O2-1 Significance of Premature Restriction or Closure of Foramen
... and without structural heart disease. Methods: 10 year review of 2324 foetuses that were referred for cardiac screening to the University Hospital of Wales. Results: Premature restriction or closure of foramen ovale was encountered in 35 fetuses, of which 25 had isolated restrictive foramen ovale (I ...
... and without structural heart disease. Methods: 10 year review of 2324 foetuses that were referred for cardiac screening to the University Hospital of Wales. Results: Premature restriction or closure of foramen ovale was encountered in 35 fetuses, of which 25 had isolated restrictive foramen ovale (I ...
arrhythmias in adult congenital heart disease
... There are now more adults living with congenital heart disease (CHD) than children with CHD, due to the remarkable improvements in medical, interventional, and surgical care of these complex patients. However, despite increased survival and longevity, the longterm hemodynamic abnormalities and sutur ...
... There are now more adults living with congenital heart disease (CHD) than children with CHD, due to the remarkable improvements in medical, interventional, and surgical care of these complex patients. However, despite increased survival and longevity, the longterm hemodynamic abnormalities and sutur ...
11 Shocking Heart Facts
... all of the body’s 75 trillion cells, only bypassing the corneas. The average adult heart beats 72 times a minute, 100,000 times a day, and 2.5 billion times over the course of a lifetime. ...
... all of the body’s 75 trillion cells, only bypassing the corneas. The average adult heart beats 72 times a minute, 100,000 times a day, and 2.5 billion times over the course of a lifetime. ...
cardiovascular system
... Veins: The inferior and superior vena cava carries the de-oxygenated blood to the heart. Arteries: Pulmonary Artery carries the oxygen to the lungs. Diseases: Cardiovascular diseases include a number of affecting the structures of or the function of the heart. Coronary artery disease, also cal ...
... Veins: The inferior and superior vena cava carries the de-oxygenated blood to the heart. Arteries: Pulmonary Artery carries the oxygen to the lungs. Diseases: Cardiovascular diseases include a number of affecting the structures of or the function of the heart. Coronary artery disease, also cal ...
Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia (AVRT)
... This is a heart rhythm condition in which the heart rate can become abnormally fast This is a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). This is related to an abnormal “short circuit” in the electrical connections of the heart between the atria and the ventricles (heart chambers.) Episodes of fast ...
... This is a heart rhythm condition in which the heart rate can become abnormally fast This is a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). This is related to an abnormal “short circuit” in the electrical connections of the heart between the atria and the ventricles (heart chambers.) Episodes of fast ...
10 .Congenitally corrected TGA- A case diagnosed incidentally
... multiple cardiac morphological abnormalities and conduction defects. Data from the Baltimore-Washington Infant Study supported the fact that congenitally corrected transposition is a rare disorder (1). As many as 40 infants per 100,000 live births are affected by congenitally corrected transposition ...
... multiple cardiac morphological abnormalities and conduction defects. Data from the Baltimore-Washington Infant Study supported the fact that congenitally corrected transposition is a rare disorder (1). As many as 40 infants per 100,000 live births are affected by congenitally corrected transposition ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... • Electrocardiograph (ECG, EKG) shows electrical events of heart beat • App called cardiograph ...
... • Electrocardiograph (ECG, EKG) shows electrical events of heart beat • App called cardiograph ...
Slide ()
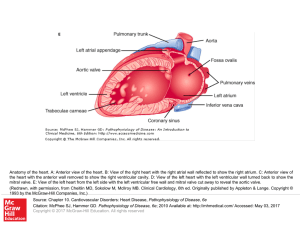
... Anatomy of the heart. A: Anterior view of the heart. B: View of the right heart with the right atrial wall reflected to show the right atrium. C: Anterior view of the heart with the anterior wall removed to show the right ventricular cavity. D: View of the left heart with the left ventricular wall t ...
... Anatomy of the heart. A: Anterior view of the heart. B: View of the right heart with the right atrial wall reflected to show the right atrium. C: Anterior view of the heart with the anterior wall removed to show the right ventricular cavity. D: View of the left heart with the left ventricular wall t ...
