Diffraction-of-light
... We usually think of light as always traveling in straight lines, but when light waves pass near a barrier they tend to bend around that barrier and become spread out. Diffraction of light occurs when a light wave passes by a corner or through an opening or slit that is physically the approximate siz ...
... We usually think of light as always traveling in straight lines, but when light waves pass near a barrier they tend to bend around that barrier and become spread out. Diffraction of light occurs when a light wave passes by a corner or through an opening or slit that is physically the approximate siz ...
Course Syllabus
... impossible to do justice to all of these topics so no attempt will be made to touch on all of them. Rather, the interaction of light with matter touches both fundamental and applied atomic physics so the second term of advanced atomic physics will concentrate on that subject. The course outline refl ...
... impossible to do justice to all of these topics so no attempt will be made to touch on all of them. Rather, the interaction of light with matter touches both fundamental and applied atomic physics so the second term of advanced atomic physics will concentrate on that subject. The course outline refl ...
Chapter #35 Light and Optics Wave Fronts Electromagnetic Wave
... • Electromagnetic Wave moves outwards from a small source in three dimensions. It forms spherical wave. At far distance from the source front becomes flat and rays become parallel. ...
... • Electromagnetic Wave moves outwards from a small source in three dimensions. It forms spherical wave. At far distance from the source front becomes flat and rays become parallel. ...
Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Waves
... are oscillating perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels. The cross product E B always gives the direction in which the wave travels. • Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or a material substance. • All electromagnetic waves move through a vacuum at the same speed, an ...
... are oscillating perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels. The cross product E B always gives the direction in which the wave travels. • Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or a material substance. • All electromagnetic waves move through a vacuum at the same speed, an ...
Section 9.4: Light: Wave or Particle?
... diffraction were a result of collisions between light particles at the edges of the slit, and not a result of waves of light spreading out. By the time Newton wrote Opticks, his book on light, he explained diffraction as a kind of refraction. This is since understood to be incorrect. Newton’s greate ...
... diffraction were a result of collisions between light particles at the edges of the slit, and not a result of waves of light spreading out. By the time Newton wrote Opticks, his book on light, he explained diffraction as a kind of refraction. This is since understood to be incorrect. Newton’s greate ...
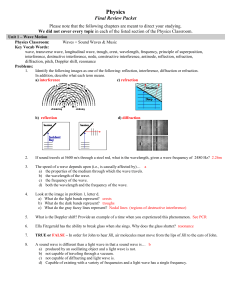
Physics Final Review Packet
... The diagrams depict a sheet of paper being illuminated with white light (ROYGBIV). The papers are impregnated with a chemical capable of absorbing one or more of the colors of white light. In each case, determine which color(s) of light are reflected by the paper and what color the paper will appear ...
... The diagrams depict a sheet of paper being illuminated with white light (ROYGBIV). The papers are impregnated with a chemical capable of absorbing one or more of the colors of white light. In each case, determine which color(s) of light are reflected by the paper and what color the paper will appear ...
Properties of Light and Visual Function
... nearby and some black dots a little further away also seem to appear. More black dots seem to appear as the eye is scanned across the image (as opposed to focusing on a single point). Strangely, the effect seems to be reduced, but not eliminated, when the head is cocked at a 45° angle. The effect se ...
... nearby and some black dots a little further away also seem to appear. More black dots seem to appear as the eye is scanned across the image (as opposed to focusing on a single point). Strangely, the effect seems to be reduced, but not eliminated, when the head is cocked at a 45° angle. The effect se ...
Need for Development of Quantum Mechanics
... Classical physics failed to explain this, Lenard won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1905. ...
... Classical physics failed to explain this, Lenard won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1905. ...
test1_review
... Quantities: Intensity/Radiance, Flux Density (spectral vs. monochromatic) = Irradiance, power, energy. Know the units on every such quantity we’ve talked about. Equation for flux density from radiance (angular integration). Remember the cosine term and why it is there. Planck’s function: What it des ...
... Quantities: Intensity/Radiance, Flux Density (spectral vs. monochromatic) = Irradiance, power, energy. Know the units on every such quantity we’ve talked about. Equation for flux density from radiance (angular integration). Remember the cosine term and why it is there. Planck’s function: What it des ...
Science Olympiad 2011 Practice Optics C
... 13. What do you see if you hold up a spoon at arm’s length, so that the concave surface is facing you? Why? 14. Why does white light disperse into different colors in a prism? 15. Which color of visible light bends the most in a prism? 16. In the year 1800, William Herschel set up a prism to separat ...
... 13. What do you see if you hold up a spoon at arm’s length, so that the concave surface is facing you? Why? 14. Why does white light disperse into different colors in a prism? 15. Which color of visible light bends the most in a prism? 16. In the year 1800, William Herschel set up a prism to separat ...
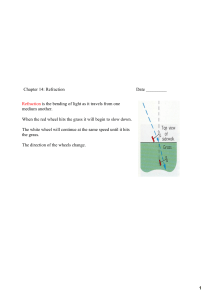
1 Chapter 14: Refraction
... dimensionless number that is always greater than one. The larger the index of refraction the slower light travels in that substance. The amount that light bends when entering a medium depends on the wavelength of the light as well as the speed. ...
... dimensionless number that is always greater than one. The larger the index of refraction the slower light travels in that substance. The amount that light bends when entering a medium depends on the wavelength of the light as well as the speed. ...
PHY 108 – Atoms to Galaxies
... experiments on the composition of light, and established the modern study of optics. He adopted the corpuscular theory of light according to which light is made of tiny particles emitted in all directions by a source. The theory explained well reflection: a reflecting force would push the light part ...
... experiments on the composition of light, and established the modern study of optics. He adopted the corpuscular theory of light according to which light is made of tiny particles emitted in all directions by a source. The theory explained well reflection: a reflecting force would push the light part ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".














![[2012 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881815_1-f519c09d51fa08989c44092ef48b677c-300x300.png)