Refraction and Lenses Learning Guide
... refraction for water, glass, most plastic depends on wavelength 15. Which is greater, the index of refraction for blue light or red light? greater for blue than red 16. What is chromatic aberration and how can it be reduced with lenses? since different colors are refracted at different angles, they ...
... refraction for water, glass, most plastic depends on wavelength 15. Which is greater, the index of refraction for blue light or red light? greater for blue than red 16. What is chromatic aberration and how can it be reduced with lenses? since different colors are refracted at different angles, they ...
Imaging the near field
... deleterious effects of absorption in the metal are reduced for thinner layers. ...
... deleterious effects of absorption in the metal are reduced for thinner layers. ...
Advanced Optics Lab at San Jose State University Ramen
... illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolution. • (b) building a telescope The students select two doublet lenses for the telescope keeping in mind the fact that they have to overfill the pupil of their eyes so that the spectrum does not disappear on moving one's ...
... illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolution. • (b) building a telescope The students select two doublet lenses for the telescope keeping in mind the fact that they have to overfill the pupil of their eyes so that the spectrum does not disappear on moving one's ...
Tutor 4
... errors, resulting in image degradation. If, however, the angle of illumination were chosen such that, for a given feature, the zero order and one of the first diffraction orders are spaced evenly about the center of the objective lens (Fig. 2), the phase change due to defocus will be the same for b ...
... errors, resulting in image degradation. If, however, the angle of illumination were chosen such that, for a given feature, the zero order and one of the first diffraction orders are spaced evenly about the center of the objective lens (Fig. 2), the phase change due to defocus will be the same for b ...
Microscope Objective
... photography using white light, most apochromats suffer some curvature of field but this is corrected for in plan apochromats. This large amount of color correction makes plan apochromats ideal for fluorescent imaging. This design also supports large numerical apertures (NA). The NA is the square roo ...
... photography using white light, most apochromats suffer some curvature of field but this is corrected for in plan apochromats. This large amount of color correction makes plan apochromats ideal for fluorescent imaging. This design also supports large numerical apertures (NA). The NA is the square roo ...
Multiple side imaging and measurement at 90
... inspect and measure parts from their side without any need of rotation.Four orthonormal views of an object are provided by a telecentric lens through an array of mirrors. The optical path is designed so that the displacement angle between the views is exactly 90°; this optical layout ensures complet ...
... inspect and measure parts from their side without any need of rotation.Four orthonormal views of an object are provided by a telecentric lens through an array of mirrors. The optical path is designed so that the displacement angle between the views is exactly 90°; this optical layout ensures complet ...
Monomolecular Layers and Light
... evanescent wave we are interested in) where k is the propagation vector for the electric field and ω is the angular frequency. Equation 3 is the condition that arises when sinθi > nti by which our evanescent wave exists. Lastly, Equation 4 is the mathematical equation for the evanescent wave that sh ...
... evanescent wave we are interested in) where k is the propagation vector for the electric field and ω is the angular frequency. Equation 3 is the condition that arises when sinθi > nti by which our evanescent wave exists. Lastly, Equation 4 is the mathematical equation for the evanescent wave that sh ...
Imaging
... 600 x 300 pixels, while high cost arrays for scientific applications have dimensions closer to 3000 x 3000 pixels. Each pixel has two, three, or four electrodes in it with three being the most common. ...
... 600 x 300 pixels, while high cost arrays for scientific applications have dimensions closer to 3000 x 3000 pixels. Each pixel has two, three, or four electrodes in it with three being the most common. ...
Light Waves
... Which type of electromagnetic radiation is used to kill cancer cells? a.microwaves c.ultraviolet rays b.gamma rays d.sunlight ...
... Which type of electromagnetic radiation is used to kill cancer cells? a.microwaves c.ultraviolet rays b.gamma rays d.sunlight ...
Lesson-2 Light Microscopy
... Microscopes are instruments designed to produce magnified visual or photographic images of objects too small to be seen with the naked eye. The microscope must accomplish three tasks: produce a magnified image of the specimen, separate the details in the image, and render the details visible to the ...
... Microscopes are instruments designed to produce magnified visual or photographic images of objects too small to be seen with the naked eye. The microscope must accomplish three tasks: produce a magnified image of the specimen, separate the details in the image, and render the details visible to the ...
Light waves Review
... c) infrared, ultraviolet, gamma, x-rays, microwaves d) green, orange, red, violet ...
... c) infrared, ultraviolet, gamma, x-rays, microwaves d) green, orange, red, violet ...
DYNAMICS OF THE CELL MEMBRANE OBSERVED UNDER THE
... The lens has a high performance in three respects. 1) It is the brightest lens ever made in the history of optics. 2) The resolution reaches the highest level among all optics: the smallest resolvable distance is smaller than 150 imi. 3) It creates thinnest evanescent field (< 50 nm) easily when use ...
... The lens has a high performance in three respects. 1) It is the brightest lens ever made in the history of optics. 2) The resolution reaches the highest level among all optics: the smallest resolvable distance is smaller than 150 imi. 3) It creates thinnest evanescent field (< 50 nm) easily when use ...
Lens Characteristics
... ‘black hole’ effect where reflected light is effectively quenched, thereby increasing the sunlight readability by increasing the contrast ratio. This explains how a lamp with a lower luminous intensity can have better sunlight readability than a lamp with a higher luminous intensity. ANTI-REFLECTION ...
