Photon Sidebands of the Ground State and First Excited State of a
... bias is applied between source and drain and the resulting dc source-drain current is measured. From standard dc measurements we find that the effective electron temperature is approximately T 200 mK and the charging energy Ec 1.2 6 0.1 meV. We independently determine the level splitting D´ for ...
... bias is applied between source and drain and the resulting dc source-drain current is measured. From standard dc measurements we find that the effective electron temperature is approximately T 200 mK and the charging energy Ec 1.2 6 0.1 meV. We independently determine the level splitting D´ for ...
Show all work – Homework 5 –
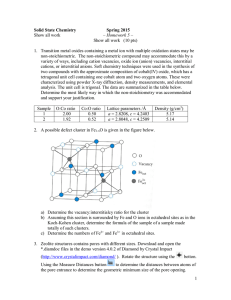
... 1. Transition metal oxides containing a metal ion with multiple oxidation states may be non-stoichiometric. The non-stoichiometric compound may accommodate this by a variety of ways, including cation vacancies, oxide ion (anion) vacancies, interstitial cations, or interstitial anions. Soft chemistry ...
... 1. Transition metal oxides containing a metal ion with multiple oxidation states may be non-stoichiometric. The non-stoichiometric compound may accommodate this by a variety of ways, including cation vacancies, oxide ion (anion) vacancies, interstitial cations, or interstitial anions. Soft chemistry ...
Exploring the Interatomic Forces between Tip and Single Molecules
... Because the driving force of the manipulation is directional and depends on both the tip height and bias voltage, the process is likely driven by the electric field in the junction. It is known that electric-field-induced forces come into play when working with an STM:12 Electric-field-induced diffu ...
... Because the driving force of the manipulation is directional and depends on both the tip height and bias voltage, the process is likely driven by the electric field in the junction. It is known that electric-field-induced forces come into play when working with an STM:12 Electric-field-induced diffu ...
Instrumental Methods of Analysis
... plot of weight change v/s temp.or time,which is known as TG curve. Weight should plotted on Y-axis,and temp.or time on X-axis,increasing from left to right. ...
... plot of weight change v/s temp.or time,which is known as TG curve. Weight should plotted on Y-axis,and temp.or time on X-axis,increasing from left to right. ...
`Cutoff Frequency` of Quantum-Dot Single-Electron Pump - e-SI-Amp
... is a promising candidate for the quantum current standard [1]-[3]. In order to obtain 10−8 level accuracy with a single electron pump [4], either precision measurement technique is to be improved or the output level of a pump must be increased at least with an order of magnitude. The simplest way to ...
... is a promising candidate for the quantum current standard [1]-[3]. In order to obtain 10−8 level accuracy with a single electron pump [4], either precision measurement technique is to be improved or the output level of a pump must be increased at least with an order of magnitude. The simplest way to ...
Conroy2005-SurfaceMetrology.pdf
... entire instrument. An essential component in the SPM is a sensor with very high spatial resolution. These sensors can routinely sense height changes as small as 0.1 ångstrom. Two common types of sensors are tunneling sensors (STM) and force sensors (AFM). STM uses a tunneling sensor to measure the c ...
... entire instrument. An essential component in the SPM is a sensor with very high spatial resolution. These sensors can routinely sense height changes as small as 0.1 ångstrom. Two common types of sensors are tunneling sensors (STM) and force sensors (AFM). STM uses a tunneling sensor to measure the c ...
Voltage-dependent conductance states of a single
... simultaneously recorded (figure 2(a)). It grows exponentially in the tunnelling region as expected. A sharp increase from ∼0.06 to ∼0.78 µA signals the transition to contact. Once contact to the molecule was established, the STM feedback loop was disabled and current–time (I(t)) traces were recorded ...
... simultaneously recorded (figure 2(a)). It grows exponentially in the tunnelling region as expected. A sharp increase from ∼0.06 to ∼0.78 µA signals the transition to contact. Once contact to the molecule was established, the STM feedback loop was disabled and current–time (I(t)) traces were recorded ...
Cornil Jerome - Lancaster University
... amplified [1]. Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the origin of the NDR signal and are still hotly debated. In this contribution, we demonstrate on the basis of quantum-chemical calculations that the incorporation of saturated spacers [2] or the introduction of ring twists [3] along co ...
... amplified [1]. Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the origin of the NDR signal and are still hotly debated. In this contribution, we demonstrate on the basis of quantum-chemical calculations that the incorporation of saturated spacers [2] or the introduction of ring twists [3] along co ...
paper - HPCS 2003
... The transmission coefficient obtained from Eq.(6) is presented on Fig.2 as a function of the electron energy E for three different bias voltages at zero gate potential. The sharp peak in T (E, Vb ) is the result of a resonance transmission through the LUMO of the C60 . At zero bias, this resonance l ...
... The transmission coefficient obtained from Eq.(6) is presented on Fig.2 as a function of the electron energy E for three different bias voltages at zero gate potential. The sharp peak in T (E, Vb ) is the result of a resonance transmission through the LUMO of the C60 . At zero bias, this resonance l ...
ppt
... The inset schematically shows the size and displacement of the electron from the GaSb (shaded region) for (a) WL, (b) QD under low intensity illumination and (c) QD under high intensity illumination. The number of holes in (b) and (c) are intended to signify a greater or lesser occupation, rather t ...
... The inset schematically shows the size and displacement of the electron from the GaSb (shaded region) for (a) WL, (b) QD under low intensity illumination and (c) QD under high intensity illumination. The number of holes in (b) and (c) are intended to signify a greater or lesser occupation, rather t ...
Photon mapping of individual Ag particles on MgO/Mo(001)
... at 1.65 eV that does not only appear on the cluster edges but also on the bare MgO relates to radiative electron transitions via field-emission resonances in front of the surface, as discussed before.24 The other two bands are assigned to the in-plane (2.1 eV) and out-of-plane Ag plasmon modes (2.75 ...
... at 1.65 eV that does not only appear on the cluster edges but also on the bare MgO relates to radiative electron transitions via field-emission resonances in front of the surface, as discussed before.24 The other two bands are assigned to the in-plane (2.1 eV) and out-of-plane Ag plasmon modes (2.75 ...
Live Cell Heating Option Components
... This is a flowmeter (on the left) for the CO2 input. This requires premixed 5% CO2, or whatever gas mixture desired. On the right is the humidifier that the gas will flow through prior to coming into contact with the sample. ...
... This is a flowmeter (on the left) for the CO2 input. This requires premixed 5% CO2, or whatever gas mixture desired. On the right is the humidifier that the gas will flow through prior to coming into contact with the sample. ...
Chapter 9 - Lecture 1
... • Particle is not free • ∴ For acceptable ψ, boundary conditions must be set: • ψ must vanish at x = 0 and x = L ...
... • Particle is not free • ∴ For acceptable ψ, boundary conditions must be set: • ψ must vanish at x = 0 and x = L ...
Appendix I.
... comparison to a light microscope. The SEM also has a superior magnification of approximately x100,000. The electrons are typically generated by a thermal emission source (such as a tungsten filament) and are accelerated to a higher energy at the operating voltage. ...
... comparison to a light microscope. The SEM also has a superior magnification of approximately x100,000. The electrons are typically generated by a thermal emission source (such as a tungsten filament) and are accelerated to a higher energy at the operating voltage. ...
Ballistic Transport in a two-dimensional Electron System
... Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is not only the material of choice for producing highfrequency electronic semiconductor devices (e.g. the High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT)) used in wireless telecommunications, it also plays an important role in basic research on semiconductors. In particular, combini ...
... Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is not only the material of choice for producing highfrequency electronic semiconductor devices (e.g. the High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT)) used in wireless telecommunications, it also plays an important role in basic research on semiconductors. In particular, combini ...
Document
... obtained by combining the results of a number of impurity configurations. Right: The 11th to 16th eigenstates of the silicon quantum dot. S. N. Milicic, D. Vasileska, R. Akis, A. Gunther, and S. M Goodnick, "Discrete impurity effects in silicon quantum dots," Proceedings of the 3rd International Con ...
... obtained by combining the results of a number of impurity configurations. Right: The 11th to 16th eigenstates of the silicon quantum dot. S. N. Milicic, D. Vasileska, R. Akis, A. Gunther, and S. M Goodnick, "Discrete impurity effects in silicon quantum dots," Proceedings of the 3rd International Con ...
Optically triggered spin entanglement of electrons
... Schrödinger-like and quantum jump part due to Heff and i Li ρL†i , respectively, which, within the spirit of Boltzmann’s equation, can be considered as generalized out- and in-scatterings. At each instant of time ρ can then be written as a mixture of two parts, P ...
... Schrödinger-like and quantum jump part due to Heff and i Li ρL†i , respectively, which, within the spirit of Boltzmann’s equation, can be considered as generalized out- and in-scatterings. At each instant of time ρ can then be written as a mixture of two parts, P ...
A study of laser-induced self
... A sharp tip is scanned over the sample surface the tip is maintained at a constant force (to obtain height information), or height (to obtain force information) above the sample surface Tips are typically made from Si3N4 or Si, and extended down from the end of a cantilever An optical detect ...
... A sharp tip is scanned over the sample surface the tip is maintained at a constant force (to obtain height information), or height (to obtain force information) above the sample surface Tips are typically made from Si3N4 or Si, and extended down from the end of a cantilever An optical detect ...
Imaging scanning tunneling microscope
... shown that scanning tunneling microscope 共STM兲-electroluminescence, the radiative decay of SPs induced by inelastically tunneling electrons, observed in Fourier space yields distinct features that reflect the degree of delocalization and spatial distribution of SP modes. The propagating SP is isolat ...
... shown that scanning tunneling microscope 共STM兲-electroluminescence, the radiative decay of SPs induced by inelastically tunneling electrons, observed in Fourier space yields distinct features that reflect the degree of delocalization and spatial distribution of SP modes. The propagating SP is isolat ...
Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy
... There were two IR lasers used to provide the illuminated IR light necessary in s-SNOM. The first is a CO2 gas laser which emits light with a wavelength of around 10.6 µm. The second is called a Quantum Cascade Laser (QCL) and uses a series of semiconductors stacked on one another to tunnel electron ...
... There were two IR lasers used to provide the illuminated IR light necessary in s-SNOM. The first is a CO2 gas laser which emits light with a wavelength of around 10.6 µm. The second is called a Quantum Cascade Laser (QCL) and uses a series of semiconductors stacked on one another to tunnel electron ...
Tunneling spectroscopy of disordered two
... features that are shown to vanish for temperatures significantly smaller than the energy gap VC00 . Our model reproduces this strong temperature dependence: besides the trivial broadening of the Fermi function in the metal gate, temperature also affects the occupation of states in the 2DEG. Since th ...
... features that are shown to vanish for temperatures significantly smaller than the energy gap VC00 . Our model reproduces this strong temperature dependence: besides the trivial broadening of the Fermi function in the metal gate, temperature also affects the occupation of states in the 2DEG. Since th ...
5.33 Lecture Notes: Introduction to Spectroscopy
... Spectroscopy is a general methodology that can be adapted in many ways to extract the information you need (energies of electronic, vibrational, rotational states, structure and symmetry of molecules, dynamic information). Goals: • Understand how light interacts with matter and how you can use this ...
... Spectroscopy is a general methodology that can be adapted in many ways to extract the information you need (energies of electronic, vibrational, rotational states, structure and symmetry of molecules, dynamic information). Goals: • Understand how light interacts with matter and how you can use this ...
Photoelectric effect
... the lamp passes through a grating monochromator, which can be adjusted to emit a beam of light at any wavelength from 350-700nm (and its higher energy harmonics - if you don’t know why, remind yourself how a diffraction grating works). The light then passes through a chopper that is connected to a ...
... the lamp passes through a grating monochromator, which can be adjusted to emit a beam of light at any wavelength from 350-700nm (and its higher energy harmonics - if you don’t know why, remind yourself how a diffraction grating works). The light then passes through a chopper that is connected to a ...
Analytical Expressions and Numerical simulation of single electron
... 5. Effects beyond the Orthodox Theory regime Our simulation above is largely based on the orthodox theory, which doesn’t take account of some important effects. In the Coulomb blockade regime, where the first order tunnel rate is very low, conduction is dominated by cotunneling processes. Second ord ...
... 5. Effects beyond the Orthodox Theory regime Our simulation above is largely based on the orthodox theory, which doesn’t take account of some important effects. In the Coulomb blockade regime, where the first order tunnel rate is very low, conduction is dominated by cotunneling processes. Second ord ...
Scanning tunneling spectroscopy

Scanning tunneling spectroscopy (STS), an extension of scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), is used to provide information about the density of electrons in a sample as a function of their energy.In scanning tunneling microscopy, a metal tip is moved over a conducting sample without making mechanical contact. A bias voltage between the sample and tip allows a current to flow between the tip and the sample even though they are not in contact. This can occur because of quantum mechanical tunneling, hence the name of the instrument.The scanning tunneling microscope is used to obtain ""topographs"" - topographic maps - of surfaces. The tip is rastered across a surface and (in constant current mode), a constant current is maintained between the tip and the sample by adjusting the height of the tip. A plot of the tip height at all measurement positions on the raster provides the topograph. These topographic images can obtain information that is atomically resolved, and images of metal and semiconductor surfaces can be obtained with atomic precision.However, the scanning tunneling microscope does not measure the height of surface features. This can be shown when a molecule is adsorbed on a surface. The STM image may appear to have either increased or decreased height at that feature, although the geometry alone is certainly an increased height. A detailed analysis of the way in which an image is formed shows that the transmission of the electric current between the tip and the sample depends on two factors: (1) the geometry of the sample and (2) the arrangement of the electrons in the sample. The arrangement of the electrons in the sample is described quantum mechanically by an ""electron density"". The electron density is a function of both position and energy, and is formally described as the local density of electron states, abbreviated as local density of states (LDOS), which is a function of energy.Spectroscopy, in its most general sense, refers to a measurement of the number of something as a function of energy. For scanning tunneling spectroscopy the scanning tunneling microscope is used to measure the number of electrons (the LDOS) as a function of the electron energy. The electron energy is set by the electrical potential difference (voltage) between the sample and the tip. The location is set by the position of the tip.At its simplest, a ""scanning tunneling spectrum"" is obtained by placing a scanning tunneling microscope tip above a particular place on the sample. With the height of the tip fixed, the electron tunneling current is then measured as a function of electron energy by varying the voltage between the tip and the sample (the tip to sample voltage sets the electron energy). The change of the current with the energy of the electrons is the simplest spectrum that can be obtained, it is often referred to as an I-V curve. As is shown below, it is the slope of the I-V curve at each voltage (often called the dI/dV-curve) which is more fundamental because dI/dV corresponds to the electron density of states at the local position of the tip, the LDOS.