L32.ppt
... bent (refracted) when it travels from one medium into another. • However, light is a WAVE, and there are certain properties that can only be understood by taking into account the wave nature of light. ...
... bent (refracted) when it travels from one medium into another. • However, light is a WAVE, and there are certain properties that can only be understood by taking into account the wave nature of light. ...
BLUE PRINT FOR QUESTION PAPER APPLIED PHYSICS – II (R
... Interference in thin film – Introduction, interference due to reflected and transmitted light by thin transparent parallel film, origin of colours in thin film, Wedge shaped thin film, Newton’s rings Applications of interference- Determination of thickness of very thin wire or foil, determination of ...
... Interference in thin film – Introduction, interference due to reflected and transmitted light by thin transparent parallel film, origin of colours in thin film, Wedge shaped thin film, Newton’s rings Applications of interference- Determination of thickness of very thin wire or foil, determination of ...
Diapositiva 1 - Instituto de Astronomía
... In the case of light, the wavelength is so short that a specific distance, called the ångstrom (Å), has been defined. One ångstrom = 10-10 m or 10-8 cm. Visible light 3900 Å to 7700 Å Electromagnetic energy outside this range is no longer visible to the human eye. ...
... In the case of light, the wavelength is so short that a specific distance, called the ångstrom (Å), has been defined. One ångstrom = 10-10 m or 10-8 cm. Visible light 3900 Å to 7700 Å Electromagnetic energy outside this range is no longer visible to the human eye. ...
Tutorial 1
... When an electromagnetic wave passes through a dielectric, the equation of motion for an electron in the material can be written: ...
... When an electromagnetic wave passes through a dielectric, the equation of motion for an electron in the material can be written: ...
Lecture 23 - Purdue Physics
... • A polarizer often consists of a thin, plastic film that allows only the component of the electric field parallel to a particular direction to pass through. This direction is called the axis of the polarizer. • A polarizer absorbs the component of the electric field that is perpendicular to the pol ...
... • A polarizer often consists of a thin, plastic film that allows only the component of the electric field parallel to a particular direction to pass through. This direction is called the axis of the polarizer. • A polarizer absorbs the component of the electric field that is perpendicular to the pol ...
Notes on Quantum Theory
... One of the most interesting ideas of quantum mechanics is the uncertainty principle, first proposed by Heisenberg. Essentially, this says that (at least for very small scale objects) we can never know both a particle's location and its momentum precisely. Rather, the more precisely you know one, the ...
... One of the most interesting ideas of quantum mechanics is the uncertainty principle, first proposed by Heisenberg. Essentially, this says that (at least for very small scale objects) we can never know both a particle's location and its momentum precisely. Rather, the more precisely you know one, the ...
Chapter 4 Many properties of light can be understood using a wave
... The distance between the highest point (crest) on a wave and the rest position; also, the distance between the lowest point (trough) and the ...
... The distance between the highest point (crest) on a wave and the rest position; also, the distance between the lowest point (trough) and the ...
Chapter 24
... Change of phase due to reflection When light reflects off of a medium that has a higher index of refraction than the initial medium, the electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of 1800. ...
... Change of phase due to reflection When light reflects off of a medium that has a higher index of refraction than the initial medium, the electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of 1800. ...
types_of_questions
... balls are at the same horizontal level at the beginning of the experiment. The same quantity of heat is supplied to both balls. The change of temperature of both balls is same. (All kinds of heat losses are negligible) (see fig.) ...
... balls are at the same horizontal level at the beginning of the experiment. The same quantity of heat is supplied to both balls. The change of temperature of both balls is same. (All kinds of heat losses are negligible) (see fig.) ...
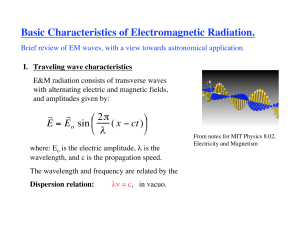
Basic Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation.
... From notes for MIT Physics 8.02, Electricity and Magnetism ...
... From notes for MIT Physics 8.02, Electricity and Magnetism ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".