Distributed Temperature Sensing Using Stimulated
... an optical coupler. Light signals of different frequencies experience different phase delays after passing through the same fiber. These phase differences depend on the locations of the sensing FBGs and can be measured with the help of interference. This way wavelength-sensitive devices are not requ ...
... an optical coupler. Light signals of different frequencies experience different phase delays after passing through the same fiber. These phase differences depend on the locations of the sensing FBGs and can be measured with the help of interference. This way wavelength-sensitive devices are not requ ...
Plasmonic Metamaterials
... layer is small.37 Interestingly, for the high-frequency, antisymmetric SPP mode (between the surface plasmon resonance frequency and the bulk plasmon frequency), the dispersion curve exhibits negative slope, leading to negative group velocity ( v g d dk ). In contrast, the phase velocity ( v p ...
... layer is small.37 Interestingly, for the high-frequency, antisymmetric SPP mode (between the surface plasmon resonance frequency and the bulk plasmon frequency), the dispersion curve exhibits negative slope, leading to negative group velocity ( v g d dk ). In contrast, the phase velocity ( v p ...
labs for the photon/photon2 experiment kit
... We can learn a lot about a light source by studying its spectrum. For example, the spectrum of the sun is composed of a complete “rainbow” crossed by dark lines due to absorption of certain wavelengths by the sun’s atmosphere. An excited gas at low pressure produces an emission spectrum, bright line ...
... We can learn a lot about a light source by studying its spectrum. For example, the spectrum of the sun is composed of a complete “rainbow” crossed by dark lines due to absorption of certain wavelengths by the sun’s atmosphere. An excited gas at low pressure produces an emission spectrum, bright line ...
Chapter 2 - Handbook of Optics
... The phase difference changes by 2π every time the OPD increases by a wavelength. The OPD is therefore constant along a fringe. Constructiy e interference occurs when the two waves are in phase, and a bright fringe or maximum in the intensity pattern results. This corresponds to a phase difference of ...
... The phase difference changes by 2π every time the OPD increases by a wavelength. The OPD is therefore constant along a fringe. Constructiy e interference occurs when the two waves are in phase, and a bright fringe or maximum in the intensity pattern results. This corresponds to a phase difference of ...
Part 2 . Physical Optics
... The phase difference changes by 2π every time the OPD increases by a wavelength. The OPD is therefore constant along a fringe. Constructiy e interference occurs when the two waves are in phase, and a bright fringe or maximum in the intensity pattern results. This corresponds to a phase difference of ...
... The phase difference changes by 2π every time the OPD increases by a wavelength. The OPD is therefore constant along a fringe. Constructiy e interference occurs when the two waves are in phase, and a bright fringe or maximum in the intensity pattern results. This corresponds to a phase difference of ...
Practical Notes: Tropical Bacteriology
... Many bacteria secrete around themselves a polysaccharide substance often referred to as a slime layer. This may become sufficiently thick to form a definite capsule around de organism. This capsule increases the pathogenicity of an organism by resistance against phagocytosis by host cells. Special t ...
... Many bacteria secrete around themselves a polysaccharide substance often referred to as a slime layer. This may become sufficiently thick to form a definite capsule around de organism. This capsule increases the pathogenicity of an organism by resistance against phagocytosis by host cells. Special t ...
Light manipulation with encoded plasmonic nanostructures Chenglong Zhao , Jiasen Zhang
... powerful approach for controlling both the field profile and the polarization state of free-space propagating light. It is striking that both the 2D and free-space propagating light can be well controlled by encoding 2D metallic surfaces with nanostructures of varying geometries, termed as metasurfa ...
... powerful approach for controlling both the field profile and the polarization state of free-space propagating light. It is striking that both the 2D and free-space propagating light can be well controlled by encoding 2D metallic surfaces with nanostructures of varying geometries, termed as metasurfa ...
Recent advances in transformation optics
... such as illusion optics,27–30 optical black holes,31–34 beam shifters and rotators,35–37 lossless waveguide bends38–41 as well as various lenses42–50 have been proposed. In particular, combining the concept of complementary medium51 with transformation optics, Yang et al. proposed a superscatter whi ...
... such as illusion optics,27–30 optical black holes,31–34 beam shifters and rotators,35–37 lossless waveguide bends38–41 as well as various lenses42–50 have been proposed. In particular, combining the concept of complementary medium51 with transformation optics, Yang et al. proposed a superscatter whi ...
