Fibre Optics - Westmount High School
... In physics, the critical angle is described with respect to the normal line. In fibre optics, the critical angle is described with respect to the parallel axis running down the middle of the fibre. Therefore, the fibre-optic critical angle = (90 degrees - physics critical angle). ...
... In physics, the critical angle is described with respect to the normal line. In fibre optics, the critical angle is described with respect to the parallel axis running down the middle of the fibre. Therefore, the fibre-optic critical angle = (90 degrees - physics critical angle). ...
physics
... 8. The level of water in a clear colorless glass can be seen easily, but that of liquid helium cannot be. Why? 9. At what angle of incidence should a beam strike the glass slab of refractive index √3, such that the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other. 10. The sun looks reddi ...
... 8. The level of water in a clear colorless glass can be seen easily, but that of liquid helium cannot be. Why? 9. At what angle of incidence should a beam strike the glass slab of refractive index √3, such that the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other. 10. The sun looks reddi ...
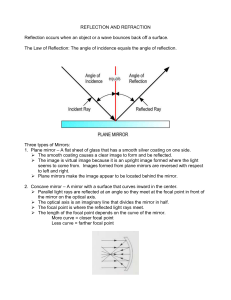
Plane Mirrors
... Homework: ALL answers must be written on looseleaf paper. No answers placed on this sheet will be accepted. 1) A plane mirror produces a real / virtual (choose one) image. This is known as the image’s TYPE. 2) A plane mirror produces an upright / inverted (choose one) image. This is known as the im ...
... Homework: ALL answers must be written on looseleaf paper. No answers placed on this sheet will be accepted. 1) A plane mirror produces a real / virtual (choose one) image. This is known as the image’s TYPE. 2) A plane mirror produces an upright / inverted (choose one) image. This is known as the im ...
Understanding Waves: Seismic Waves and Ultrasound
... reflects in all directions – DIFFUSE REFLECTION. • When light reflects from an even surface it’s all reflected at the same angle – CLEAR REFLECTION. • Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection ...
... reflects in all directions – DIFFUSE REFLECTION. • When light reflects from an even surface it’s all reflected at the same angle – CLEAR REFLECTION. • Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection ...
4.6 Optical Fibres
... interactive digital video and data channels. There are many types of optical fibre. This experiment uses polymer fibre with a core diameter of 1000microns (1mm). Long distance communication grade fibre is made of very pure silica and has a core diameter of 5 microns or less, about the same size as a ...
... interactive digital video and data channels. There are many types of optical fibre. This experiment uses polymer fibre with a core diameter of 1000microns (1mm). Long distance communication grade fibre is made of very pure silica and has a core diameter of 5 microns or less, about the same size as a ...
Reflection - TeacherWeb
... REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Reflection occurs when an object or a wave bounces back off a surface. The Law of Reflection: The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. ...
... REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Reflection occurs when an object or a wave bounces back off a surface. The Law of Reflection: The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. ...
Airway Luminal Diameter and Shape Measurement by Means of an
... perpendicular to the surface (dotted line) is reflected (up-trending arrow) away at the same angle θ. B, In diffuse reflection, light incident on the surface is reflected randomly in all directions (up-trending arrows). Date of download: 5/4/2017 ...
... perpendicular to the surface (dotted line) is reflected (up-trending arrow) away at the same angle θ. B, In diffuse reflection, light incident on the surface is reflected randomly in all directions (up-trending arrows). Date of download: 5/4/2017 ...
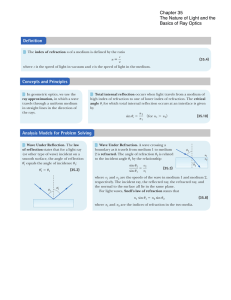
Ch. 35: Reflection and Refraction of Light
... Light propagates in straight lines (rays). This is valid as long as the light does not change the medium through which it propagates (air, water, glass, plastic), or finds an obstacle (interface). The velocity of light in air is c c = 3x108 m/s The velocity of light in other media may be different f ...
... Light propagates in straight lines (rays). This is valid as long as the light does not change the medium through which it propagates (air, water, glass, plastic), or finds an obstacle (interface). The velocity of light in air is c c = 3x108 m/s The velocity of light in other media may be different f ...
6.2 Refraction
... When the object is off-axis such that the ray bundle does not satisfy sinθ = θ, the rays impinging on the outer edge of the lens are focused ___________ from the optical axis than center rays. This is called coma and gives comet-shaped images. With an off-axis object the rays in the plane of the ima ...
... When the object is off-axis such that the ray bundle does not satisfy sinθ = θ, the rays impinging on the outer edge of the lens are focused ___________ from the optical axis than center rays. This is called coma and gives comet-shaped images. With an off-axis object the rays in the plane of the ima ...
To understand the basics of reflection and refraction
... will get all of these in different amounts. • 1) reflection – the light in essence bounces off of the surface. • In this case the angle which the light leaves is the same as it hits (θr = θi), as is the wavelength of light (in the perspective of the object it is ...
