Heart Defect Closure Without Surgery
... The PDA allows a high pressure flow of blood into the lung’s blood vessels. This causes damage to the lung vessels over time. The damage can become permanent if the defect is not closed in time or may be a risk factor in developing bacterial infection of the heart. ...
... The PDA allows a high pressure flow of blood into the lung’s blood vessels. This causes damage to the lung vessels over time. The damage can become permanent if the defect is not closed in time or may be a risk factor in developing bacterial infection of the heart. ...
Congenital Heart Disease-Overview
... Congenital aortic stenosis Hypoplastic left heart syndrome Congenital mitral stenosis Cor triatriatum Obstruction to venous return from lungs O ...
... Congenital aortic stenosis Hypoplastic left heart syndrome Congenital mitral stenosis Cor triatriatum Obstruction to venous return from lungs O ...
ventricular septal defect (vsd)
... A VSD is the most common type of congenital heart problem. They occur in about 2 in ...
... A VSD is the most common type of congenital heart problem. They occur in about 2 in ...
resynchronisation therapy in adults with congenital heart disease
... Objectives:Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be of particular benefit to adults with congenital heart disease (CHD) and ventricular dysfunction (VD). Methods : Retrospective hospital records review.Results:Between 2001 & 2004, 6 patients (pt) had 5 successful implants, 4 with defibrillator ...
... Objectives:Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be of particular benefit to adults with congenital heart disease (CHD) and ventricular dysfunction (VD). Methods : Retrospective hospital records review.Results:Between 2001 & 2004, 6 patients (pt) had 5 successful implants, 4 with defibrillator ...
Guidelines for Management of Congenital Heart Disease in Adults
... source of illness and death in ACHD. Even usually straightforward procedures, such ...
... source of illness and death in ACHD. Even usually straightforward procedures, such ...
Congenital Heart Disease
... Pressure on the right side has had to increase in order to pump blood to lungs and shunt reverses to Right-left shunt which is a cyanotic condition. Fatal outcome or heart and lung transplant is needed. Coarctation of the Aorta Narrowing of the aorta Usually located near the insertion of the d ...
... Pressure on the right side has had to increase in order to pump blood to lungs and shunt reverses to Right-left shunt which is a cyanotic condition. Fatal outcome or heart and lung transplant is needed. Coarctation of the Aorta Narrowing of the aorta Usually located near the insertion of the d ...
DIY DIY t Thes love ( Mate • • • • • • Heart Sach tutorial create e
... and seew the two larrge heart piecees together ussing a runnin ng stitch. Advaanced stitcherrs could incorrporate a blan nket stitch herre as well. Leaave an openin ng at one end so that you caan still stuff itt with the fiber-fill. ...
... and seew the two larrge heart piecees together ussing a runnin ng stitch. Advaanced stitcherrs could incorrporate a blan nket stitch herre as well. Leaave an openin ng at one end so that you caan still stuff itt with the fiber-fill. ...
Cardiac Defects: Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
... What is the follow-up care for HLHS? Between the Norwood and Glenn Operations Though early outcomes for patients with single ventricle heart defects after staged reconstruction have improved dramatically, the period between the Norwood procedure and the Glenn operation remains a very vulnerable time ...
... What is the follow-up care for HLHS? Between the Norwood and Glenn Operations Though early outcomes for patients with single ventricle heart defects after staged reconstruction have improved dramatically, the period between the Norwood procedure and the Glenn operation remains a very vulnerable time ...
35 jmscr
... CCTGA, is a rare (less than 1% of all CHD) and complex heart defect [5]. It is characterized by AV and ventriculoatrial discordance. The aorta is located closer to the anterior and more to the left than the pulmonary artery. The AV valves follow their respective ventricles. Because of the displaceme ...
... CCTGA, is a rare (less than 1% of all CHD) and complex heart defect [5]. It is characterized by AV and ventriculoatrial discordance. The aorta is located closer to the anterior and more to the left than the pulmonary artery. The AV valves follow their respective ventricles. Because of the displaceme ...
Slide ()
... lines in ventral view. The white arrowheads in (b′)–(d′) mark the position of a cluster of beads used to visualize HT rotation; rotation angle θ is defined by orientation of lumen, as shown in (b″). ((a)–(a″)) Stage-10 heart with SPL intact. ((b)–(b″)) The heart with SPL removed after 3 h culture. ( ...