... ‘black hole’ effect where reflected light is effectively quenched, thereby increasing the sunlight readability by increasing the contrast ratio. This explains how a lamp with a lower luminous intensity can have better sunlight readability than a lamp with a higher luminous intensity. ANTI-REFLECTION ...
Converging Lens
... telescopes. The refractive telescope that Galileo constructed, for instance, uses two converging lenses in series. Telescopes that use mirrors as their objective are called reflective telescopes. Sir Issac Newton was the first to figure out that mirrors could be used to focus light instead of lenses ...
... telescopes. The refractive telescope that Galileo constructed, for instance, uses two converging lenses in series. Telescopes that use mirrors as their objective are called reflective telescopes. Sir Issac Newton was the first to figure out that mirrors could be used to focus light instead of lenses ...
Light microscopy
... The light microscope can be used to observe whole cells plus large internal structures e.g. nuclei, chloroplasts and mitochondria. ...
... The light microscope can be used to observe whole cells plus large internal structures e.g. nuclei, chloroplasts and mitochondria. ...
lab9 - University of Puget Sound
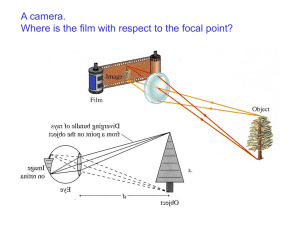
... Last week you observed and quantified the phenomena of reflection, refraction, and dispersion. This week you will see how these physical processes can lead to imaging. Refraction in a lens or reflection from a mirror redirects light rays. If the lens or mirror is shaped correctly, the rays emanating ...
... Last week you observed and quantified the phenomena of reflection, refraction, and dispersion. This week you will see how these physical processes can lead to imaging. Refraction in a lens or reflection from a mirror redirects light rays. If the lens or mirror is shaped correctly, the rays emanating ...
Direct detection of acoustic waves by laser light diffraction and
... has not ever been treated. In the present study, the Fraunhofer diffraction method, which was developed as a new means to detect the electromagnetic radiation scattered within the penetrating laser beam in the plasma nuclear fusion research, are applied to the measurement of the audible sound waves, ...
... has not ever been treated. In the present study, the Fraunhofer diffraction method, which was developed as a new means to detect the electromagnetic radiation scattered within the penetrating laser beam in the plasma nuclear fusion research, are applied to the measurement of the audible sound waves, ...
Waves and Radiation
... How does ultrasound work? Ultrasonic waves are partly _________ at the boundary as they pass from one _______ to another. The time taken for these reflections can be used to measure the _______ of the reflecting surface and this information is used to build up a __________ of the object. ...
... How does ultrasound work? Ultrasonic waves are partly _________ at the boundary as they pass from one _______ to another. The time taken for these reflections can be used to measure the _______ of the reflecting surface and this information is used to build up a __________ of the object. ...
Optical Polarimetry
... In a typical polarimetry experiment, monochromatic light is passed through the sample. A sodium lamp is usually used as the light source and the wavelength of its D line is 589.3 nm. The light provided by the source is not polarized so its electromagnetic waves oscillate in all planes perpendicular ...
... In a typical polarimetry experiment, monochromatic light is passed through the sample. A sodium lamp is usually used as the light source and the wavelength of its D line is 589.3 nm. The light provided by the source is not polarized so its electromagnetic waves oscillate in all planes perpendicular ...
Slide 1
... Sharp maximum intensity at x=0, and intensity goes through 0 at integer multiples of one-half number. ...
... Sharp maximum intensity at x=0, and intensity goes through 0 at integer multiples of one-half number. ...
Aberration File
... The converging lens can be thought of as a series of prisms. A prism disperses light of different frequencies The objective lens brings each image to a slightly different focus. The eyepiece lens has to be 1 focal length from the principal focus of the objective lens. Choosing this distance for gree ...
... The converging lens can be thought of as a series of prisms. A prism disperses light of different frequencies The objective lens brings each image to a slightly different focus. The eyepiece lens has to be 1 focal length from the principal focus of the objective lens. Choosing this distance for gree ...
f = l - UCSD Department of Physics
... “near point”, L = 25 cm. So, the largest angular size of a fine-print object with height h is a = h/L. A magnifying glass creates a virtual image with the same angular size as the object, but you can now have the object at a small distance f from your eye. So, the angular size is ...
... “near point”, L = 25 cm. So, the largest angular size of a fine-print object with height h is a = h/L. A magnifying glass creates a virtual image with the same angular size as the object, but you can now have the object at a small distance f from your eye. So, the angular size is ...
HW2_ASTR 289_2016_v2
... other words what is θ / h , where the units of θ are radians and the units of h are meters? You may assume that θ is small, so that sin θ ~ θ and cos θ ~ 1 . ii) What is the ratio θ / h where the units of θ are seconds of arc and the units of h are mm? [Since a full circle is 2π radians = 360 deg, o ...
... other words what is θ / h , where the units of θ are radians and the units of h are meters? You may assume that θ is small, so that sin θ ~ θ and cos θ ~ 1 . ii) What is the ratio θ / h where the units of θ are seconds of arc and the units of h are mm? [Since a full circle is 2π radians = 360 deg, o ...
Superlens

A practical superlens, or super lens, is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limit. The diffraction limit is a feature of conventional lenses and microscopes that limits the fineness of their resolution. Many lens designs have been proposed that go beyond the diffraction limit in some way, but there are constraints and obstacles involved in realizing each of them.