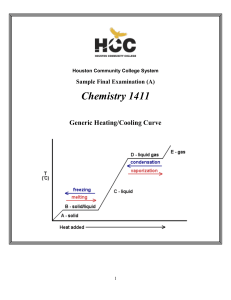
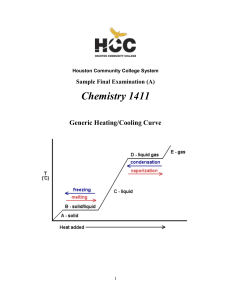
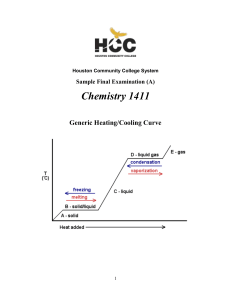
Basic Chemical Concepts I
... H2O. Find its molecular formula if its molar mass has been determined to be 116.2 g molG1. ...
... H2O. Find its molecular formula if its molar mass has been determined to be 116.2 g molG1. ...
Basic Chemical Concepts I
... Calculate the molar concentration of the solute in the following solutions: (a) 12.42 g of HCl dissolved in enough H2O to make 250.0 mL of solution (b) 3.618 g of Cd(NO3)2 dissolved in enough H2O to make 2.000 L of solution. ...
... Calculate the molar concentration of the solute in the following solutions: (a) 12.42 g of HCl dissolved in enough H2O to make 250.0 mL of solution (b) 3.618 g of Cd(NO3)2 dissolved in enough H2O to make 2.000 L of solution. ...
Reaction Energy
... 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g) + 483.6 kJ • The expression above is an example of a thermochemical equation, an equation that includes the quantity of energy released or absorbed as heat during the reaction as written. • Chemical coefficients in a thermochemical equation should be interpreted as numbers o ...
... 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g) + 483.6 kJ • The expression above is an example of a thermochemical equation, an equation that includes the quantity of energy released or absorbed as heat during the reaction as written. • Chemical coefficients in a thermochemical equation should be interpreted as numbers o ...
Chem 1B Fa2015 FinalExam Review
... order rate law, such that: Rate = k[N2O5]. When the reaction was carried out at a certain temperature using an initial concentration [N2O5]0 = 0.100 M, the concentration of N2O5 after 5.00 minutes (300 seconds) was found to be 0.0125 M. (a) Determine the rate constant k (s–1) for the above reaction. ...
... order rate law, such that: Rate = k[N2O5]. When the reaction was carried out at a certain temperature using an initial concentration [N2O5]0 = 0.100 M, the concentration of N2O5 after 5.00 minutes (300 seconds) was found to be 0.0125 M. (a) Determine the rate constant k (s–1) for the above reaction. ...
Kinetics and Mechanism of Uncatalyzed and Ag (I) Catalyzed
... The concentration of cerium (IV) was varied from 4.3×10-4 to 2.4×10-3 mol dm-3 at fixed concentration of Hydroxylysine (LysOH)=1.0×10-2 mol dm-3 and [H+]=1.0 mol dm-3 for uncatalyzed reaction. Pseudo first order plots were made, and pseudo first order rate constant (kʹ) were found to be independent ...
... The concentration of cerium (IV) was varied from 4.3×10-4 to 2.4×10-3 mol dm-3 at fixed concentration of Hydroxylysine (LysOH)=1.0×10-2 mol dm-3 and [H+]=1.0 mol dm-3 for uncatalyzed reaction. Pseudo first order plots were made, and pseudo first order rate constant (kʹ) were found to be independent ...
Multiple Choice Math Practice File
... (raw score) (Raw score) x 0.95 = _________________ (weighted MC score) The following statement is at the top of the multiple choice section…please be familiar with the symbols used on the test. Note: For all questions, assume that the temperature is 298 K, the pressure is 1.00 atmospheres and soluti ...
