Weathering & Erosion
... South-Facing Areas: areas facing the south receive more sunlight more vegetation more soil than areas facing other directions ...
... South-Facing Areas: areas facing the south receive more sunlight more vegetation more soil than areas facing other directions ...
Save 0 - Science Lec | Home
... Sedimentology is the branch of the geological science which deals with the study of sediments, sedimentary deposits and sedimentary rocks. All rocks at the Earth's surface (igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary) disintegrate slowly by chemical and physical weathering. The products of weathering are b ...
... Sedimentology is the branch of the geological science which deals with the study of sediments, sedimentary deposits and sedimentary rocks. All rocks at the Earth's surface (igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary) disintegrate slowly by chemical and physical weathering. The products of weathering are b ...
Changes to Texas Land (7
... rainfall ranges between 30-50 inches and soils are clay or sand-rich in various locations. The dominant plant species are tall grasses, live oak trees, and mesquite. Along the Gulf Coast, waves can erode beaches in one area and redeposit the sand in a different location along the coast. The sand may ...
... rainfall ranges between 30-50 inches and soils are clay or sand-rich in various locations. The dominant plant species are tall grasses, live oak trees, and mesquite. Along the Gulf Coast, waves can erode beaches in one area and redeposit the sand in a different location along the coast. The sand may ...
Common Rocks Lab - WHS
... 2. All three types of rocks contain crystals. What unique factor about the arrangement of mineral crystals occurs in many metamorphic rocks? 3. How would you describe the difference between a detrtial sedimentary rock and a chemical sedimentary rock to an elementary school aged student? 4. Of the th ...
... 2. All three types of rocks contain crystals. What unique factor about the arrangement of mineral crystals occurs in many metamorphic rocks? 3. How would you describe the difference between a detrtial sedimentary rock and a chemical sedimentary rock to an elementary school aged student? 4. Of the th ...
Nickel - Cometal S.A.
... Nickel is the chemical element with the atomic number 28, located in the 10th group on the periodic table. Nickel is a fairly abundant element making about 0.008% of the Earth's crust and 0.01% of igneous rocks. It is assumed that there are large quantities of this metal in the Earth's core. The min ...
... Nickel is the chemical element with the atomic number 28, located in the 10th group on the periodic table. Nickel is a fairly abundant element making about 0.008% of the Earth's crust and 0.01% of igneous rocks. It is assumed that there are large quantities of this metal in the Earth's core. The min ...
Chapter 10 Chapter Review Answer Key
... The scientist’s theory is correct because heavy rain will leach the nutrients out of the soil, which will make the topsoil thin. 21. Analyzing Processes What forms of mechanical and chemical weathering would be most common in the desert? Explain your answer. ...
... The scientist’s theory is correct because heavy rain will leach the nutrients out of the soil, which will make the topsoil thin. 21. Analyzing Processes What forms of mechanical and chemical weathering would be most common in the desert? Explain your answer. ...
Assessment
... temperature and/or pressure. If conditions are right, these changes could cause recrystallization of minerals in the sandstone and change the rock to quartzite. 28. The metamorphic rocks often have a different composition; they can be foliated, unlike the parent rocks; the minerals might be larger t ...
... temperature and/or pressure. If conditions are right, these changes could cause recrystallization of minerals in the sandstone and change the rock to quartzite. 28. The metamorphic rocks often have a different composition; they can be foliated, unlike the parent rocks; the minerals might be larger t ...
Rocks & Minerals
... earth above and heat from the mantle below cause them to change shape, color, grain and crystal structure http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es0607/es06 07page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization ...
... earth above and heat from the mantle below cause them to change shape, color, grain and crystal structure http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es0607/es06 07page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization ...
Part A. What makes up soil? Part B. Soil Formation
... 2. Why would you NOT find soils on Mars or Venus? Not all materials that make up soil can be found on other planets, such as water, organic materials 3. Where do the minerals (inorganic materials) that form soil come from? From the weathering and erosion of rocks 4. How is the air found in soils dif ...
... 2. Why would you NOT find soils on Mars or Venus? Not all materials that make up soil can be found on other planets, such as water, organic materials 3. Where do the minerals (inorganic materials) that form soil come from? From the weathering and erosion of rocks 4. How is the air found in soils dif ...
powerpoint
... Parent material is especially significant in the early development of soil and its mineral content. It can vary from solid bedrock to a wide range of unconsolidated deposits including alluvium, wind blown sand and glacial till. ...
