Paraxial Optics
... the longitudinal size of the objects, images, and constructive parameters of the optical systems. For an imageforming system, it corresponds with the ideal status where the system can be considered as perfect. Geometrical optics uses the advantages of the paraxial approach to provide a first-order d ...
... the longitudinal size of the objects, images, and constructive parameters of the optical systems. For an imageforming system, it corresponds with the ideal status where the system can be considered as perfect. Geometrical optics uses the advantages of the paraxial approach to provide a first-order d ...
Composite optical vortices - RIT Center for Imaging Science
... carries orbital angular momentum.12 In general, when one beam is superimposed with another, the phase of the composite field differs from that of the component beams. Being a topological phase structure, an optical vortex is readily affected when it is combined with other fields. The new or ‘‘compos ...
... carries orbital angular momentum.12 In general, when one beam is superimposed with another, the phase of the composite field differs from that of the component beams. Being a topological phase structure, an optical vortex is readily affected when it is combined with other fields. The new or ‘‘compos ...
Paper - University of Queensland
... animals, these photosensitive cells detect different wavelengths of light through pigmented cells, resulting in color vision. In other animals, integration of microvilli above the photosensitive cells has allowed polarization-sensitive vision. A variety of electronic sensors have been developed to m ...
... animals, these photosensitive cells detect different wavelengths of light through pigmented cells, resulting in color vision. In other animals, integration of microvilli above the photosensitive cells has allowed polarization-sensitive vision. A variety of electronic sensors have been developed to m ...
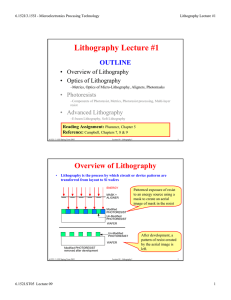
Lithography Lecture #1
... – Direct contact to mask results in mask damage, particulates and defects ...
... – Direct contact to mask results in mask damage, particulates and defects ...
Analysis And Design Of Wide-angle Foveated Optical
... optimization of fast wide-angle FOSs based on the current transmissive LC SLM technology. The amplitude and phase diffraction effects caused by the pixelated aperture of the SLM are explained and quantified, revealing fundamental limitations imposed by the current transmissive LC SLM technology. As ...
... optimization of fast wide-angle FOSs based on the current transmissive LC SLM technology. The amplitude and phase diffraction effects caused by the pixelated aperture of the SLM are explained and quantified, revealing fundamental limitations imposed by the current transmissive LC SLM technology. As ...
Representation of Wavefront Aberrations
... In everyday life we measure distances in physical units of meters. However, in optics it is common to measure distances with a ruler that is calibrated in wavelengths of light. Such a ruler effectively measures the number of times light must oscillate in traveling from the object to the image. If al ...
... In everyday life we measure distances in physical units of meters. However, in optics it is common to measure distances with a ruler that is calibrated in wavelengths of light. Such a ruler effectively measures the number of times light must oscillate in traveling from the object to the image. If al ...
Monte Carlo Simulation of Light Scattering on a Sound Wave
... confocal imaging. While effective, these spatial techniques may have difficulty rejecting light that has been multiply scattered back into the ballistic direction. The time domain technique requires expensive short–pulse laser and fast light detectors [4]. It has been shown that ballistic imaging is ...
... confocal imaging. While effective, these spatial techniques may have difficulty rejecting light that has been multiply scattered back into the ballistic direction. The time domain technique requires expensive short–pulse laser and fast light detectors [4]. It has been shown that ballistic imaging is ...
Holographic Fabrication of Designed Functional Defect Lines in
... defects will modify the photonic lattice near the defects. After we fully understand the phase-related lattice shift and compare them in five-beam interference patterns with those in three-beam interference patterns (Sections 3–5), we design and realize functional defects that can be registered in t ...
... defects will modify the photonic lattice near the defects. After we fully understand the phase-related lattice shift and compare them in five-beam interference patterns with those in three-beam interference patterns (Sections 3–5), we design and realize functional defects that can be registered in t ...
Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Fiber-Optic Bio-Sensors
... based mainly on SiO2. They are Single-Mode—SM, Multi-Mode—MM with Step Index—SI such as PCS (Polymer Cladding Silica) fibers or Gradient Index (GI) or fiber bundles made from those fibers [17]. Specially designed fibers of the same material include microstructure fibers or PCF fibers (Polymer clad M ...
... based mainly on SiO2. They are Single-Mode—SM, Multi-Mode—MM with Step Index—SI such as PCS (Polymer Cladding Silica) fibers or Gradient Index (GI) or fiber bundles made from those fibers [17]. Specially designed fibers of the same material include microstructure fibers or PCF fibers (Polymer clad M ...
LINEAR AND NONLINEAR LIGHT BULLETS: RECENT
... It is well known that optical solitons in media with a cubic (Kerr-like) selffocusing optical nonlinearity, obeying the nonlinear Schrödinger (NLS) equation, are unstable in two and three dimensions, because of the occurrence of optical beam collapse [8,9]. However, in the past decades, several poss ...
... It is well known that optical solitons in media with a cubic (Kerr-like) selffocusing optical nonlinearity, obeying the nonlinear Schrödinger (NLS) equation, are unstable in two and three dimensions, because of the occurrence of optical beam collapse [8,9]. However, in the past decades, several poss ...
Medical applications of Terahertz Imaging: a Review of Current
... clinically prepared tissue samples, and secondly by imaging surface features using reflection geometry imaging. Transmission imaging, for obvious reasons, can only be carried out in vitro, whereas a reflection geometry set-up allows the possibility of in vivo imaging [11, 12]. The limited penetratio ...
... clinically prepared tissue samples, and secondly by imaging surface features using reflection geometry imaging. Transmission imaging, for obvious reasons, can only be carried out in vitro, whereas a reflection geometry set-up allows the possibility of in vivo imaging [11, 12]. The limited penetratio ...
Appendix D – Raman Spectra
... wavelength of 785 nm, there were two peaks visible in the RBM range (100-400 cm-1) and were quite visible in the spectrum. The D-peak (1300-1400 cm-1) was somewhat visible, although more difficult to detect because of its wide shape and because of the noisy baseline. The G-peak was sharp and visible ...
... wavelength of 785 nm, there were two peaks visible in the RBM range (100-400 cm-1) and were quite visible in the spectrum. The D-peak (1300-1400 cm-1) was somewhat visible, although more difficult to detect because of its wide shape and because of the noisy baseline. The G-peak was sharp and visible ...
Microscopic Probing and Manipulation of Ultracold
... states and properties in the field of condensed matter physics. The emergence of phenomena such as superfluidity, superconductivity, the Kondo effect or the fractional quantum Hall effect, has stimulated the development of new conceptual frameworks for our basic understanding of many-body physics. I ...
... states and properties in the field of condensed matter physics. The emergence of phenomena such as superfluidity, superconductivity, the Kondo effect or the fractional quantum Hall effect, has stimulated the development of new conceptual frameworks for our basic understanding of many-body physics. I ...
Biomedical Optical Imaging
... Figure 1.4 shows a schematic of a typical high speed, ultrahigh resolution spectral / Fourier domain OCT system. The light source can be either a femtosecond laser or a broadband superluminescent diode (SLD). Our earlier studies used a femtosecond Ti:Sapphire laser for ultrahigh-resolution imaging, ...
... Figure 1.4 shows a schematic of a typical high speed, ultrahigh resolution spectral / Fourier domain OCT system. The light source can be either a femtosecond laser or a broadband superluminescent diode (SLD). Our earlier studies used a femtosecond Ti:Sapphire laser for ultrahigh-resolution imaging, ...
Jonesresub
... it to students. Along with the theoretical formalism, we describe an intermediate to advanced optics laboratory experiment to prepare light beams in Poincaré modes, which have spatially variable polarization. The determination of the polarization states of the beam is used as an exercise to help st ...