... lines in ventral view. The white arrowheads in (b′)–(d′) mark the position of a cluster of beads used to visualize HT rotation; rotation angle θ is defined by orientation of lumen, as shown in (b″). ((a)–(a″)) Stage-10 heart with SPL intact. ((b)–(b″)) The heart with SPL removed after 3 h culture. ( ...
Pediatric-Cardiology-Elective
... f. Become familiar with the differential diagnosis and initial evaluation, management, and appropriate referral for the child presenting with symptoms/signs related to the CV system: 1. Cyanosis 2. Hypertension. 3. Palpitations 4. Bradycardia 5. Syncope 6. Chest pain 7. Heart murmurs g. An introduct ...
... f. Become familiar with the differential diagnosis and initial evaluation, management, and appropriate referral for the child presenting with symptoms/signs related to the CV system: 1. Cyanosis 2. Hypertension. 3. Palpitations 4. Bradycardia 5. Syncope 6. Chest pain 7. Heart murmurs g. An introduct ...
Pediatric Cardiology
... f. Become familiar with the differential diagnosis and initial evaluation, management, and appropriate referral for the child presenting with symptoms/signs related to the CV system: 1. Cyanosis 2. Hypertension. 3. Palpitations 4. Bradycardia 5. Syncope 6. Chest pain 7. Heart murmurs g. An introduct ...
... f. Become familiar with the differential diagnosis and initial evaluation, management, and appropriate referral for the child presenting with symptoms/signs related to the CV system: 1. Cyanosis 2. Hypertension. 3. Palpitations 4. Bradycardia 5. Syncope 6. Chest pain 7. Heart murmurs g. An introduct ...
For Referring Physicians to ACHD Program
... Given the long-term medical issues that can occur in adults with congenital heart disease, it is recommended by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology that these individuals receive regular follow-up by a specialist in ACHD and at a regional center of ACHD excellence. ...
... Given the long-term medical issues that can occur in adults with congenital heart disease, it is recommended by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology that these individuals receive regular follow-up by a specialist in ACHD and at a regional center of ACHD excellence. ...
l-Transposition of the Great Arteries
... inverted ventricles, this lesion is also called “congenitally corrected TGA.” Some children may also have ventricular septal defects or obstruction to flow into the pulmonary artery. What causes it? The cause is unknown, but genetic factors may contribute to it. How does it affect the heart? In this ...
... inverted ventricles, this lesion is also called “congenitally corrected TGA.” Some children may also have ventricular septal defects or obstruction to flow into the pulmonary artery. What causes it? The cause is unknown, but genetic factors may contribute to it. How does it affect the heart? In this ...
contraception for patients with congenital heart disease
... It is perfectly possible for many women with congenital cardiac defects to have normal pregnancies and deliveries. It is important that Pre-conception counselling and assessment be available. Patients can be divided into mild, moderate and severe risk groups. Attention should be paid not only to mat ...
... It is perfectly possible for many women with congenital cardiac defects to have normal pregnancies and deliveries. It is important that Pre-conception counselling and assessment be available. Patients can be divided into mild, moderate and severe risk groups. Attention should be paid not only to mat ...
Obstructive Congenital Heart Disease
... I. Definitions/Epidemiology 1.Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) o ...
... I. Definitions/Epidemiology 1.Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) o ...
Congential heart disease
... Innocent murmur It is functional,normal,insignificent. Patient is asymptomatic. Murmur heard on routine cardiac ...
... Innocent murmur It is functional,normal,insignificent. Patient is asymptomatic. Murmur heard on routine cardiac ...
Congential heart disease
... Innocent murmur It is functional,normal,insignificent. Patient is asymptomatic. Murmur heard on routine cardiac ...
... Innocent murmur It is functional,normal,insignificent. Patient is asymptomatic. Murmur heard on routine cardiac ...
Heart development. Heart defects.
... in the atrial as well as in the ventricular portion of the cardiac partitions. B – Valves in the atrioventricular orifices under normal conditions. C – Split valves in a persistent atrioventricular canal. D and E – Ostium primum defect caused by incomplete fusion of the atrioventricular endocardial ...