... (raw score) (Raw score) x 0.95 = _________________ (weighted MC score) The following statement is at the top of the multiple choice section…please be familiar with the symbols used on the test. Note: For all questions, assume that the temperature is 298 K, the pressure is 1.00 atmospheres and soluti ...
LABORATORY MANUAL CHEMISTRY 121
... g) of trans-[Co(en)2Cl2]Cl, and dissolve them in separate test tubes each containing 8.0 mL of icecold 1 M sulfuric acid, then place these and all following solutions in an ice bath. With a pipet transfer exactly 2 mL (save the rest for the next part) from each of these solutions to separate test tu ...
... g) of trans-[Co(en)2Cl2]Cl, and dissolve them in separate test tubes each containing 8.0 mL of icecold 1 M sulfuric acid, then place these and all following solutions in an ice bath. With a pipet transfer exactly 2 mL (save the rest for the next part) from each of these solutions to separate test tu ...
Chp 5 Circle the correct answer Consider three 1
... d) No, ΔE never equals zero because work is always being done on the system or by the system. ...
... d) No, ΔE never equals zero because work is always being done on the system or by the system. ...
Student Review Packet
... Similar concentrations of a weak acid and its conjugate base -orSimilar concentrations of a weak base and its conjugate acid If these concentrations are large in comparison to SMALL amounts of added acid or base, equilibrium will be shifted slightly and the pH change resisted. Consider: HA H+ + A- ...
... Similar concentrations of a weak acid and its conjugate base -orSimilar concentrations of a weak base and its conjugate acid If these concentrations are large in comparison to SMALL amounts of added acid or base, equilibrium will be shifted slightly and the pH change resisted. Consider: HA H+ + A- ...
Gas Laws
... A mixture in which the particles can only be seen with a laser and do NOT settle out upon standing is called a colloid. The amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent at a given temperature is described as solubility. Due to the fact that so many substances dissolve in water, water has been ...
... A mixture in which the particles can only be seen with a laser and do NOT settle out upon standing is called a colloid. The amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent at a given temperature is described as solubility. Due to the fact that so many substances dissolve in water, water has been ...
Gas Laws
... A mixture in which the particles can only be seen with a laser and do NOT settle out upon standing is called a colloid. The amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent at a given temperature is described as solubility. Due to the fact that so many substances dissolve in water, water has been ...
... A mixture in which the particles can only be seen with a laser and do NOT settle out upon standing is called a colloid. The amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent at a given temperature is described as solubility. Due to the fact that so many substances dissolve in water, water has been ...
1994 AP Chemistry Multiple Choice
... 37. A sample of 3.30 grams of an ideal gas at 150.0_C and 1.25 atmospheres pressure has a volume of 2.00 liters. What is the molar mass of the gas? The gas constant, R, is 0.0821 (L.atm)/(mol.K). (A) 0.0218 gram/mole (B) 16.2 grams/mole (C) 37.0 grams/mole (D) 45.8 grams/mole (E) 71.6 grams/mole 38 ...
... 37. A sample of 3.30 grams of an ideal gas at 150.0_C and 1.25 atmospheres pressure has a volume of 2.00 liters. What is the molar mass of the gas? The gas constant, R, is 0.0821 (L.atm)/(mol.K). (A) 0.0218 gram/mole (B) 16.2 grams/mole (C) 37.0 grams/mole (D) 45.8 grams/mole (E) 71.6 grams/mole 38 ...
m5zn_1ed95c16cede0b1
... Acidic solutions are those having [H+] > 1 x 10-7 or [OH-] < 1 x 10-7 Basic solution are those having [OH-] > 1 x 10-7 or [H+] < 1 x 10-7 A neutral solution must have [H+] = = 7.00 The pH of solution is the negative logarithm of the hydronium ion concentration. That is: pH = - log[H+] Hence if H+ co ...
