Document
... • All matter is made of indivisible particles called atoms. • All atoms of a given element are identical in mass & properties. • Atoms are not created or destroyed - just rearranged in reactions. • Different atoms can combine in simple ratios to make compounds. Atoms, according to Dalton: ...
... • All matter is made of indivisible particles called atoms. • All atoms of a given element are identical in mass & properties. • Atoms are not created or destroyed - just rearranged in reactions. • Different atoms can combine in simple ratios to make compounds. Atoms, according to Dalton: ...
Elementary Particles: A Brief History
... initially in cosmic ray interactions and then with accelerators with their energies steadily increasing over the years. They were also complemented by new and more sensitive detection methods. These particles both confirmed existing theories of particle physics, and inspired new ideas about the work ...
... initially in cosmic ray interactions and then with accelerators with their energies steadily increasing over the years. They were also complemented by new and more sensitive detection methods. These particles both confirmed existing theories of particle physics, and inspired new ideas about the work ...
Zealey Phys-in-Cont
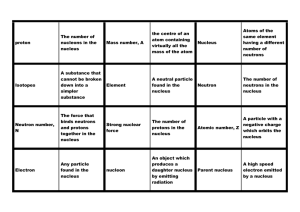
... The atomic number (Z) of an atom or nucleus is the number of protons contained within the nucleus. Since atoms are electrically neutral and contain the same number of positive and negative charges, this is also the number of electrons in the atom. The chemical symbol given to the atom depends on it ...
... The atomic number (Z) of an atom or nucleus is the number of protons contained within the nucleus. Since atoms are electrically neutral and contain the same number of positive and negative charges, this is also the number of electrons in the atom. The chemical symbol given to the atom depends on it ...
1-Introduction
... Firstly, alpha particles are a type of ionizing radiation ejected by the nuclei of certain unstable atoms. They have two protons and two neutrons giving them a charge of 2+ (identical to the nucleus of the helium atom). It is a relatively heavy, high-energy particle with a velocity in air that is ro ...
... Firstly, alpha particles are a type of ionizing radiation ejected by the nuclei of certain unstable atoms. They have two protons and two neutrons giving them a charge of 2+ (identical to the nucleus of the helium atom). It is a relatively heavy, high-energy particle with a velocity in air that is ro ...
Monday, March 2, 2015
... If a photon can create an electron, it must also create a positive charge to balance charge conservation. In 1932, C. D. Anderson observed a positively charged electron (e+) in cosmic radiation. This particle, called the positron, had been predicted to exist several years earlier by P. A. M. Dirac. ...
... If a photon can create an electron, it must also create a positive charge to balance charge conservation. In 1932, C. D. Anderson observed a positively charged electron (e+) in cosmic radiation. This particle, called the positron, had been predicted to exist several years earlier by P. A. M. Dirac. ...
Homework Book
... A nucleus of large mass number splits into two nuclei, releasing several electrons. ...
... A nucleus of large mass number splits into two nuclei, releasing several electrons. ...
Lesson 1 Assignment - Rocky View Schools
... b. Use the charge-to-mass ratio of the particle to determine whether it is an alpha particle, electron, or proton. Hint: Check your physics data sheet for the charges and masses. ...
... b. Use the charge-to-mass ratio of the particle to determine whether it is an alpha particle, electron, or proton. Hint: Check your physics data sheet for the charges and masses. ...
atom
... properties; atoms of different elements differ in properties. • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed • Atoms of different elements can combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds • In chemical rxn, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ...
... properties; atoms of different elements differ in properties. • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed • Atoms of different elements can combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds • In chemical rxn, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ...