Diffracted Light Contrast: Improving the Resolution - Microscopy-UK
... To date, efforts to image the periodicity within individual molecules, e.g., the 67-nm periodicity of type I collagen, have proven unsuccessful. The difficulty may not be one of resolution because Figs. 2a and 3F would certainly suggest DLC is capable of generating sufficient resolution. Instead, i ...
... To date, efforts to image the periodicity within individual molecules, e.g., the 67-nm periodicity of type I collagen, have proven unsuccessful. The difficulty may not be one of resolution because Figs. 2a and 3F would certainly suggest DLC is capable of generating sufficient resolution. Instead, i ...
OPTICS
... a. Lenses in a slide projector or a camera produce real images C. Virtual Image-formed when the light rays from a common point pass through or are reflected by an optical system that causes them to diverge and appear to come to a single point. ...
... a. Lenses in a slide projector or a camera produce real images C. Virtual Image-formed when the light rays from a common point pass through or are reflected by an optical system that causes them to diverge and appear to come to a single point. ...
Medical Imaging Group Research Contributions/Areas
... Biomedical optical imaging enables continuous monitoring of disease (bed-side), which is highly desirable in the clinic, as optical imaging equipment are portable and non-ionizing. The challenging task here is that the quantitative accuracy provided by the reconstructed images depend on the reconstr ...
... Biomedical optical imaging enables continuous monitoring of disease (bed-side), which is highly desirable in the clinic, as optical imaging equipment are portable and non-ionizing. The challenging task here is that the quantitative accuracy provided by the reconstructed images depend on the reconstr ...
Introduction to Metamaterials
... In convenUonal materials, the dielectric response derives from the consUtuent atoms. As discussed, negaUve or posiUve ε(ω) is possible over a broad spectral range. However, natural materials with a resonant m ...
... In convenUonal materials, the dielectric response derives from the consUtuent atoms. As discussed, negaUve or posiUve ε(ω) is possible over a broad spectral range. However, natural materials with a resonant m ...
Physics 1252 Sec.B Exam #1E Instructions:
... A virtual image is generated by a divergent lens. The image is to the left of the lens, at an absolute distance from the lens which is greater than the absolute value of the lens’s focal length. Use a ruler to draw a clean ray diagram for the formation of the image, showing at least two of the princ ...
... A virtual image is generated by a divergent lens. The image is to the left of the lens, at an absolute distance from the lens which is greater than the absolute value of the lens’s focal length. Use a ruler to draw a clean ray diagram for the formation of the image, showing at least two of the princ ...
Chapter 25
... The ability of an optical system to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited due to the wave nature of light If two sources of light are close together, they can be treated as non-coherent sources Because of diffraction, the images consist of bright central regions flanked by weaker ...
... The ability of an optical system to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited due to the wave nature of light If two sources of light are close together, they can be treated as non-coherent sources Because of diffraction, the images consist of bright central regions flanked by weaker ...
Diffraction-managed superlensing using metallodielectric heterostructures
... entrance surface of the diffraction-managed superlens. Thus the deep-subwavelength wave field in the input is diffracted inside the first multilayered medium; subsequently it is compressed in the transverse direction as it propagates along the GaP superlattice. The output magnetic field consists of a str ...
... entrance surface of the diffraction-managed superlens. Thus the deep-subwavelength wave field in the input is diffracted inside the first multilayered medium; subsequently it is compressed in the transverse direction as it propagates along the GaP superlattice. The output magnetic field consists of a str ...
Light Rays
... The principal axis is the line passing through the optical centre and perpendicular to the lens. Rays parallel to the principal axis converge to or diverge from the focus or focal point of a lens. The principal focus is the point that rays parallel to the principal axis converge to (for convex l ...
... The principal axis is the line passing through the optical centre and perpendicular to the lens. Rays parallel to the principal axis converge to or diverge from the focus or focal point of a lens. The principal focus is the point that rays parallel to the principal axis converge to (for convex l ...
