INTERFERENCE
... Both of these involve splitting the light from a single source into two beams. Division of amplitude This involves splitting a single light beam into two beams, a reflected beam and a transmitted beam, at a surface between two media of different refractive index. ...
... Both of these involve splitting the light from a single source into two beams. Division of amplitude This involves splitting a single light beam into two beams, a reflected beam and a transmitted beam, at a surface between two media of different refractive index. ...
Analysing the potential for application of the phase shift method in
... grating gaps are generated by vibrating points situated on the same wave front, which means the presence of a constant phase difference between them). To provide opportunities for complete and accurate 3D mapping of the examined surface, the phase shift method makes use of a system of two diffractio ...
... grating gaps are generated by vibrating points situated on the same wave front, which means the presence of a constant phase difference between them). To provide opportunities for complete and accurate 3D mapping of the examined surface, the phase shift method makes use of a system of two diffractio ...
Interference
... fields add according to the superposition principle. If the two waves are in phase, they add constructively to produce a new wave with greater amplitude. If the two waves are 180° out of phase and have the same amplitude, they add destructively - the combined amplitude is zero. The result of adding ...
... fields add according to the superposition principle. If the two waves are in phase, they add constructively to produce a new wave with greater amplitude. If the two waves are 180° out of phase and have the same amplitude, they add destructively - the combined amplitude is zero. The result of adding ...
Slide
... number of parameters. One commonly used model is the Cauchy model. Best fit is determined through a regression algorithm, varying the values of the thickness and selected dispersion model parameters in the equation until the best correlation is obtained between theoretical and measured spectra. ...
... number of parameters. One commonly used model is the Cauchy model. Best fit is determined through a regression algorithm, varying the values of the thickness and selected dispersion model parameters in the equation until the best correlation is obtained between theoretical and measured spectra. ...
Machine Vision Systems as Shop Floor Metrology Tool
... seen along that particular angle, and potentially decide on which signals are the correct ones. Reflections that do not go along the view axis are not seen at all. The limitations of this approach can be more time consumed in seeking each point, and low light collection to maintain high angle separa ...
... seen along that particular angle, and potentially decide on which signals are the correct ones. Reflections that do not go along the view axis are not seen at all. The limitations of this approach can be more time consumed in seeking each point, and low light collection to maintain high angle separa ...
CT_optics
... A diffraction grating is illuminated with yellow light at normal incidence. The pattern seen on a screen behind the grating consists of three yellow spots, one at zero degrees (straight through) and one each at ±45°.You now add red light of equal intensity, coming in the same direction as the yello ...
... A diffraction grating is illuminated with yellow light at normal incidence. The pattern seen on a screen behind the grating consists of three yellow spots, one at zero degrees (straight through) and one each at ±45°.You now add red light of equal intensity, coming in the same direction as the yello ...
Slow light in room-temperature optical waveguides
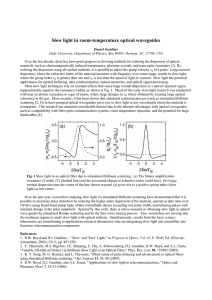
... Most slow light techniques rely on resonant effects that cause large normal dispersion in a narrow spectral region (approximately equal to the resonance width), as shown in Fig. 1. Much of the early slow-light research was conducted with near an atomic resonance in a gas of atoms, where large change ...
... Most slow light techniques rely on resonant effects that cause large normal dispersion in a narrow spectral region (approximately equal to the resonance width), as shown in Fig. 1. Much of the early slow-light research was conducted with near an atomic resonance in a gas of atoms, where large change ...
Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water
... 3. The wave number of the water waves can be determined by measuring the maxima of an interference pattern from the diffraction of the light off the surface of the water. 4. The air-water interface acts as a diffraction grating for the laser light. The experimental apparatus was set up as shown abov ...
... 3. The wave number of the water waves can be determined by measuring the maxima of an interference pattern from the diffraction of the light off the surface of the water. 4. The air-water interface acts as a diffraction grating for the laser light. The experimental apparatus was set up as shown abov ...
Review - misshoughton.net
... characteristics Using mirror and magnification equations appropriately 4. Refraction of Light Definition, properties, characteristics Index of refraction Dispersion 5. Partial Refraction and Total Internal Reflection Definition, properties, characteristics Large angles of incidence Cri ...
... characteristics Using mirror and magnification equations appropriately 4. Refraction of Light Definition, properties, characteristics Index of refraction Dispersion 5. Partial Refraction and Total Internal Reflection Definition, properties, characteristics Large angles of incidence Cri ...
Chapter 8 Wave Optics
... The results are involved in interferences and diffractions. It is known that for the interference of the double-slit, the fringes are equally bright. But when we consider the diffraction by a slit, the final pattern actually observed is a combination of both effects. The interference pattern locates ...