... Acidic solutions are those having [H+] > 1 x 10-7 or [OH-] < 1 x 10-7 Basic solution are those having [OH-] > 1 x 10-7 or [H+] < 1 x 10-7 A neutral solution must have [H+] = = 7.00 The pH of solution is the negative logarithm of the hydronium ion concentration. That is: pH = - log[H+] Hence if H+ co ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya NKJ Katni
... 16. Why SO2 is a better reducing agent in alkaline medium as compared to that in acidic medium ? Explain. ...
... 16. Why SO2 is a better reducing agent in alkaline medium as compared to that in acidic medium ? Explain. ...
CHEM-1411 Final Practice Exam
... Sample CHEM 1411Final Exam (B) –Answers PART – I (2 POINTS EACH) 1. B 2. C 3. E 4. B (P1V1/T1) = (P2V2/T2) (P1V1/T1) = (3P1V2/2T1) V2 = 2/3 V1 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. B Ma = ( nbMbVb / naVa) Ma = ( 25x0.75x1)/ (1x150) Ma = 0.125 M 9. E 10. C 11. D 12. D M = mRT/PV (2.56x0.0821x295)/(753/760)x(1 ...
... Sample CHEM 1411Final Exam (B) –Answers PART – I (2 POINTS EACH) 1. B 2. C 3. E 4. B (P1V1/T1) = (P2V2/T2) (P1V1/T1) = (3P1V2/2T1) V2 = 2/3 V1 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. B Ma = ( nbMbVb / naVa) Ma = ( 25x0.75x1)/ (1x150) Ma = 0.125 M 9. E 10. C 11. D 12. D M = mRT/PV (2.56x0.0821x295)/(753/760)x(1 ...
1411FINALSAMPLE+KEY - Houston Community College
... Sample CHEM 1411Final Exam (B) –Answers PART – I (2 POINTS EACH) 1. B 2. C 3. E 4. B (P1V1/T1) = (P2V2/T2) (P1V1/T1) = (3P1V2/2T1) V2 = 2/3 V1 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. B Ma = ( nbMbVb / naVa) Ma = ( 25x0.75x1)/ (1x150) Ma = 0.125 M 9. E 10. C 11. D 12. D M = mRT/PV (2.56x0.0821x295)/(753/760)x(1 ...
... Sample CHEM 1411Final Exam (B) –Answers PART – I (2 POINTS EACH) 1. B 2. C 3. E 4. B (P1V1/T1) = (P2V2/T2) (P1V1/T1) = (3P1V2/2T1) V2 = 2/3 V1 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. B Ma = ( nbMbVb / naVa) Ma = ( 25x0.75x1)/ (1x150) Ma = 0.125 M 9. E 10. C 11. D 12. D M = mRT/PV (2.56x0.0821x295)/(753/760)x(1 ...
Chapter 04
... Fe(NO3)2(aq) with Na2CO3(aq). Solution: Step 1: Write and balance the molecular equation, predicting the products by assuming that the cations trade anions; checking the solubility of ...
... Fe(NO3)2(aq) with Na2CO3(aq). Solution: Step 1: Write and balance the molecular equation, predicting the products by assuming that the cations trade anions; checking the solubility of ...
Energetics - chemistryatdulwich
... size of ion: the smaller the ion , the larger the electrostatic attraction and the more energy is needed to sublime the ions. charge of the ion: the larger the charge, the greater the electrostatic attraction. The smaller the ionic radius and the greater the charge of the ion the greater the charg ...
... size of ion: the smaller the ion , the larger the electrostatic attraction and the more energy is needed to sublime the ions. charge of the ion: the larger the charge, the greater the electrostatic attraction. The smaller the ionic radius and the greater the charge of the ion the greater the charg ...
Examination - SCSA - School Curriculum and Standards Authority
... The following 1.00 mol L–1 solutions are diluted by the addition of water. In which solution will the pH not change but the electrical conductivity will decrease? (a) (b) (c) (d) ...
