Topic 4 Waves - MrSimonPorter
... Wavelength is the shortest distance along a wave between two points that are in phase. Phase difference is the time difference or phase angle by which one wave leads or lags another. Wave speed is the speed at which wavefronts pass a stationary observer. Intensity - The average amount of energy tran ...
... Wavelength is the shortest distance along a wave between two points that are in phase. Phase difference is the time difference or phase angle by which one wave leads or lags another. Wave speed is the speed at which wavefronts pass a stationary observer. Intensity - The average amount of energy tran ...
Modern Physics - Tarleton State University
... Scanning-tunneling microscope image of individual atoms ...
... Scanning-tunneling microscope image of individual atoms ...
Generalizations of the Brachistochrone Problem
... Advisor, Dr. Nolan Consider a frictionless surface in a gravitational field that need not be uniform. Given two points A and B on the surface, what curve is traced out by a particle that starts at A and reaches B in the shortest time? This paper discusses studies this problem for simple surfaces suc ...
... Advisor, Dr. Nolan Consider a frictionless surface in a gravitational field that need not be uniform. Given two points A and B on the surface, what curve is traced out by a particle that starts at A and reaches B in the shortest time? This paper discusses studies this problem for simple surfaces suc ...
Waves, incl. Electromagnetic Waves, Light
... disappears if either source A or source B is turned off. This implies a seemingly paradoxical situation: adding a 2nd source reduces the wave effect at certain locations (marked 0)! Precisely the nature of interference, though. Also very important: the two sources A & B must be synchronized, i.e. if ...
... disappears if either source A or source B is turned off. This implies a seemingly paradoxical situation: adding a 2nd source reduces the wave effect at certain locations (marked 0)! Precisely the nature of interference, though. Also very important: the two sources A & B must be synchronized, i.e. if ...
INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM OPTICS
... agree on the extraordinary role that light – the gift of the Sun-god – plays in nature and in their own existence. Optical impressions mediated by light enable us to form our views of the surrounding world and to adapt to it. The warming power of the sun’s rays is a phenomenon experienced in ancient ...
... agree on the extraordinary role that light – the gift of the Sun-god – plays in nature and in their own existence. Optical impressions mediated by light enable us to form our views of the surrounding world and to adapt to it. The warming power of the sun’s rays is a phenomenon experienced in ancient ...
Practice and review problems for the first physics 570 midterm.
... (b) What are Maxwell’s equations (general form without use of D, H, ε, μ)? (c) What is a typical energy for an optical photon (within a factor of 2)? (d) Is 250 nm light in the IR, optical, or UV spectrum? (e) Red and blue laser beams that are initially coincident enter a prism as shown. Which of th ...
... (b) What are Maxwell’s equations (general form without use of D, H, ε, μ)? (c) What is a typical energy for an optical photon (within a factor of 2)? (d) Is 250 nm light in the IR, optical, or UV spectrum? (e) Red and blue laser beams that are initially coincident enter a prism as shown. Which of th ...
Stramski_IOCCG 2016_Interaction of Light and Matter
... is the speed of photons (phase velocity) in free space. The speed of photons (phase velocity) in water is vw = c / nw where nw is refractive index of water nw = c / vw The energy qw of photon in water is: ...
... is the speed of photons (phase velocity) in free space. The speed of photons (phase velocity) in water is vw = c / nw where nw is refractive index of water nw = c / vw The energy qw of photon in water is: ...
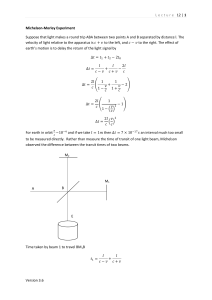
Lecture 12 | 1 Version 3.6 Michelson
... Thus time difference for two beams to reach the same spot according to ether hypothesis ...
... Thus time difference for two beams to reach the same spot according to ether hypothesis ...
Document
... c. a type of energy b. a type of sound wave d. a type of water wave 3. How is light different from other kinds of waves? Light does not require matter through which to travel. Other kinds of waves must travel through matter. 4. A wave that consists of changing electric and magnetic fields and that c ...
... c. a type of energy b. a type of sound wave d. a type of water wave 3. How is light different from other kinds of waves? Light does not require matter through which to travel. Other kinds of waves must travel through matter. 4. A wave that consists of changing electric and magnetic fields and that c ...
Syllabus Physics 1 BA113
... Introduction to current electricity, Ohm’s law, resistors in series and parallel, Kirchhoff’ rules Introduction to the theory of magnetism and different applications, Electromagnetic induction Optics and waves, nature of light, properties of light waves, Interference e.m. waves using Young’s double ...
... Introduction to current electricity, Ohm’s law, resistors in series and parallel, Kirchhoff’ rules Introduction to the theory of magnetism and different applications, Electromagnetic induction Optics and waves, nature of light, properties of light waves, Interference e.m. waves using Young’s double ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".