... The results are involved in interferences and diffractions. It is known that for the interference of the double-slit, the fringes are equally bright. But when we consider the diffraction by a slit, the final pattern actually observed is a combination of both effects. The interference pattern locates ...
Diffractive Optical Elements
... (2) Acrylate-on-polymer elements, the diffractive layer is created by UV curing on a polymer substrate (3) Acrylate-on-glass elements, the diffractive layer is created by UV curing on a glass substrate (4) Fused silica elements, the diffractive micro-relief surface is created by reactive ion etching ...
... (2) Acrylate-on-polymer elements, the diffractive layer is created by UV curing on a polymer substrate (3) Acrylate-on-glass elements, the diffractive layer is created by UV curing on a glass substrate (4) Fused silica elements, the diffractive micro-relief surface is created by reactive ion etching ...
Optical Interferometers
... cos θ cos θ Recalling that cos 2θ = 2(cos θ)2 − 1, we obtain ∆l = 2d cos θ. The two rays interfere constructively for any angle θc for which ∆l = 2d cos θ = mλ (m=integer); at the same time, two beams traveling at the angle θd interfere destructively when ∆l = 2d cos θ = (m + 1/2)λ (m=integer). Beca ...
... cos θ cos θ Recalling that cos 2θ = 2(cos θ)2 − 1, we obtain ∆l = 2d cos θ. The two rays interfere constructively for any angle θc for which ∆l = 2d cos θ = mλ (m=integer); at the same time, two beams traveling at the angle θd interfere destructively when ∆l = 2d cos θ = (m + 1/2)λ (m=integer). Beca ...
A new optical configuration in speckle interferometry for contouring
... configuration. Unlike the Leendertz configuration, the proposed configuration uses single beam illumination and dual directions of observation but the sensitivity is large and is equal to that of Leendertz’s method. In this configuration an object point is viewed symmetrically with respect to the su ...
... configuration. Unlike the Leendertz configuration, the proposed configuration uses single beam illumination and dual directions of observation but the sensitivity is large and is equal to that of Leendertz’s method. In this configuration an object point is viewed symmetrically with respect to the su ...
Wollaston and Nomarski Prisms
... prisms are composed of two precisely ground and polished wedge-shaped slabs produced from high-grade optical quartz, a uniaxial birefringent crystal. Two quartz wedges having perpendicular orientations of the optical axis must be fabricated to produce a single Wollaston (or Nomarski) prism. The wedg ...
... prisms are composed of two precisely ground and polished wedge-shaped slabs produced from high-grade optical quartz, a uniaxial birefringent crystal. Two quartz wedges having perpendicular orientations of the optical axis must be fabricated to produce a single Wollaston (or Nomarski) prism. The wedg ...
Young`s Double Slits
... Operational Hazard – Semiconductor laser diodes The two laser sources you will be using emit green and red visible light. Both are categorised as class 2 sources and thus defined to be eye safe (i.e. the human blink reflex will be sufficient to prevent damaging exposure), having a power output < 1mW ...
... Operational Hazard – Semiconductor laser diodes The two laser sources you will be using emit green and red visible light. Both are categorised as class 2 sources and thus defined to be eye safe (i.e. the human blink reflex will be sufficient to prevent damaging exposure), having a power output < 1mW ...
Reflecting And Refracting Light
... • We describe the path of light as straight-line rays • Reflection off a flat surface follows a simple rule: – angle in (incidence) equals angle out (reflection) – angles measured from surface “normal” (perpendicular) ...
... • We describe the path of light as straight-line rays • Reflection off a flat surface follows a simple rule: – angle in (incidence) equals angle out (reflection) – angles measured from surface “normal” (perpendicular) ...
11.1 law of reflection and curved mirrors
... mirror are reflected right back along the same path That means a point on your left side is reflected off the right side of the mirror – therefore making it look like the image is reversed when it returns to your eyes ...
... mirror are reflected right back along the same path That means a point on your left side is reflected off the right side of the mirror – therefore making it look like the image is reversed when it returns to your eyes ...
Nineteen Ways to do 3-Dimensional Imaging
... light, that is, from a laser, is split by a beamsplitter and directed both onto the scene and onto the reference surface. The scene is imaged onto an image sensor that is also illuminated by light from the reference surface. When an object in the scene moves, its speckle pattern changes and the inte ...
... light, that is, from a laser, is split by a beamsplitter and directed both onto the scene and onto the reference surface. The scene is imaged onto an image sensor that is also illuminated by light from the reference surface. When an object in the scene moves, its speckle pattern changes and the inte ...
el-1
... When a wave moves from one medium into another in which the light’s speed is different, the direction of the wave’s travel bends. The wavefronts remain continuous across the boundary between the two media. ...
... When a wave moves from one medium into another in which the light’s speed is different, the direction of the wave’s travel bends. The wavefronts remain continuous across the boundary between the two media. ...