... it to students. Along with the theoretical formalism, we describe an intermediate to advanced optics laboratory experiment to prepare light beams in Poincaré modes, which have spatially variable polarization. The determination of the polarization states of the beam is used as an exercise to help st ...
Lecture-10-Optics
... Note that if n1 > nf > n2 or n1 < nf < n2, the - phase shift would not be present. ...
... Note that if n1 > nf > n2 or n1 < nf < n2, the - phase shift would not be present. ...
Chapter 02 Tools of the Laboratory: The Methods for Studying
... Topic: Tools and Methods of Culturing, Classifying, and Identifying Microorganisms ...
... Topic: Tools and Methods of Culturing, Classifying, and Identifying Microorganisms ...
Journal of Nonlinear Optical - Research School of Physics and
... phenomenon for optically-induced lattices, but can be applied to other types of periodic structures with electro-optic tunability. In particular, various possibilities for beam control were demonstrated in liquid-crystal cells with periodical modulation induced by an array of electrodes.40 – 45 The ...
... phenomenon for optically-induced lattices, but can be applied to other types of periodic structures with electro-optic tunability. In particular, various possibilities for beam control were demonstrated in liquid-crystal cells with periodical modulation induced by an array of electrodes.40 – 45 The ...
Optical field profile evaluation on silica high Optical field profile
... NFP. Another possible reason for this could be that the photo detector detects the light that propagates by diffracting from the upper and lower optical waveguide but not the light that simulataneously propagates through the core. However, we experimentally confirmed that a certain portion of optica ...
... NFP. Another possible reason for this could be that the photo detector detects the light that propagates by diffracting from the upper and lower optical waveguide but not the light that simulataneously propagates through the core. However, we experimentally confirmed that a certain portion of optica ...
The Sampling Pattern Cube
... devices are becoming cheaper and are providing even more built-in features. Digital photography has made it easy in relation to capturing, sending and storing high quality images all at a reasonable price. In addition to conventional cameras that have become very popular and for which there are an e ...
... devices are becoming cheaper and are providing even more built-in features. Digital photography has made it easy in relation to capturing, sending and storing high quality images all at a reasonable price. In addition to conventional cameras that have become very popular and for which there are an e ...
diffraction gratings
... 1. An entrance slit or aperture stop. 2. A collimating element to make the rays parallel which pass though one point of the entrance slit or field-stop. This collimator may be a lens, a mirror or an integral part of the dispersing element, as in a concave grating spectrometer. 3. A dispersing elemen ...
... 1. An entrance slit or aperture stop. 2. A collimating element to make the rays parallel which pass though one point of the entrance slit or field-stop. This collimator may be a lens, a mirror or an integral part of the dispersing element, as in a concave grating spectrometer. 3. A dispersing elemen ...
Partially coherent beam shaping and imaging
... order to make numerical calculations feasible, so-called modal approaches [46–51] are used extensively, especially to describe partial spatial coherence. Such modal approaches, in which the partially coherent field is represented as a superposition of fully coherent fields, lead to the evaluation of ...
... order to make numerical calculations feasible, so-called modal approaches [46–51] are used extensively, especially to describe partial spatial coherence. Such modal approaches, in which the partially coherent field is represented as a superposition of fully coherent fields, lead to the evaluation of ...
Fluctuations in Quantum Degenerate Fermi Gases
... New ways to probe interesting quantum phases . . . . . . . . ...
... New ways to probe interesting quantum phases . . . . . . . . ...
Image transmission through a stable paraxial cavity
... free-propagation of a field changes its transverse distribution, but in some planes, such as conjugate planes, or Fourier plane, one get simple transformations of the image. On the other hand, transmission through cavity has a drastic effect on the transverse distribution of the field, as one must t ...
... free-propagation of a field changes its transverse distribution, but in some planes, such as conjugate planes, or Fourier plane, one get simple transformations of the image. On the other hand, transmission through cavity has a drastic effect on the transverse distribution of the field, as one must t ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.