09Optics
... – A material through which a wave propagates. – Light can travel through a medium and it can travel through a vacuum. – Sound can only travel through a medium (since it depends on vibrations of atoms). – When a Ray hits an interface between two media it can be reflected, transmitted, and/or absorbed ...
... – A material through which a wave propagates. – Light can travel through a medium and it can travel through a vacuum. – Sound can only travel through a medium (since it depends on vibrations of atoms). – When a Ray hits an interface between two media it can be reflected, transmitted, and/or absorbed ...
CHAPTER 6 Human Eye Notes FIB
... • ____________ ____________ of a camera • To focus a camera, change the ____________ between the lens and the and the human ____________ both protect the lens from damage. detector. In humans, the lens changes ____________ to focus. • The ____________ (series of opaque circles) of a camera a ...
... • ____________ ____________ of a camera • To focus a camera, change the ____________ between the lens and the and the human ____________ both protect the lens from damage. detector. In humans, the lens changes ____________ to focus. • The ____________ (series of opaque circles) of a camera a ...
Lenses: Bending Light
... liking. But Steve wanted to know what made these things work. Now he runs his own laboratory at the Australian National University, where he works on harnessing the power of optics to detect and treat diseases. Steve spends his days developing new optical technologies and techniques – the sort of wo ...
... liking. But Steve wanted to know what made these things work. Now he runs his own laboratory at the Australian National University, where he works on harnessing the power of optics to detect and treat diseases. Steve spends his days developing new optical technologies and techniques – the sort of wo ...
SIMG-733-20092 Optics for Imaging Solutions to Final Exam
... that produces the largest cutoff frequency (of the first zero). For a pinhole with diameter d0 that is sufficiently large for geometrical optics to be valid, the cutoff frequency increases with decreasing diameter. Eventually the pinhole diameter will be small enough for the Fraunhofer approximation to ...
... that produces the largest cutoff frequency (of the first zero). For a pinhole with diameter d0 that is sufficiently large for geometrical optics to be valid, the cutoff frequency increases with decreasing diameter. Eventually the pinhole diameter will be small enough for the Fraunhofer approximation to ...
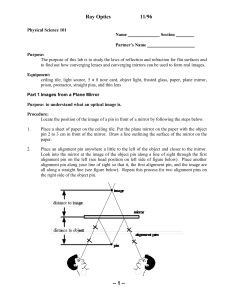
Lab #8 Ray Optics
... Purpose: to show that white light is composed of a spectrum of colors and that each color of light interacts with the prism material differently. When light travels through a transparent object its speed is reduced relative to its speed in a vacuum. This change in speed can cause bending or refracti ...
... Purpose: to show that white light is composed of a spectrum of colors and that each color of light interacts with the prism material differently. When light travels through a transparent object its speed is reduced relative to its speed in a vacuum. This change in speed can cause bending or refracti ...
Lab 2: Abbe Theory of Imaging
... dots which are on the x- and y-axis with a white paper pasted on an index card. These locations will be useful to make various spatial filters in the following experiments. Determine the period (s) and calculate the square mesh spacing (d). Carry out experiments in sequence with square mesh object a ...
... dots which are on the x- and y-axis with a white paper pasted on an index card. These locations will be useful to make various spatial filters in the following experiments. Determine the period (s) and calculate the square mesh spacing (d). Carry out experiments in sequence with square mesh object a ...
Lab 2: Abbe Theory of Imaging
... about twice the size as the object slide when the card at the back focal point of the lens is removed. Remove any slides attached to the slide holder. At the back focal plane we see a single focal spot. The position of the spot locates the ‘dc level’ of illumination of the beam entering the lens. An ...
... about twice the size as the object slide when the card at the back focal point of the lens is removed. Remove any slides attached to the slide holder. At the back focal plane we see a single focal spot. The position of the spot locates the ‘dc level’ of illumination of the beam entering the lens. An ...