... The following 1.00 mol L–1 solutions are diluted by the addition of water. In which solution will the pH not change but the electrical conductivity will decrease? (a) (b) (c) (d) ...
Basic Organic Chemistry Laboratory Course
... Aliphatic compounds burn in air with a yellow, nearly smokeless flame, while aromatic compounds show a yellow, strongly sooting flame. In general one can say that the larger the degree of unsaturation of a certain compound, the sootier its flame. The test is carried out by burning a small amount o ...
... Aliphatic compounds burn in air with a yellow, nearly smokeless flame, while aromatic compounds show a yellow, strongly sooting flame. In general one can say that the larger the degree of unsaturation of a certain compound, the sootier its flame. The test is carried out by burning a small amount o ...
Unit 3: Thermochemistry
... exothermic reaction - the energy required to break bonds is less than the energy released when bonds form. ie. energy is produced ...
... exothermic reaction - the energy required to break bonds is less than the energy released when bonds form. ie. energy is produced ...
1411FINALSAMPLEs and Key
... Sample CHEM 1411Final Exam (B) –Answers PART – I (2 POINTS EACH) 1. B 2. C 3. E 4. B (P1V1/T1) = (P2V2/T2) (P1V1/T1) = (3P1V2/2T1) V2 = 2/3 V1 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. B Ma = ( nbMbVb / naVa) Ma = ( 25x0.75x1)/ (1x150) Ma = 0.125 M 9. E 10. C 11. D 12. D M = mRT/PV (2.56x0.0821x295)/(753/760)x(1 ...
... Sample CHEM 1411Final Exam (B) –Answers PART – I (2 POINTS EACH) 1. B 2. C 3. E 4. B (P1V1/T1) = (P2V2/T2) (P1V1/T1) = (3P1V2/2T1) V2 = 2/3 V1 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. B Ma = ( nbMbVb / naVa) Ma = ( 25x0.75x1)/ (1x150) Ma = 0.125 M 9. E 10. C 11. D 12. D M = mRT/PV (2.56x0.0821x295)/(753/760)x(1 ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... a score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the "Blue Book" should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing materials including scratch paper should be turned in and kept secure until April 28, 2014, after which tests can be returned to students ...
... a score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the "Blue Book" should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing materials including scratch paper should be turned in and kept secure until April 28, 2014, after which tests can be returned to students ...
Stoichiometry - VernonScienceLSA
... Problem Calculate the [H2PO4] if 23.46 mL of 0.750 M KOH is required to titrate 15.00 mL of H3PO4 according to the reaction: H3PO4 + 3KOH K3PO4 + 3H2O Solution ___________________________________________ ...
... Problem Calculate the [H2PO4] if 23.46 mL of 0.750 M KOH is required to titrate 15.00 mL of H3PO4 according to the reaction: H3PO4 + 3KOH K3PO4 + 3H2O Solution ___________________________________________ ...
Thermometric titration

A thermometric titration is one of a number of instrumental titration techniques where endpoints can be located accurately and precisely without a subjective interpretation on the part of the analyst as to their location. Enthalpy change is arguably the most fundamental and universal property of chemical reactions, so the observation of temperature change is a natural choice in monitoring their progress. It is not a new technique, with possibly the first recognizable thermometric titration method reported early in the 20th century (Bell and Cowell, 1913). In spite of its attractive features, and in spite of the considerable research that has been conducted in the field and a large body of applications that have been developed; it has been until now an under-utilized technique in the critical area of industrial process and quality control. Automated potentiometric titration systems have pre-dominated in this area since the 1970s. With the advent of cheap computers able to handle the powerful thermometric titration software, development has now reached the stage where easy to use automated thermometric titration systems can in many cases offer a superior alternative to potentiometric titrimetry.The applications of thermometric titrimetry discussed on this page are by no means exhaustive. The reader is referred to the bibliography for further reading on the subject.