Chapter 37 Wave Optics (I)
... and glass (n=1.5), about 4% of the energy is reflected and 96% is transmitted. Thus, a camera with 6 lenses has 12 air-glass interfaces, which means that only (0.96)12=0.61 or 61% of the incident energy is transmitted. How to optimize the transmission of signal intensity? Lens coating. The loss due ...
... and glass (n=1.5), about 4% of the energy is reflected and 96% is transmitted. Thus, a camera with 6 lenses has 12 air-glass interfaces, which means that only (0.96)12=0.61 or 61% of the incident energy is transmitted. How to optimize the transmission of signal intensity? Lens coating. The loss due ...
Lens Types
... from the object to the lens, z2 is the length from the lens to the focal point, and f is the focal length the equation to find the magnification is , M=-(z2/z1) You would place a sensor at the focal point to get a focused image Convex have a + focal length (image is on the other side of light) Conca ...
... from the object to the lens, z2 is the length from the lens to the focal point, and f is the focal length the equation to find the magnification is , M=-(z2/z1) You would place a sensor at the focal point to get a focused image Convex have a + focal length (image is on the other side of light) Conca ...
February 6 pptx
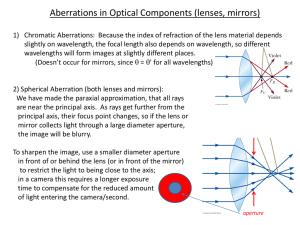
... Aberrations in Optical Components (lenses, mirrors) 1) Chromatic Aberrations: Because the index of refraction of the lens material depends slightly on wavelength, the focal length also depends on wavelength, so different wavelengths will form images at slightly different places. (Doesn’t occur for m ...
... Aberrations in Optical Components (lenses, mirrors) 1) Chromatic Aberrations: Because the index of refraction of the lens material depends slightly on wavelength, the focal length also depends on wavelength, so different wavelengths will form images at slightly different places. (Doesn’t occur for m ...
Adiabatic far-field sub-diffraction imaging ARTICLE Hu Cang *, Alessandro Salandrino
... lthough a tsunami is devastating near land, it is barely noticeable in the open ocean. This is because the sea floor near the land slows down the tsunami, compressing its wavelength from hundreds of kilometres1 to metres and rapidly increasing its amplitude to be destructive. Recently, a similar opti ...
... lthough a tsunami is devastating near land, it is barely noticeable in the open ocean. This is because the sea floor near the land slows down the tsunami, compressing its wavelength from hundreds of kilometres1 to metres and rapidly increasing its amplitude to be destructive. Recently, a similar opti ...
Stop Faking It! Light
... light through matter (air or objects). Transparent: materials that allow all light to pass through – i.e., glass window, water Translucent: letting light through but scattering it – i.e., wax paper Opaque: materials that do not let light through - reflects - i.e., wood, metal ...
... light through matter (air or objects). Transparent: materials that allow all light to pass through – i.e., glass window, water Translucent: letting light through but scattering it – i.e., wax paper Opaque: materials that do not let light through - reflects - i.e., wood, metal ...
Lab 7, The Basics of Optics and Telescopes
... A mirror with a large diameter will give bright images, which makes faint objects visible. The second most important purpose of a telescope is to resolve detail. For example, when viewed with the unaided eye, the images of two closely spaced stars may appear to merge into a single image. A telescope ...
... A mirror with a large diameter will give bright images, which makes faint objects visible. The second most important purpose of a telescope is to resolve detail. For example, when viewed with the unaided eye, the images of two closely spaced stars may appear to merge into a single image. A telescope ...
R1B p4 - CenSSIS - Northeastern University
... There has been increasing interest in recent years in techniques for microscopic examination of optically thick transparent objects. A number of phase imaging modalities have been developed to address this need. If a stack of images is acquired through focusing, the image at a given focal plane is c ...
... There has been increasing interest in recent years in techniques for microscopic examination of optically thick transparent objects. A number of phase imaging modalities have been developed to address this need. If a stack of images is acquired through focusing, the image at a given focal plane is c ...
LEVEL –A QESTIONS-OPTICS 1. Draw a ray diagram to show the
... A equiconvex lens of focal length 15cm is cut into two equal halves as shown in fig. What is the focal length of each half? Name the factors on which the angle of deviation produced by a prism depends. A lens immersed in a transparent liquid is not visible. Under what condition can it happen? An obj ...
... A equiconvex lens of focal length 15cm is cut into two equal halves as shown in fig. What is the focal length of each half? Name the factors on which the angle of deviation produced by a prism depends. A lens immersed in a transparent liquid is not visible. Under what condition can it happen? An obj ...
Lenses (docx)
... e. Present your data and your result for f. Find the relative error by comparing the experimental result to the manufacturer’s data. ...
... e. Present your data and your result for f. Find the relative error by comparing the experimental result to the manufacturer’s data. ...
Optics 101 for non-optical engineers
... Basic Optical Terms / Definitions Diffraction = As a wavefront of light passes by an opaque edge or through an opening, secondary weaker wavefronts are generated. These secondary wavefronts will interfere with the primary wavefront as well as each other to form various diffraction patterns. Diffrac ...
... Basic Optical Terms / Definitions Diffraction = As a wavefront of light passes by an opaque edge or through an opening, secondary weaker wavefronts are generated. These secondary wavefronts will interfere with the primary wavefront as well as each other to form various diffraction patterns. Diffrac ...
lecture 2
... With age, the lens becomes less flexible and accommodation becomes fixed at some distance. This fixing of the focal length of the lens is called PRESBYOPIA. The refracting power of the eye may not be the same in all dimensions. This is called ASTIGMATISM. ...
