Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Grating Interference by Thin
... Example: In a double-slit experiment it is found that blue light of wavelength 460 nm gives a second-order maximum at a certain location on the screen. What wavelength of visible light would have a minimum at the same location? Answer: For constructive interference d sinΘ=mλ=2x460nm=920nm For destru ...
... Example: In a double-slit experiment it is found that blue light of wavelength 460 nm gives a second-order maximum at a certain location on the screen. What wavelength of visible light would have a minimum at the same location? Answer: For constructive interference d sinΘ=mλ=2x460nm=920nm For destru ...
PPT - Tensors for Tots
... Every point of a wave front can be considered the origin of a new circular or spherical wave, the so-called elemetary wave. The new position of the wave front results from the superposition of all of the elementary waves. The Huygens wave front is a series of concentric circles originating from the ...
... Every point of a wave front can be considered the origin of a new circular or spherical wave, the so-called elemetary wave. The new position of the wave front results from the superposition of all of the elementary waves. The Huygens wave front is a series of concentric circles originating from the ...
CE2
... You should mark only ONE answer for each question. If you mark more than one answer, you will receive NO MARKS for that question. ...
... You should mark only ONE answer for each question. If you mark more than one answer, you will receive NO MARKS for that question. ...
PRACTICAL 10: Wavelength of Laser Light
... List the NAMES of all participants on the first page of each day’s write-up. Note if any participants arrived late or left early. Put the DATE (including year!) at the top of every page in your notebook. NUMBER the pages in your notebook, in case you need to refer back to previous work. Today’ ...
... List the NAMES of all participants on the first page of each day’s write-up. Note if any participants arrived late or left early. Put the DATE (including year!) at the top of every page in your notebook. NUMBER the pages in your notebook, in case you need to refer back to previous work. Today’ ...
Electromagnetic Radiation
... (EMR) • A form of energy emitted by charged particles that exhibits a wave-like behavior as it travels through space • This energy is created by moving electric and magnetic fields ...
... (EMR) • A form of energy emitted by charged particles that exhibits a wave-like behavior as it travels through space • This energy is created by moving electric and magnetic fields ...
Modern Physics 2015, Learning Aims
... • explain the fundamental elements of Dirac’s Bra-Ket notation and write an eigenvalue equation on Bra-Ket form that gives you the result of a measuring experiment; • define the requirement on the potential in order to separate the full Schrödinger equation into a time-dependent and a time-independe ...
... • explain the fundamental elements of Dirac’s Bra-Ket notation and write an eigenvalue equation on Bra-Ket form that gives you the result of a measuring experiment; • define the requirement on the potential in order to separate the full Schrödinger equation into a time-dependent and a time-independe ...
HW8 not graded v3 - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... The graph shows the distribution of photon energies for a light source that emits 4 million photons per second. In the energy range 0 – 0.1 eV, there are 105 photons per second. In the energy range 0.1 – 0.2 eV, there are 105 photons per second, and ...
... The graph shows the distribution of photon energies for a light source that emits 4 million photons per second. In the energy range 0 – 0.1 eV, there are 105 photons per second. In the energy range 0.1 – 0.2 eV, there are 105 photons per second, and ...
Purdue University PHYS221 EXAM II Solutions are
... Which ray(s) will pass through F after reflection? (a) 1 only(*) (c) 3 only (e) 1, 2, and 3 (b) 2 only (d) both 1 and 2 3.Which one of the following statements concerning electromagnetic waves is false? (a) Electromagnetic waves are longitudinal waves. (*) (b) Electromagnetic waves transfer energy t ...
... Which ray(s) will pass through F after reflection? (a) 1 only(*) (c) 3 only (e) 1, 2, and 3 (b) 2 only (d) both 1 and 2 3.Which one of the following statements concerning electromagnetic waves is false? (a) Electromagnetic waves are longitudinal waves. (*) (b) Electromagnetic waves transfer energy t ...
PPT
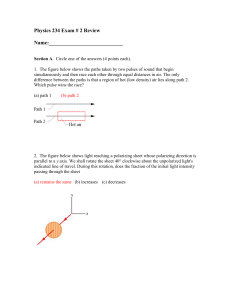
... Initially unpolarized light of intensity I0 is sent into a system of three polarizers as shown. What fraction of the initial intensity emerges from the system? What is the polarization of the exiting light? • Through the first polarizer: unpolarized to polarized, so I1=½I0. • Into the second polariz ...
... Initially unpolarized light of intensity I0 is sent into a system of three polarizers as shown. What fraction of the initial intensity emerges from the system? What is the polarization of the exiting light? • Through the first polarizer: unpolarized to polarized, so I1=½I0. • Into the second polariz ...
Topic 5 Core Questions
... divide the length by 2 to find wavelength. The speed (in m/s) will be frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m). Some of it will be reflected (bounced off) and some will be refracted (bent through). Refraction is the bending (change of direction) of a wave as it passes between different materials. It is cause ...
... divide the length by 2 to find wavelength. The speed (in m/s) will be frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m). Some of it will be reflected (bounced off) and some will be refracted (bent through). Refraction is the bending (change of direction) of a wave as it passes between different materials. It is cause ...
Waves and Radiation
... A high frequency (short wavelength) wave doesn’t get diffracted much – the house won’t be able to receive it… ...
... A high frequency (short wavelength) wave doesn’t get diffracted much – the house won’t be able to receive it… ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".