Lecture 02
... 2. Light rays that enter the lens parallel to the optical axis leaves through Focal Point 3. Light rays that enter the lens from the focal point, exit parallel to the optical axis. ...
... 2. Light rays that enter the lens parallel to the optical axis leaves through Focal Point 3. Light rays that enter the lens from the focal point, exit parallel to the optical axis. ...
Chapter 2 System Evaluation
... specified in MIL-STD-150A. The following improvements have been made: - The chart has direct frequency labeling in c/mm eliminating the need for cross reference documentation of frequencies. - Numeric labeling is enhanced, based on OCR-A extended font for ...
... specified in MIL-STD-150A. The following improvements have been made: - The chart has direct frequency labeling in c/mm eliminating the need for cross reference documentation of frequencies. - Numeric labeling is enhanced, based on OCR-A extended font for ...
Exam 4 Solutions
... is then connected to a 120 V source. What is the total power output of the combination? Answer: 12 W | 18 W | 24 W Solution: We get the resistance R for each bulb from P = V 2 / R . When they are put in series, the total resistance is tripled, so the current is 1/3 the original current. Thus the pow ...
... is then connected to a 120 V source. What is the total power output of the combination? Answer: 12 W | 18 W | 24 W Solution: We get the resistance R for each bulb from P = V 2 / R . When they are put in series, the total resistance is tripled, so the current is 1/3 the original current. Thus the pow ...
Plane mirrors
... 2. Image- a copy of an object formed by reflected or refracted rays of light. 3. Plane mirrors produce a virtual image. 4. Virtual Image- an upright image that forms where light seems to come from. The image appears to behind the mirror. B. Concave Mirrors: 1. Concave mirror- a mirror with a surface ...
... 2. Image- a copy of an object formed by reflected or refracted rays of light. 3. Plane mirrors produce a virtual image. 4. Virtual Image- an upright image that forms where light seems to come from. The image appears to behind the mirror. B. Concave Mirrors: 1. Concave mirror- a mirror with a surface ...
Final Exam - Department of Physics and Astronomy : University of
... the driving force are one-quarter cycle (π/2 or 90°) out of phase with each other. The displacement is zero when the driving force is a maximum, and the displacement is a maximum (+A0 or –A0) when the driving force is zero. (c) ...
... the driving force are one-quarter cycle (π/2 or 90°) out of phase with each other. The displacement is zero when the driving force is a maximum, and the displacement is a maximum (+A0 or –A0) when the driving force is zero. (c) ...
Chapter1 Fundamental law of geometrical optics 第一章 几何光学的
... ﹡ The fine structure and distribution of light with an image are determined by wave method . ﹡The study of ray phenomenon is known as geometrical optics. The study of light wave is known as physical optics. Ⅲ. Real and Visual images ﹡Real image :formed outside the system, and can be allowed to fall ...
... ﹡ The fine structure and distribution of light with an image are determined by wave method . ﹡The study of ray phenomenon is known as geometrical optics. The study of light wave is known as physical optics. Ⅲ. Real and Visual images ﹡Real image :formed outside the system, and can be allowed to fall ...
Interference I - Galileo and Einstein
... • The pattern is identical to Waves from slits add the sound waves from two • . constructively at central spot speakers. • However, the wavelength of Flashlet! light is much shorter than the distance between slits, First dark place from center: so there are many dark and first-order minimum bright f ...
... • The pattern is identical to Waves from slits add the sound waves from two • . constructively at central spot speakers. • However, the wavelength of Flashlet! light is much shorter than the distance between slits, First dark place from center: so there are many dark and first-order minimum bright f ...
Superlens

A practical superlens, or super lens, is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limit. The diffraction limit is a feature of conventional lenses and microscopes that limits the fineness of their resolution. Many lens designs have been proposed that go beyond the diffraction limit in some way, but there are constraints and obstacles involved in realizing each of them.