... will get all of these in different amounts. • 1) reflection – the light in essence bounces off of the surface. • In this case the angle which the light leaves is the same as it hits (θr = θi), as is the wavelength of light (in the perspective of the object it is ...
NOTES – Refraction of Light - Helpline for ICSE Students (Class 10)
... Have you ever thought why do stars twinkle??? Or do the stars really twinkle?? No, they don’t. They just appear to twinkle. Why?? Of course due to Refraction. Let’s discuss the same in detail. The light rays from the stars passes through layers of air of different densities. In other words it travel ...
... Have you ever thought why do stars twinkle??? Or do the stars really twinkle?? No, they don’t. They just appear to twinkle. Why?? Of course due to Refraction. Let’s discuss the same in detail. The light rays from the stars passes through layers of air of different densities. In other words it travel ...
Overview of Surface Plasmon Resonance
... refracted beam at the critical angle is shown in red. All light is reflected at incident angle greater than c. If a semitransparent noble metal film is placed at the interface (Figure 2), then under conditions of total internal reflection surface plasmon resonance can occur. This is commonly known ...
... refracted beam at the critical angle is shown in red. All light is reflected at incident angle greater than c. If a semitransparent noble metal film is placed at the interface (Figure 2), then under conditions of total internal reflection surface plasmon resonance can occur. This is commonly known ...
A new method for measuring the diffusivity of liquid binary mixtures
... number of smoothing routines is selected automatically, so that every line x i must have the same number of maxima and minima *2 with respect to x i - , , and the spatial frequency must not vary abruptly. In this way. the interferometric information is transferred to thinned skeletonized fringes. No ...
... number of smoothing routines is selected automatically, so that every line x i must have the same number of maxima and minima *2 with respect to x i - , , and the spatial frequency must not vary abruptly. In this way. the interferometric information is transferred to thinned skeletonized fringes. No ...
Image formation with broad bundles of rays
... Wave surfaces near O for rays passing through O are spheres. Same for O’. Wave surfaces are surfaces of constant phase. The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two given wave surfaces is the same. The total change in phase between the points O and O’ is the same ...
... Wave surfaces near O for rays passing through O are spheres. Same for O’. Wave surfaces are surfaces of constant phase. The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two given wave surfaces is the same. The total change in phase between the points O and O’ is the same ...
Optical Fiber communication
... used in Fiber-optic communications, which permits transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than other forms of communication. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are also immune to electromagnetic interference. ...
... used in Fiber-optic communications, which permits transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than other forms of communication. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are also immune to electromagnetic interference. ...
A list of some commonly used formulas in optics
... planes, H1, H2, at distances P1, P2 from the vertices of the lens, V1, V2. The two back focal lengths, BFL1 and BFL2, are measured from the vertices. The thin lens equations may be used, provided all quantities are measured from the principal planes. ...
... planes, H1, H2, at distances P1, P2 from the vertices of the lens, V1, V2. The two back focal lengths, BFL1 and BFL2, are measured from the vertices. The thin lens equations may be used, provided all quantities are measured from the principal planes. ...
PRACTICAL 10: Wavelength of Laser Light
... In 1801 Thomas Young was able to make a measurement of the wavelength of light using a two-slit experiment. Today you will try to reproduce this experiment using laser-light, which is monochromatic. Theory In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely spaced, narrow slit ...
... In 1801 Thomas Young was able to make a measurement of the wavelength of light using a two-slit experiment. Today you will try to reproduce this experiment using laser-light, which is monochromatic. Theory In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely spaced, narrow slit ...
Near-field optical micromanipulation
... micromanipulation • To guide a particle… particle trapped within E.W. above surface • To trap a particle… two counter propagating waves • Larger the particle size… easier to trap smaller the Brownian motion (high drag) higher polarizability (stronger trapping force) • Should be able to perform on th ...
... micromanipulation • To guide a particle… particle trapped within E.W. above surface • To trap a particle… two counter propagating waves • Larger the particle size… easier to trap smaller the Brownian motion (high drag) higher polarizability (stronger trapping force) • Should be able to perform on th ...
Document
... that will allow multiple users to work and interact. Perceptive Pixel’s technology is currently being utilized, in the form of the Multi-Touch Collaboration Wall. ...
... that will allow multiple users to work and interact. Perceptive Pixel’s technology is currently being utilized, in the form of the Multi-Touch Collaboration Wall. ...
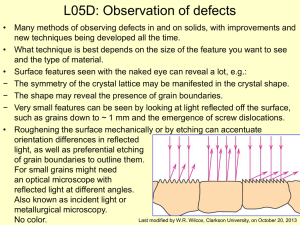
L05D - Clarkson University
... • Many methods of observing defects in and on solids, with improvements and new techniques being developed all the time. • What technique is best depends on the size of the feature you want to see and the type of material. • Surface features seen with the naked eye can reveal a lot, e.g.: − The symm ...
... • Many methods of observing defects in and on solids, with improvements and new techniques being developed all the time. • What technique is best depends on the size of the feature you want to see and the type of material. • Surface features seen with the naked eye can reveal a lot, e.g.: − The symm ...