... Parent material is especially significant in the early development of soil and its mineral content. It can vary from solid bedrock to a wide range of unconsolidated deposits including alluvium, wind blown sand and glacial till. ...
Interactive Text Weathering
... metal react with? In most cases, the answer is air. The oxygen in the air can react with many metals. These reactions are a kind of chemical weathering called oxidation. Rust is a common example of oxidation. Rocks can rust if they have a lot of iron in them. Many people think that rust forms only w ...
... metal react with? In most cases, the answer is air. The oxygen in the air can react with many metals. These reactions are a kind of chemical weathering called oxidation. Rust is a common example of oxidation. Rocks can rust if they have a lot of iron in them. Many people think that rust forms only w ...
Proceedings Eighth International Congress
... Results of field and office studies, supplemented by observations made during an aerial flyover, suggest that most of Guam may be divided into three physiographic regions: plateau regions, incised regions, and limestone regions. The plateau regions consist of relatively flat and gently rolling uplan ...
... Results of field and office studies, supplemented by observations made during an aerial flyover, suggest that most of Guam may be divided into three physiographic regions: plateau regions, incised regions, and limestone regions. The plateau regions consist of relatively flat and gently rolling uplan ...
silicate agrominerals as nutrient sources and as soil conditioners for
... the challenges nowadays are dedicated on the efficient supply of nutrients for agriculture. The efficiency of the management of these soluble sources must improve to ensure the best use of the nutrients that are derived from finite mineral resources and high energy cost of production and transportat ...
... the challenges nowadays are dedicated on the efficient supply of nutrients for agriculture. The efficiency of the management of these soluble sources must improve to ensure the best use of the nutrients that are derived from finite mineral resources and high energy cost of production and transportat ...
Minerals-Earth`s Jewels
... inorganic, solid materials found in nature. – Inorganic means not formed by plants or animals. They have no carbon. ...
... inorganic, solid materials found in nature. – Inorganic means not formed by plants or animals. They have no carbon. ...
UNIT 3 MINERALS, ROCKS, AND RESOURCES
... in which the rocks formed. Seashells would indicate a marine environment whereas footprints would indicate a land environment. ...
... in which the rocks formed. Seashells would indicate a marine environment whereas footprints would indicate a land environment. ...
Processes of Change
... • Hard rocks weather more slowly than softer rocks. • The more surface area of a rock that is exposed to weathering, the faster the rock will be worn down. • Chemical weathering occurs faster in warm, humid climates. • Weathering occurs faster at high elevations because of an increase in ice, rain, ...
... • Hard rocks weather more slowly than softer rocks. • The more surface area of a rock that is exposed to weathering, the faster the rock will be worn down. • Chemical weathering occurs faster in warm, humid climates. • Weathering occurs faster at high elevations because of an increase in ice, rain, ...
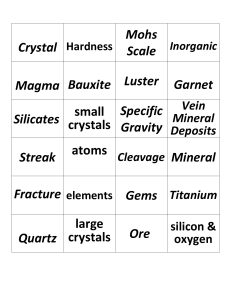
Crystal Hardness Mohs Scale Magma Bauxite Luster Garnet
... more other elements. cools slowly, makes up about 30 They include most ____________ percent of Earth’s common rockform. continental crust. forming minerals. As magma cools, its the property of a mineral that shows its color in ...
... more other elements. cools slowly, makes up about 30 They include most ____________ percent of Earth’s common rockform. continental crust. forming minerals. As magma cools, its the property of a mineral that shows its color in ...
Sedimentary Materials
... – Montmorillonite – (Ca, Na)0.20.4(Al,Mg,Fe)2(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2*nH2O – Vermicullite - (Ca, Mg)0.30.4(Al,Mg,Fe)3(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2*nH2O – Swelling clays – can take up extra water in their interlayers and are the major components of bentonite (NOT a mineral, but a mix of different clay minerals) ...
... – Montmorillonite – (Ca, Na)0.20.4(Al,Mg,Fe)2(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2*nH2O – Vermicullite - (Ca, Mg)0.30.4(Al,Mg,Fe)3(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2*nH2O – Swelling clays – can take up extra water in their interlayers and are the major components of bentonite (NOT a mineral, but a mix of different clay minerals) ...
Lecture W2-L4-6
... “felsic” (feldspath + silica) = feldspars (plagioclase and K-Feldspar), quartz, feldpathoids (rare) “mafic” (magnesium + ferric iron) = biotite, amphibole, pyroxene, olivine For classification purpose: use quartz, Alkali feldspar, plagioclase feldspar, feldspathoid, mafics. ...
