To What Type of Logic Does the "Tetralemma" Belong?
... related to the distinction between what, using a different language, might have been called “positive” and “negative” propositions. Consider the (“unasserted”) propositions, A = “the electron is here” and Ā = “the electron is elsewhere”. A statement like “I see the electron here” is in some sense po ...
... related to the distinction between what, using a different language, might have been called “positive” and “negative” propositions. Consider the (“unasserted”) propositions, A = “the electron is here” and Ā = “the electron is elsewhere”. A statement like “I see the electron here” is in some sense po ...
Programming and Problem Solving with Java: Chapter 14
... Propositional Logic Propsitional logic is a logical system. It deals with propositions. Propositional Calculus is the language we use to reason about propositional logic. A sentence in propositional logic is called a well-formed formula (wff). ...
... Propositional Logic Propsitional logic is a logical system. It deals with propositions. Propositional Calculus is the language we use to reason about propositional logic. A sentence in propositional logic is called a well-formed formula (wff). ...
What is Time in Quantum Mechanics?
... “It thus seems, that the axioms about the time of arrival omit quite a number of physical aspects. It brings little comfort that they give a unique probability. On the contrary, it brings new difficulties.” Kijowski, in reply [24], essentially agreed with Mielnik: “... My construction of “arrival time ...
... “It thus seems, that the axioms about the time of arrival omit quite a number of physical aspects. It brings little comfort that they give a unique probability. On the contrary, it brings new difficulties.” Kijowski, in reply [24], essentially agreed with Mielnik: “... My construction of “arrival time ...
Title PI name/institution
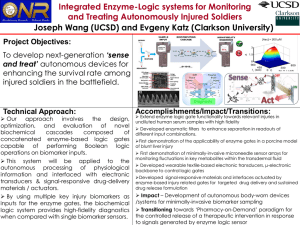
... Project Objectives: To develop next-generation ‘sense and treat’ autonomous devices for enhancing the survival rate among A) injured soldiers in the battlefield. B) ...
... Project Objectives: To develop next-generation ‘sense and treat’ autonomous devices for enhancing the survival rate among A) injured soldiers in the battlefield. B) ...
Quantum Mechanics
... Features of phase space trajectories (these are not particle coordinate trajectories in time) 1) Constants of motion do not change along a phase space trajectory (PST) 2) Isolated system moves in a small part of PST along which the constants of motion are fixed 3) Ergodic hypothesis: A trajectory p ...
... Features of phase space trajectories (these are not particle coordinate trajectories in time) 1) Constants of motion do not change along a phase space trajectory (PST) 2) Isolated system moves in a small part of PST along which the constants of motion are fixed 3) Ergodic hypothesis: A trajectory p ...
Quantum Field Theory
... high energies requires the use of special relativity. In some circumstances - think about elementary particle physics e.g. - one gets confronted with phenomena which simultaneously occur at high energies and small scales. The framework which unifies special relativity with quantum mechanics is relat ...
... high energies requires the use of special relativity. In some circumstances - think about elementary particle physics e.g. - one gets confronted with phenomena which simultaneously occur at high energies and small scales. The framework which unifies special relativity with quantum mechanics is relat ...
l - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... Erwin Schrodinger (mathematical equations using probability, quantum numbers) ...
... Erwin Schrodinger (mathematical equations using probability, quantum numbers) ...
Electron Configuration - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... Erwin Schrodinger (mathematical equations using probability, quantum numbers) ...
... Erwin Schrodinger (mathematical equations using probability, quantum numbers) ...
AtomicOrbitals_PeriodicTable
... returning to the n=2 level and are called the Balmer Series Another series of lines called the Lyman Series are due to electrons returning to the n=1 level. The DE values are higher and the lines appear in the ultra-violet region. ...
... returning to the n=2 level and are called the Balmer Series Another series of lines called the Lyman Series are due to electrons returning to the n=1 level. The DE values are higher and the lines appear in the ultra-violet region. ...
Quantum Fields in Curved Spacetime
... • The next order subtracts the constant in D0: the contribution to the effective action diverges at both small s and large s • This term modifies the IR so it is not a local term in the IR. • It is wrong to subtract it. ...
... • The next order subtracts the constant in D0: the contribution to the effective action diverges at both small s and large s • This term modifies the IR so it is not a local term in the IR. • It is wrong to subtract it. ...
Lecture 7: Why is Quantum Gravity so Hard?
... • Suppose we throw a hard drive with contents of Wikipedia into the black hole • After the black hole radiates away, where did all of the information go? • The problem is sharper than this. . . • The radiation is entangled with the particles that fall into the black hole • Missing information about ...
... • Suppose we throw a hard drive with contents of Wikipedia into the black hole • After the black hole radiates away, where did all of the information go? • The problem is sharper than this. . . • The radiation is entangled with the particles that fall into the black hole • Missing information about ...
Negative translation - Homepages of UvA/FNWI staff
... Excluded Middle ϕ ∨ ¬ϕ). However, the opposite point of view makes sense as well: one could also think of intuitionistic logic as an extension of classical logic. The reason for this is that there is a faithful copy of classical logic inside intuitionistic logic: such a copy is called a negative tra ...
... Excluded Middle ϕ ∨ ¬ϕ). However, the opposite point of view makes sense as well: one could also think of intuitionistic logic as an extension of classical logic. The reason for this is that there is a faithful copy of classical logic inside intuitionistic logic: such a copy is called a negative tra ...
PH302 Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
... Statistical mechanics is branch of physics that deals with understand collective response from the single particle behavior. This course explains how the statistical approach is effective in predicting the thermodynamics of system from the constituent particles. Methods of statistical mechanics are ...
... Statistical mechanics is branch of physics that deals with understand collective response from the single particle behavior. This course explains how the statistical approach is effective in predicting the thermodynamics of system from the constituent particles. Methods of statistical mechanics are ...
powerpoint
... Superposition creates regions of constructive and destructive diffraction according to the relative incidence of the waves. The light intensity is distributed by the square of the wave envelope: ...
... Superposition creates regions of constructive and destructive diffraction according to the relative incidence of the waves. The light intensity is distributed by the square of the wave envelope: ...
Fulltext
... the QD ensemble and figure 2b shows for the first time by us the red light filtered CL image. There is a clear distribution of sizes present, see regions shown inside the triangles. The larger particles show CL activity (e.g. region shown by the arrow in a and b and circled in c) but the smaller par ...
... the QD ensemble and figure 2b shows for the first time by us the red light filtered CL image. There is a clear distribution of sizes present, see regions shown inside the triangles. The larger particles show CL activity (e.g. region shown by the arrow in a and b and circled in c) but the smaller par ...
list of abstracts - Faculdade de Ciências
... Based on a family of indefinite unitary representations of the diffeomorphism group of an oriented smooth 4-manifold, a manifestly covariant 4dimensional and non-perturbative algebraic quantum field theory formulation of gravity is exhibited. More precisely among the bounded linear operators acting ...
... Based on a family of indefinite unitary representations of the diffeomorphism group of an oriented smooth 4-manifold, a manifestly covariant 4dimensional and non-perturbative algebraic quantum field theory formulation of gravity is exhibited. More precisely among the bounded linear operators acting ...
Quantum Gravity - General overview and recent developments
... Time, and therefore spacetime, have disappeared from the ...
... Time, and therefore spacetime, have disappeared from the ...