Determination of Planck`s Constant
... bodies hot enough to be luminous, Planck assumed that the radiation is emitted discontinuously as bursts of energy called quanta. Planck found that the quanta associated with a particular frequency ν of light all have the same energy, E = hν, where h = 6.626 × 10–34 J·s = 4.136 × 10–15 eV·s (Planck’ ...
... bodies hot enough to be luminous, Planck assumed that the radiation is emitted discontinuously as bursts of energy called quanta. Planck found that the quanta associated with a particular frequency ν of light all have the same energy, E = hν, where h = 6.626 × 10–34 J·s = 4.136 × 10–15 eV·s (Planck’ ...
Surface waves
... Propagation of the wave requires k 2 > 0 thus, being ε1 ε2 < 0, we get the additional condition ε1 + ε2 < 0. g) Since ε2 < −ε1 = −1 must hold, we may choose a metal√(a free electron gas, or an ideal plasma) for which ε2 = 1 − ωp2 /ω 2 , and a frequency such that ωp > 2ω. The above described EM modes ...
... Propagation of the wave requires k 2 > 0 thus, being ε1 ε2 < 0, we get the additional condition ε1 + ε2 < 0. g) Since ε2 < −ε1 = −1 must hold, we may choose a metal√(a free electron gas, or an ideal plasma) for which ε2 = 1 − ωp2 /ω 2 , and a frequency such that ωp > 2ω. The above described EM modes ...
Let There Be Light
... Which one of the following statements concerning electromagnetic waves is false? A) Electromagnetic waves are longitudinal waves. B) Electromagnetic waves transfer energy through space. C) The existence of electromagnetic waves was predicted by Maxwell. D) Electromagnetic waves can propagate throug ...
... Which one of the following statements concerning electromagnetic waves is false? A) Electromagnetic waves are longitudinal waves. B) Electromagnetic waves transfer energy through space. C) The existence of electromagnetic waves was predicted by Maxwell. D) Electromagnetic waves can propagate throug ...
Unit Study Guide - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... iris - a ring of muscles that contracts and relaxes automatically to regulate the amount of light entering the eye; controls the size of the pupil lens – a curved, transparent device that causes light to refract as it passes through; gathers light from an object and produces an image of the object n ...
... iris - a ring of muscles that contracts and relaxes automatically to regulate the amount of light entering the eye; controls the size of the pupil lens – a curved, transparent device that causes light to refract as it passes through; gathers light from an object and produces an image of the object n ...
Part V
... If the atoms are excited and then emit light, the atomic beam spreads much more than if the atoms are not excited and do not emit. ...
... If the atoms are excited and then emit light, the atomic beam spreads much more than if the atoms are not excited and do not emit. ...
Class07
... What have we learned? • Any traveling sinusoidal wave may be described by y = ym sin(kx wt + f) • Light always reflects with an angle of reflection equal to the angle of incidence (angles are measured to the normal). • When light travels into a denser medium from a rarer medium, it slows down and ...
... What have we learned? • Any traveling sinusoidal wave may be described by y = ym sin(kx wt + f) • Light always reflects with an angle of reflection equal to the angle of incidence (angles are measured to the normal). • When light travels into a denser medium from a rarer medium, it slows down and ...
PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
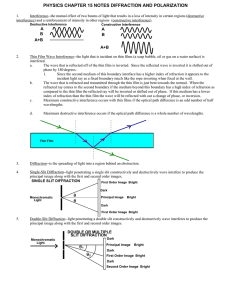
... The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When the refracted ray comes to the second boundary if the medium beyond this boundary has a high index of refraction as compared to the thin film the reflected ray will be inverted or shifted out of ph ...
... The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When the refracted ray comes to the second boundary if the medium beyond this boundary has a high index of refraction as compared to the thin film the reflected ray will be inverted or shifted out of ph ...
Lecture_Feb18_2015
... transmitted (T) radiation at a boundary (Snell’s Law), as well as the fraction of light transmitted versus reflected (Fresnel Equations). • By conservation of energy, R + T = 1 • The index of refraction has a real and imaginary part, and is the square root of the dielectric constant for non-magnetic ...
... transmitted (T) radiation at a boundary (Snell’s Law), as well as the fraction of light transmitted versus reflected (Fresnel Equations). • By conservation of energy, R + T = 1 • The index of refraction has a real and imaginary part, and is the square root of the dielectric constant for non-magnetic ...
Electricity & Optics Physics 24100 Lecture 22 – Chapter 31 sec. 1-4,6
... Light of uniform intensity shines perpendicularly on a surface. If the area of the surface is increased, which of the following is true? (a) The radiation pressure on the surface increases (b) The radiation pressure on the surface stays the same (c) The radiation pressure on the surface decreases ...
... Light of uniform intensity shines perpendicularly on a surface. If the area of the surface is increased, which of the following is true? (a) The radiation pressure on the surface increases (b) The radiation pressure on the surface stays the same (c) The radiation pressure on the surface decreases ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".