the slits affect the pattern created by the laser ...
... 6. Name the optical device that causes reflected light rays to converge. 7. Describe the image of an object far away when viewed through a convex lens. 8. In the index of refraction lab which test tube was hardest to see? Why? 9. How did the size of the slits affect the pattern created by the laser ...