... With age, the lens becomes less flexible and accommodation becomes fixed at some distance. This fixing of the focal length of the lens is called PRESBYOPIA. The refracting power of the eye may not be the same in all dimensions. This is called ASTIGMATISM. ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... image distance is therefore fixed at 1.8 cm (or 0.018 m). 3. When the eye cannot adequately focus an image on the retina, correction may be needed 4. The 4 common vision problems: a. Myopia (near sightedness, short far & near point) b. Hypermetropia (far sightedness, long far & near point) c. Astigm ...
... image distance is therefore fixed at 1.8 cm (or 0.018 m). 3. When the eye cannot adequately focus an image on the retina, correction may be needed 4. The 4 common vision problems: a. Myopia (near sightedness, short far & near point) b. Hypermetropia (far sightedness, long far & near point) c. Astigm ...
Lecture Notes
... Two converging lenses, each with a focal length of 0.12 m, are used in combination to form an image of an object located 0.36 m to the left of the left lens in the pair. The distance between the lenses is 0.24 m. (a)Where is the final image located relative to the lens on the right? (b) What is the ...
... Two converging lenses, each with a focal length of 0.12 m, are used in combination to form an image of an object located 0.36 m to the left of the left lens in the pair. The distance between the lenses is 0.24 m. (a)Where is the final image located relative to the lens on the right? (b) What is the ...
Physics 1252 Sec.B Exam #1D Instructions:
... 1. UGA waves weren’t covered in class, but they do obey Snell’s law! They have a speed of wave propagation vA = 2097m/s in apple juice and vB = 522m/s in butter milk. Also, assume that sin(14.414o ) = 522/2097 . A narrow beam of UGA waves striking a flat horizontal interface between apple juice and ...
... 1. UGA waves weren’t covered in class, but they do obey Snell’s law! They have a speed of wave propagation vA = 2097m/s in apple juice and vB = 522m/s in butter milk. Also, assume that sin(14.414o ) = 522/2097 . A narrow beam of UGA waves striking a flat horizontal interface between apple juice and ...
Physics 263 Experiment 6 Geometric Optics 1 Refraction
... 2. Move the lens to a position where an image of the object is formed on the screen. Measure the image distance and the object distance. 3. Repeat the above procedure for a least 3 additional, different object distances. Enter the data into a spreadsheet. Plot 1/do vs. 1/di . Use trend-line informat ...
... 2. Move the lens to a position where an image of the object is formed on the screen. Measure the image distance and the object distance. 3. Repeat the above procedure for a least 3 additional, different object distances. Enter the data into a spreadsheet. Plot 1/do vs. 1/di . Use trend-line informat ...
Lens Design OPTI 517 Syllabus
... According to the Arizona Code of Academic Integrity (http://dos.web.arizona.edu/uapolicies/cai2.html), “Integrity is expected of every student in all academic work. The guiding principle of academic integrity is that a student’s submitted work must be the student’s own.” Unless otherwise noted by th ...
... According to the Arizona Code of Academic Integrity (http://dos.web.arizona.edu/uapolicies/cai2.html), “Integrity is expected of every student in all academic work. The guiding principle of academic integrity is that a student’s submitted work must be the student’s own.” Unless otherwise noted by th ...
Chapter 25
... The cornea and lens do not have sufficient focusing power to bring nearby objects into focus on the retina Condition can be corrected with converging lenses ...
... The cornea and lens do not have sufficient focusing power to bring nearby objects into focus on the retina Condition can be corrected with converging lenses ...
Physics Final Review Packet
... Answer the following questions as they pertain to mirrors: a) Describe the physical properties of the image seen in a plane mirror. Virtual, same size, same distance b) Describe the physical properties of a virtual image. Upright, can’t show up on screen c) An object produces a virtual image in a co ...
... Answer the following questions as they pertain to mirrors: a) Describe the physical properties of the image seen in a plane mirror. Virtual, same size, same distance b) Describe the physical properties of a virtual image. Upright, can’t show up on screen c) An object produces a virtual image in a co ...
Geometric optics
... cannot pass through and is entirely reflected. The critical angle is the angle of incidence above which the total internal reflection occurs. This is particularly common as an optical phenomenon, where light waves are involved, but it occurs with many types of waves, such as electromagnetic waves in ...
... cannot pass through and is entirely reflected. The critical angle is the angle of incidence above which the total internal reflection occurs. This is particularly common as an optical phenomenon, where light waves are involved, but it occurs with many types of waves, such as electromagnetic waves in ...
Science Olympiad 2011 Practice Optics C
... to highest frequency. Label which end of the spectrum has the highest energy, and which has the longest wavelength. 20. What are the two types of photoreceptor cells in the human eye? What is the specific function of each? 21. Explain why a screen, like a TV or a computer monitor, is able to trick t ...
... to highest frequency. Label which end of the spectrum has the highest energy, and which has the longest wavelength. 20. What are the two types of photoreceptor cells in the human eye? What is the specific function of each? 21. Explain why a screen, like a TV or a computer monitor, is able to trick t ...
4.Bending Light PhET
... The laser is pointing towards water. Push the red button on the laser to turn it on. You will notice that some light reflects off the surface of the water, and some light refracts as it enters the water. 1. Label each ray as “reflected” or “refracted” in the picture to the right. Place a protractor ...
... The laser is pointing towards water. Push the red button on the laser to turn it on. You will notice that some light reflects off the surface of the water, and some light refracts as it enters the water. 1. Label each ray as “reflected” or “refracted” in the picture to the right. Place a protractor ...
Superlens

A practical superlens, or super lens, is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limit. The diffraction limit is a feature of conventional lenses and microscopes that limits the fineness of their resolution. Many lens designs have been proposed that go beyond the diffraction limit in some way, but there are constraints and obstacles involved in realizing each of them.