Recent advances in transformation optics
... to be concealed, since there is no diffracted or scattered light in the presence of the object. Full-wave simulations without geometric optics approximation also verify the cloaking effect.7 It is worth mentioning that different approaches have been proposed to realize invisibility cloaks. One examp ...
... to be concealed, since there is no diffracted or scattered light in the presence of the object. Full-wave simulations without geometric optics approximation also verify the cloaking effect.7 It is worth mentioning that different approaches have been proposed to realize invisibility cloaks. One examp ...
optical properties of biaxial minerals
... Sections cut r to Optic Axes: These sections appear isotropic when viewed orthoscopically. Under conoscopic examination there appears only one hyperbola if 2V is not too small. In these sections one of the optic axis of the biaxial mineral is aligned parallel to the optic axis of the microscope and ...
... Sections cut r to Optic Axes: These sections appear isotropic when viewed orthoscopically. Under conoscopic examination there appears only one hyperbola if 2V is not too small. In these sections one of the optic axis of the biaxial mineral is aligned parallel to the optic axis of the microscope and ...
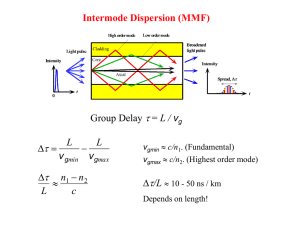
Waveguide Dispersion
... Consider a graded index fiber with a core diameter of 30 mm and a refractive index of 1.474 at the center of the core and a cladding refractive index of 1.453. Suppose that we use a laser diode emitter with a spectral linewidth of 3 nm to transmit along this fiber at a wavelength of 1300 nm. Calcula ...
... Consider a graded index fiber with a core diameter of 30 mm and a refractive index of 1.474 at the center of the core and a cladding refractive index of 1.453. Suppose that we use a laser diode emitter with a spectral linewidth of 3 nm to transmit along this fiber at a wavelength of 1300 nm. Calcula ...
Nanomechanical Motion Transducers for Miniaturized
... torsional structures—and the linear dimensions of the device as well as the device material. The stress field within the structure, either intrinsic or induced externally, also affects f r and γ, and can thus be used for tuning [25–27]. 1.2. Operation and Transducers The operation and applications o ...
... torsional structures—and the linear dimensions of the device as well as the device material. The stress field within the structure, either intrinsic or induced externally, also affects f r and γ, and can thus be used for tuning [25–27]. 1.2. Operation and Transducers The operation and applications o ...
Nanomechanical Motion Transducers for Miniaturized
... torsional structures—and the linear dimensions of the device as well as the device material. The stress field within the structure, either intrinsic or induced externally, also affects f r and γ, and can thus be used for tuning [25–27]. 1.2. Operation and Transducers The operation and applications o ...
... torsional structures—and the linear dimensions of the device as well as the device material. The stress field within the structure, either intrinsic or induced externally, also affects f r and γ, and can thus be used for tuning [25–27]. 1.2. Operation and Transducers The operation and applications o ...
Optical Fibres in Communications
... 2. Introduction:Optical fibers are arguably one of the world’s most influential scientific developments from the latter half of the 20th century. Normally we are unaware that we are using them, although many of us do frequently. The majority of telephone calls and internet traffic at some stage in ...
... 2. Introduction:Optical fibers are arguably one of the world’s most influential scientific developments from the latter half of the 20th century. Normally we are unaware that we are using them, although many of us do frequently. The majority of telephone calls and internet traffic at some stage in ...
Sample Chapter
... buffer and outer jacket. This design of fibre is light and has a very low loss, making it ideal for the transmission of information over long distances. light in a Fibre The light propagates along the fibre by the process of total internal reflection. The light is contained within the glass core and ...
... buffer and outer jacket. This design of fibre is light and has a very low loss, making it ideal for the transmission of information over long distances. light in a Fibre The light propagates along the fibre by the process of total internal reflection. The light is contained within the glass core and ...
Chapter 30 The Law of Reflection
... light travels in a straight line. The wavelength of light is so small that in a relatively short distance away from the point source of light, the waves appear plane. Even if the source of light is not a point, when we are sufficiently far away from the source, the waves are effectively plane. In al ...
... light travels in a straight line. The wavelength of light is so small that in a relatively short distance away from the point source of light, the waves appear plane. Even if the source of light is not a point, when we are sufficiently far away from the source, the waves are effectively plane. In al ...
Towards noninvasive glucose sensing using
... hLi in turbid media is a difficult quantity to define, quantify, and measure, and really represents a statistical distribution metric of a variety of photon paths that depend in a complex way on tissue optical properties and measurement geometry, (iii) other optically active chiral species are prese ...
... hLi in turbid media is a difficult quantity to define, quantify, and measure, and really represents a statistical distribution metric of a variety of photon paths that depend in a complex way on tissue optical properties and measurement geometry, (iii) other optically active chiral species are prese ...
1 Fundamental Optics www.cvimellesgriot.com
... The process of solving virtually any optical engineering problem can be broken down into two main steps. First, paraxial calculations (first order) are made to determine critical parameters such as magnification, focal length(s), clear aperture (diameter), and object and image position. These paraxi ...
... The process of solving virtually any optical engineering problem can be broken down into two main steps. First, paraxial calculations (first order) are made to determine critical parameters such as magnification, focal length(s), clear aperture (diameter), and object and image position. These paraxi ...
d - s3.amazonaws.com
... Newtonian and Cassegrainian reflecting telescopes are the styles most of the astronomical telescopes use for the reason that it is possible to make very large reflecting mirrors to high surface quality. Hale 200 inch (5.08 m) at Mt. Palomar. Keck 10 m effective diameter from 36 segments at Mauna Kea ...
... Newtonian and Cassegrainian reflecting telescopes are the styles most of the astronomical telescopes use for the reason that it is possible to make very large reflecting mirrors to high surface quality. Hale 200 inch (5.08 m) at Mt. Palomar. Keck 10 m effective diameter from 36 segments at Mauna Kea ...
Novel applications of Photonic Force Microscopy Giovanni Volpe
... The ability of detecting forces and torques at the micro- and nano-scale is fundamental. When this Thesis started, various scanning probe techniques had already been developed to probe the mechanical properties of microsystems. In 1993 Ghislain and coworkers devised a new scanning force microscopy u ...
... The ability of detecting forces and torques at the micro- and nano-scale is fundamental. When this Thesis started, various scanning probe techniques had already been developed to probe the mechanical properties of microsystems. In 1993 Ghislain and coworkers devised a new scanning force microscopy u ...
Limits of lithography - Proceedings of the IEEE
... pass. In other words, resolution performance can be doubled in principle since the aperture of the lens now must cover the zero and one of the first diffracted orders, whereas in a conventional system the aperture covers the span of the 1 to 1 orders. In practice, however, this method is limited by ...
... pass. In other words, resolution performance can be doubled in principle since the aperture of the lens now must cover the zero and one of the first diffracted orders, whereas in a conventional system the aperture covers the span of the 1 to 1 orders. In practice, however, this method is limited by ...
High-performance holographic technologies for fluid
... their dynamics. Reliable quantification of such turbulent processes appears to be a formidable experimental task. Current flow-diagnostics technologies restrict application to nearly canonical flows, whereas there is a substantial need, in both practical applications and validation of new theoretical a ...
... their dynamics. Reliable quantification of such turbulent processes appears to be a formidable experimental task. Current flow-diagnostics technologies restrict application to nearly canonical flows, whereas there is a substantial need, in both practical applications and validation of new theoretical a ...
ANALOG SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR OPTICAL COHERENCE
... personally and professionally. I am grateful for the trust, encouragement and support that she has given me in the past 3.5 years. I would also like to thank her for providing me with the opportunities, which were necessary in order for me to grow as an analog IC designer. I would like to express my ...
... personally and professionally. I am grateful for the trust, encouragement and support that she has given me in the past 3.5 years. I would also like to thank her for providing me with the opportunities, which were necessary in order for me to grow as an analog IC designer. I would like to express my ...
Chromatic Dispersion in optical Communications
... parameter reached was Q=18. BER values for the both methods are again very small and the program did not display them. Note On long links over 300 km, we can also meet with a symmetrical full compensation method of chromatic dispersion. The principle of this compensation is an application of DCF fib ...
... parameter reached was Q=18. BER values for the both methods are again very small and the program did not display them. Note On long links over 300 km, we can also meet with a symmetrical full compensation method of chromatic dispersion. The principle of this compensation is an application of DCF fib ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.