... in the atrial as well as in the ventricular portion of the cardiac partitions. B – Valves in the atrioventricular orifices under normal conditions. C – Split valves in a persistent atrioventricular canal. D and E – Ostium primum defect caused by incomplete fusion of the atrioventricular endocardial ...
atrioventricular septal defect (avsd)
... An AVSD is a common type of congenital heart defect, and accounts for about 5% of all congenital heart defects. It is the most common defect to occur in children with Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21). How will this affect my baby? The size of the hole and which parts are involved (atria, ventricle, mitral ...
... An AVSD is a common type of congenital heart defect, and accounts for about 5% of all congenital heart defects. It is the most common defect to occur in children with Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21). How will this affect my baby? The size of the hole and which parts are involved (atria, ventricle, mitral ...
Development of the Cardiovascular System - Wykłady
... •        Mixing lesions (there are both L-to-R and R-to-L shunts without significant stenosis) – truncus arteriosus, total anomalous pulmonary venous return, hypoplastic left heart syndrome      In each group cyanotic and acyanotic conditions may be present ...
... •        Mixing lesions (there are both L-to-R and R-to-L shunts without significant stenosis) – truncus arteriosus, total anomalous pulmonary venous return, hypoplastic left heart syndrome      In each group cyanotic and acyanotic conditions may be present ...
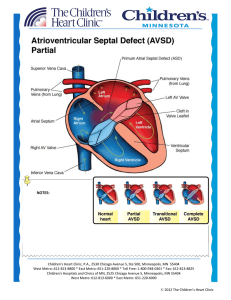
Atrioventricular Septal Defect AVSD
... Atrioventricular septal defects (also known as AV canal) result when there are abnormalities of the endocardial cushion tissue. This comprises the atrial and ventricular septum as well as the AV valves (tricuspid and mitral valves). AV canal can be classified as complete, partial, or transitional. T ...
... Atrioventricular septal defects (also known as AV canal) result when there are abnormalities of the endocardial cushion tissue. This comprises the atrial and ventricular septum as well as the AV valves (tricuspid and mitral valves). AV canal can be classified as complete, partial, or transitional. T ...
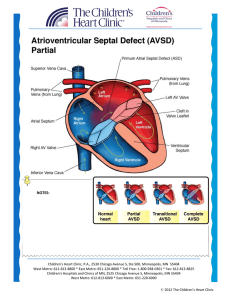
Atrioventricular Septal Defect AVSD
... Atrioventricular septal defects (also known as AV canal) result when there are abnormalities of the endocardial cushion tissue. This comprises the atrial and ventricular septum as well as the AV valves (tricuspid and mitral valves). AV canal can be classified as complete, partial, or transitional. T ...
... Atrioventricular septal defects (also known as AV canal) result when there are abnormalities of the endocardial cushion tissue. This comprises the atrial and ventricular septum as well as the AV valves (tricuspid and mitral valves). AV canal can be classified as complete, partial, or transitional. T ...
Congenital heart defect

Congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly or congenital heart disease, is a problem in the structure of the heart that is present at birth. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of problem. Symptoms can vary from none to life threatening. When present they may include rapid breathing, bluish skin, poor weight gain, and feeling tired. It does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart problems do not occur with other diseases. Complications that can result from heart defects include heart failure.The cause of a congenital heart defect is often unknown. Certain cases may be due to infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother. Having a parent with a congenital heart defect is also a risk factor. A number of genetic conditions are associated with heart defects including Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Marfan syndrome. Congenital heart defects are divided into two main groups: cyanotic heart defects and non-cyanotic heart defects, depending on whether the child has the potential to turn bluish in color. The problems may involve the interior walls of the heart, the heart valves, or the large blood vessels that lead to and from the heart.Congenital heart defects are partly preventable through rubella vaccination, the adding of iodine to salt, and the adding of folic acid to certain food products. Some defects do not need treatment. Other may be effectively treated with catheter based procedures or heart surgery. Occasionally a number of operations may be needed. Occasionally heart transplantation is required. With appropriate treatment outcomes, even with complex problems, are generally good.Heart defects are the most common birth defect. In 2013 they were present in 34.3 million people globally. They affect between 4 and 75 per 1,000 live births depending upon how they are diagnosed. About 6 to 19 per 1,000 cause a moderate to severe degree of problems. Congenital heart defects are the leading cause of birth defect-related deaths. In 2013 they resulted in 323,000 deaths down from 366,000 deaths in 1990.