... “felsic” (feldspath + silica) = feldspars (plagioclase and K-Feldspar), quartz, feldpathoids (rare) “mafic” (magnesium + ferric iron) = biotite, amphibole, pyroxene, olivine For classification purpose: use quartz, Alkali feldspar, plagioclase feldspar, feldspathoid, mafics. ...
Rocks Study Guide
... 17. Is there a relationship between the type of sedimentary rock and if it is stratified?__No, not all stratified rocks are the same type. Ex. Coal is organic and stratified and sandstone is clastic and stratified. Not all organic and not all clastic are stratified. There is no relationship between ...
... 17. Is there a relationship between the type of sedimentary rock and if it is stratified?__No, not all stratified rocks are the same type. Ex. Coal is organic and stratified and sandstone is clastic and stratified. Not all organic and not all clastic are stratified. There is no relationship between ...
Pathways 2 and 3
... Primary minerals, which occur in igneous rocks, metamorphic , and sedimentary rocks, are inherited by soil from the parent material. Secondary minerals form in soils and include layer-silicate clays, amorphous (non-crystalline) minerals, carbonates, phosphates, sulfide, sulfates, oxides, hydroxides, ...
... Primary minerals, which occur in igneous rocks, metamorphic , and sedimentary rocks, are inherited by soil from the parent material. Secondary minerals form in soils and include layer-silicate clays, amorphous (non-crystalline) minerals, carbonates, phosphates, sulfide, sulfates, oxides, hydroxides, ...
soil- erosion
... STRUCTURE OF THE SOILIf we dig a pit on land and look at the soil, we find that it consists of three layers which are called ‘horizons’. ‘Horizon A’ is the topmost zone, where organic materials have got incorporated with the mineral matter, nutrients and water, which are necessary for the growth of ...
... STRUCTURE OF THE SOILIf we dig a pit on land and look at the soil, we find that it consists of three layers which are called ‘horizons’. ‘Horizon A’ is the topmost zone, where organic materials have got incorporated with the mineral matter, nutrients and water, which are necessary for the growth of ...
File - CBSE FRIENDS OCEAN
... Minerals, elem ents, characteristics of minerals such as crystal form cleavage, fracture,lustre, colour,streak, transparency ,structure, hardness specific grvity, important minerals such as feldspar,quartz,pyroxene,amphibole,mica,olivine and their characteristics classificationof minerals, rocks,ign ...
... Minerals, elem ents, characteristics of minerals such as crystal form cleavage, fracture,lustre, colour,streak, transparency ,structure, hardness specific grvity, important minerals such as feldspar,quartz,pyroxene,amphibole,mica,olivine and their characteristics classificationof minerals, rocks,ign ...
Laterite

Laterite is a soil and rock type rich in iron and aluminium, and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by intensive and long-lasting weathering of the underlying parent rock. Tropical weathering (laterization) is a prolonged process of chemical weathering which produces a wide variety in the thickness, grade, chemistry and ore mineralogy of the resulting soils. The majority of the land area containing laterites is between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.Laterite has commonly been referred to as a soil type as well as being a rock type. This and further variation in the modes of conceptualizing about laterite (e.g. also as a complete weathering profile or theory about weathering) has led to calls for the term to be abandoned altogether. At least a few researchers specializing in regolith development have considered that hopeless confusion has evolved around the name. There is no likelihood, however, that the name will ever be abandoned; for material that looks highly similar to the Indian laterite occurs abundantly worldwide, and it is reasonable to call such material laterite.Historically, laterite was cut into brick-like shapes and used in monument-building. After 1000 CE, construction at Angkor Wat and other southeast Asian sites changed to rectangular temple enclosures made of laterite, brick and stone. Since the mid-1970s, some trial sections of bituminous-surfaced, low-volume roads have used laterite in place of stone as a base course. Thick laterite layers are porous and slightly permeable, so the layers can function as aquifers in rural areas. Locally available laterites have been used in an acid solution, followed by precipitation to remove phosphorus and heavy metals at sewage-treatment facilities.Laterites are a source of aluminium ore; the ore exists largely in clay minerals and the hydroxides, gibbsite, boehmite, and diaspore, which resembles the composition of bauxite. In Northern Ireland they once provided a major source of iron and aluminium ores. Laterite ores also were the early major source of nickel.