Ventricular Septal Defect-Moderate to Large
... cause the left side of the heart to enlarge. It can also cause too much blood flow to the lungs. These defects may vary in size. They may be present in many places in the ventricular septum. Rarely, a person may have more than one of these. Small defects rarely cause problems and have a high chance ...
... cause the left side of the heart to enlarge. It can also cause too much blood flow to the lungs. These defects may vary in size. They may be present in many places in the ventricular septum. Rarely, a person may have more than one of these. Small defects rarely cause problems and have a high chance ...
- Hart Welfare Society
... The septum is the wall that separates the chambers on the left side of the heart from those on the right. It prevents mixing of blood between the two sides of the heart. Sometimes, a baby is born with a hole in the septum. When that occurs, blood can mix between the two sides of the heart. ...
... The septum is the wall that separates the chambers on the left side of the heart from those on the right. It prevents mixing of blood between the two sides of the heart. Sometimes, a baby is born with a hole in the septum. When that occurs, blood can mix between the two sides of the heart. ...
Answer Sheet
... 3. What are vessels that carry blood FROM the heart called (3 answers~ large to small vessels) arteries, arterioles, capillaries ...
... 3. What are vessels that carry blood FROM the heart called (3 answers~ large to small vessels) arteries, arterioles, capillaries ...
Congenital Cardiovascular Defects
... severity from tiny pinholes between chambers that may resolve spontaneously to major malformations that can require multiple surgical procedures before school age and may result in death in utero, in infancy, or in childhood. The common complex defects include the following: Tetralogy of Fallot ( ...
... severity from tiny pinholes between chambers that may resolve spontaneously to major malformations that can require multiple surgical procedures before school age and may result in death in utero, in infancy, or in childhood. The common complex defects include the following: Tetralogy of Fallot ( ...
DOC
... Exercise and the heart How does the heart move blood around the body? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Where in the body would you find the heart? (be exact) __________________________________________ ...
... Exercise and the heart How does the heart move blood around the body? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Where in the body would you find the heart? (be exact) __________________________________________ ...
Happy Heart Syndrome It`s already been proven that intense
... It's already been proven that intense emotional distress -- say, after losing a loved one -- can trigger a cardiac abnormality called "broken heart syndrome." But now new research suggests sudden bursts of joy can have the same effect. The condition, known as Takotsubo syndrome (TTS), occurs when th ...
... It's already been proven that intense emotional distress -- say, after losing a loved one -- can trigger a cardiac abnormality called "broken heart syndrome." But now new research suggests sudden bursts of joy can have the same effect. The condition, known as Takotsubo syndrome (TTS), occurs when th ...
NEWBORN PULSE OXIMETRY SCREENING FOR CRITICAL
... e. Whereas, current methods for detecting congenital heart defects generally include prenatal ultrasound screening and repeated clinical examinations can identify many affected newborns; these screenings, alone, identify less than half of all cases, and critical congenital heart defect cases are oft ...
... e. Whereas, current methods for detecting congenital heart defects generally include prenatal ultrasound screening and repeated clinical examinations can identify many affected newborns; these screenings, alone, identify less than half of all cases, and critical congenital heart defect cases are oft ...
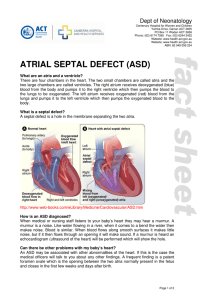
atrial septal defect (asd)
... How is an ASD diagnosed? When medical or nursing staff listens to your baby’s heart they may hear a murmur. A murmur is a noise. Like water flowing in a river, when it comes to a bend the water then makes noise. Blood is similar. When blood flows along smooth surfaces it makes little noise, but if i ...
... How is an ASD diagnosed? When medical or nursing staff listens to your baby’s heart they may hear a murmur. A murmur is a noise. Like water flowing in a river, when it comes to a bend the water then makes noise. Blood is similar. When blood flows along smooth surfaces it makes little noise, but if i ...
CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS AND ASSOCIATED GENETIC DISORDERS The
... that associated with those neural crest cells populating aortic arches 3 and 4 multigene, heterozygous, interstitial chromosomal deletion (approximately 30 genes are deleted) DiGeorge Critical Region TBX1 mutations are associated with heart defects (involved with a growth factor) ...
... that associated with those neural crest cells populating aortic arches 3 and 4 multigene, heterozygous, interstitial chromosomal deletion (approximately 30 genes are deleted) DiGeorge Critical Region TBX1 mutations are associated with heart defects (involved with a growth factor) ...
Your Heart and How it works
... atrium. It then passes through the tricuspid valve to get to the right ventricle and then through the pulmonary valve to get to the pulmonary artery, which takes the blood to the lungs. In the lungs the blood gets oxygenated and returns to the heart in the left atrium. It then passes through the mit ...
... atrium. It then passes through the tricuspid valve to get to the right ventricle and then through the pulmonary valve to get to the pulmonary artery, which takes the blood to the lungs. In the lungs the blood gets oxygenated and returns to the heart in the left atrium. It then passes through the mit ...
Grade 8 Health Circulatory System Review
... Answer all questions in this review to ensure you are ready for the test next week!! 1. What are the three main parts of the circulatory system? ...
... Answer all questions in this review to ensure you are ready for the test next week!! 1. What are the three main parts of the circulatory system? ...
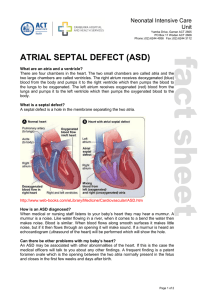
atrial septal defect (asd)
... How is an ASD diagnosed? When medical or nursing staff listens to your baby’s heart they may hear a murmur. A murmur is a noise. Like water flowing in a river, when it comes to a bend the water then makes noise. Blood is similar. When blood flows along smooth surfaces it makes little noise, but if i ...
... How is an ASD diagnosed? When medical or nursing staff listens to your baby’s heart they may hear a murmur. A murmur is a noise. Like water flowing in a river, when it comes to a bend the water then makes noise. Blood is similar. When blood flows along smooth surfaces it makes little noise, but if i ...
The Heart Continued
... changes in electrical potential across the heart – detects the contraction pulses that pass over the surface of the heart. – ECGs are useful in diagnosing heart abnormalities. ...
... changes in electrical potential across the heart – detects the contraction pulses that pass over the surface of the heart. – ECGs are useful in diagnosing heart abnormalities. ...
Congenital heart defect

Congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly or congenital heart disease, is a problem in the structure of the heart that is present at birth. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of problem. Symptoms can vary from none to life threatening. When present they may include rapid breathing, bluish skin, poor weight gain, and feeling tired. It does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart problems do not occur with other diseases. Complications that can result from heart defects include heart failure.The cause of a congenital heart defect is often unknown. Certain cases may be due to infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother. Having a parent with a congenital heart defect is also a risk factor. A number of genetic conditions are associated with heart defects including Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Marfan syndrome. Congenital heart defects are divided into two main groups: cyanotic heart defects and non-cyanotic heart defects, depending on whether the child has the potential to turn bluish in color. The problems may involve the interior walls of the heart, the heart valves, or the large blood vessels that lead to and from the heart.Congenital heart defects are partly preventable through rubella vaccination, the adding of iodine to salt, and the adding of folic acid to certain food products. Some defects do not need treatment. Other may be effectively treated with catheter based procedures or heart surgery. Occasionally a number of operations may be needed. Occasionally heart transplantation is required. With appropriate treatment outcomes, even with complex problems, are generally good.Heart defects are the most common birth defect. In 2013 they were present in 34.3 million people globally. They affect between 4 and 75 per 1,000 live births depending upon how they are diagnosed. About 6 to 19 per 1,000 cause a moderate to severe degree of problems. Congenital heart defects are the leading cause of birth defect-related deaths. In 2013 they resulted in 323,000 deaths down from 366,000 deaths in 1990.